harmony 鸿蒙二级联动
二级联动
场景介绍
列表的二级联动(Cascading List)是指根据一个列表(一级列表)的选择结果,来更新另一个列表(二级列表)的选项。这种联动可以使用户根据实际需求,快速定位到想要的选项,提高交互体验。例如,短视频中拍摄风格的选择、照片编辑时的场景的选择,本文即为大家介绍如何开发二级联动。
效果呈现
本例最终效果如下:
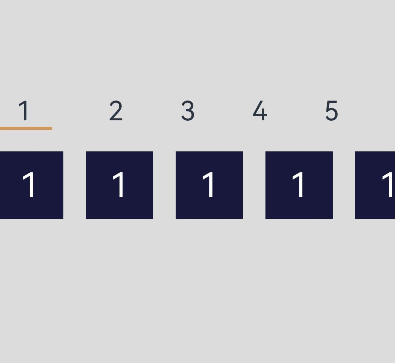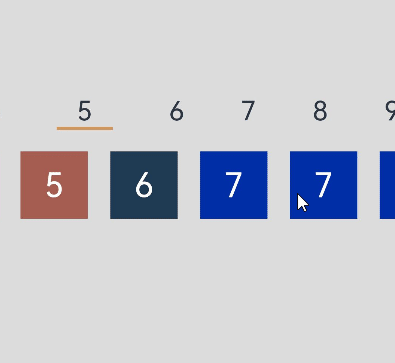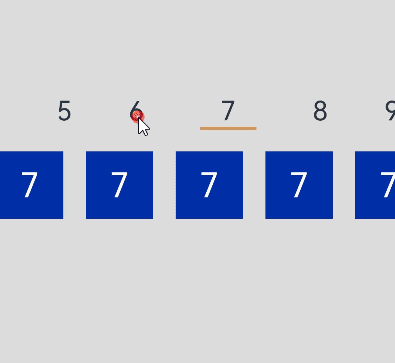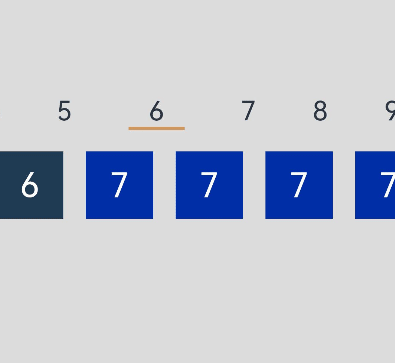
运行环境
本例基于以下环境开发,开发者也可以基于其他适配的版本进行开发: - IDE: DevEco Studio 3.1 Beta2 - SDK: Ohos_sdk_public 3.2.11.9 (API Version 9 Release)
实现思路
- 数字标题(titles)以及下方的数字列表(contents)分组展示:通过两个List组件分别承载数字标题和数字项。
- 滚动数字列表,上方数字标题也随之变动:通过List组件的onScrollIndex事件获取到当前滚动数字的索引,根据该索引计算出对应标题数字的索引,然后通过Scroller的scrollToIndex方法跳转到对应的数字标题,且通过Line组件为选中的标题添加下划线。
- 点击数字标题,下方的数字列表也随之变化:首先获取到点击数字标题的索引,通过该索引计算出下方对应数字的起始项索引,然后通过scroller的scrollToIndex方法跳转到对应索引的数字项。
开发步骤
根据实现思路,具体实现步骤如下:
1. 首先构建列表数据,在records中记录数字列表中各个数字的首项索引值,具体代码块如下:
ts
...
@State typeIndex: number = 0
private tmp: number = 0
private titles: Array<string> = ["1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", "9"]
private contents: Array<string> = ["1", "1", "1", "1", "1", "1", "1", "1", "1", "2", "2", "2", "2", "2", "2", "2", "2", "2", "2", "2", "2", "3"
, "3", "3", "3", "3", "4", "4", "4", "5", "5", "5", "5", "5", "6", "7", "7", "7", "7", "7", "7", "7", "7", "7", "7", "7", "7",
"8", "8", "8", "8", "8", "9", "9", "9", "9", "9", "9", "9", "9", "9", "9", "9"]
private records: Array<number> = [0, 9, 21, 26, 29, 34, 35, 47, 52, 63]
private classifyScroller: Scroller = new Scroller();
private scroller: Scroller = new Scroller();
...
数字标题列表:具体代码块如下:
ts
...
build() {
Column({ space: 0 }) {
List ({ space: 50, scroller: this.classifyScroller, initialIndex: 0 }) {
ForEach(this.titles, (item, index) => {
ListItem() {
Column() {
Text(item)
.fontSize(14)
...
}
}
}
...
}
.listDirection(Axis.Horizontal)
.height(50)
}
}
数字列表,具体代码块如下:
ts
List({ space: 20, scroller: this.scroller }) {
ForEach(this.contents, (item, index) => {
ListItem() {
Column({ space: 5 }) {
Image($r("app.media.app_icon"))
.width(40)
.height(40)
Text(item)
.fontSize(12)
}
...
}
}
}
.listDirection(Axis.Horizontal) //列表排列方向水平
.edgeEffect(EdgeEffect.None) //不支持滑动效果
2. 数字标题的索引值判断,根据当前滚动数字的首项索引值计算出数字标题的索引,具体代码块如下:
ts
...
findClassIndex(ind: number) { // 当前界面最左边图的索引值ind
let ans = 0
// 定义一个i 并进行遍历 this.records.length = 10
for (let i = 0; i < this.records.length; i++) {
// 判断ind在this.records中那两个临近索引值之间
if (ind >= this.records[i] && ind < this.records[i + 1]) {
ans = i
break
}
}
return ans
}
findItemIndex(ind: number) {
// 将ind重新赋值给类型标题列表的索引值
return this.records[ind]
}
...
通过Line组件构成标题下滑线,具体代码块如下:
ts
...
if (this.typeIndex == index) {
Line()
//根据长短判断下划线
.width(item.length === 2 ? 25 : item.length === 3 ? 35 : 50)
.height(3)
.strokeWidth(20)
.strokeLineCap(LineCapStyle.Round)
.backgroundColor('#ffcf9861')
}
...
3. 点击数字标题,数字列表随之滑动:首先获取到点击数字标题的索引,通过该索引计算出下方对应数字的起始项索引,然后通过scroller的scrollToIndex方法跳转到对应索引的数字项,具体代码块如下:
ts
...
.onClick(() => {
this.typeIndex = index
this.classifyScroller.scrollToIndex(index)
let itemIndex = this.findItemIndex(index)
console.log("移动元素:" + itemIndex)
this.scroller.scrollToIndex(itemIndex)
})
...
4. 数字列表的滑动或点击导致数字标题的变动:通过List组件中onScrollIndex事件获取的到屏幕中最左边数字的索引值start,然后通过该索引值计算出对应的数字标题的索引currentClassIndex,然后通过scrollToIndex控制数字标题跳转到对应索引处,具体代码块如下:
ts
...
.onScrollIndex((start) => {
let currentClassIndex = this.findClassIndex(start)
console.log("找到的类索引为: " + currentClassIndex)
if (currentClassIndex != this.tmp) {
this.tmp = currentClassIndex
console.log("类别移动到索引: " + currentClassIndex)
this.typeIndex = currentClassIndex
this.classifyScroller.scrollToIndex(currentClassIndex)
}
})
...
完整代码
完整示例代码如下:
@Entry
@Component
struct TwoLevelLink {
@State typeIndex: number = 0
private tmp: number = 0
private titles: Array<string> = ["1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", "9"]
private contents: Array<string> = ["1", "1", "1", "1", "1", "1", "1", "1", "1", "2", "2", "2", "2", "2", "2", "2", "2", "2", "2", "2", "2", "3"
, "3", "3", "3", "3", "4", "4", "4", "5", "5", "5", "5", "5", "6", "7", "7", "7", "7", "7", "7", "7", "7", "7", "7", "7", "7",
"8", "8", "8", "8", "8", "9", "9", "9", "9", "9", "9", "9", "9", "9", "9", "9"]
private colors: Array<string> = ["#18183C", "#E8A027", "#D4C3B3", "#A4AE77", "#A55D51", "#1F3B54", "#002EA6", "#FFE78F", "#FF770F"]
private records: Array<number> = [0, 9, 21, 26, 29, 34, 35, 47, 52, 63]
private classifyScroller: Scroller = new Scroller();
private scroller: Scroller = new Scroller();
// 根据数字列表索引计算对应数字标题的索引
findClassIndex(ind: number) {
let ans = 0
for (let i = 0; i < this.records.length; i++) {
if (ind >= this.records[i] && ind < this.records[i + 1]) {
ans = i
break
}
}
return ans
}
// 根据数字标题索引计算对应数字列表的索引
findItemIndex(ind: number) {
return this.records[ind]
}
build() {
Column({ space: 0 }) {
List ({ space: 50, scroller: this.classifyScroller, initialIndex: 0 }) {
ForEach(this.titles, (item, index) => {
ListItem() {
Column() {
Text(item)
.fontSize(24)
if (this.typeIndex == index) {
Line()
.width(item.length === 2 ? 25 : item.length === 3 ? 35 : 50)
.height(3)
.strokeWidth(20)
.strokeLineCap(LineCapStyle.Round)
.backgroundColor('#ffcf9861')
}
}
.onClick(() => {
this.typeIndex = index
this.classifyScroller.scrollToIndex(index)
let itemIndex = this.findItemIndex(index)
console.log("移动元素:" + itemIndex)
this.scroller.scrollToIndex(itemIndex)
})
}
})
}
.listDirection(Axis.Horizontal)
.height(50)
List({ space: 20, scroller: this.scroller }) {
ForEach(this.contents, (item, index) => {
ListItem() {
Column({ space: 5 }) {
Text(item)
.fontSize(30)
.fontColor(Color.White)
}
.width(60)
.height(60)
.backgroundColor(this.colors[item-1])
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.onClick(() => {
this.scroller.scrollToIndex(index)
})
}
})
}
.listDirection(Axis.Horizontal) //列表排列方向水平
.edgeEffect(EdgeEffect.None) //不支持滑动效果
.onScrollIndex((start) => {
let currentClassIndex = this.findClassIndex(start)
console.log("找到的类索引为: " + currentClassIndex)
if (currentClassIndex != this.tmp) {
this.tmp = currentClassIndex
console.log("类别移动到索引: " + currentClassIndex)
this.typeIndex = currentClassIndex
this.classifyScroller.scrollToIndex(currentClassIndex)
}
})
}.width('100%').height('100%').backgroundColor(0xDCDCDC).padding({ top: 5 })
}
}
参考
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙应用质量提升案例-应用Crash闪退问题案例分析
harmony 鸿蒙应用质量提升案例-稳定性测试常见JS_ERROR问题分析与定位
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签:
热门推荐
-
2、 - 优质文章
-
3、 gate.io
-
8、 golang
-
9、 openharmony
-
10、 Vue中input框自动聚焦