harmony 鸿蒙Drawing Geometric Shapes (Shape)
Drawing Geometric Shapes (Shape)
The drawing components are used to draw graphs on the page. The <Shape> component is the parent component of the drawing components. The attributes of <Shape> are universal attributes supported by all the drawing components. For details, see Shape.
Creating a Drawing Component
A drawing component can be created in either of the following ways:
- Create a drawing component with <Shape> as their parent to implement the effect similar to SVG. The API used is as follows:
Shape(value?: PixelMap)
In the API, the value parameter sets the drawing target. You can draw a graph in the specified PixelMap object. If the value parameter is not set, the graph is drawn in the current drawing target.
Shape() {
Rect().width(300).height(50)
}
- Create an independent drawing component to draw a specific shape. Seven shapes are supported: Circle, Ellipse, Line, Polyline, Polygon, Path, and Rect. The following uses the Circle API as an example:
Circle(options?: {width?: string|number, height?: string|number}
This API draws a circle on a page. The **width** parameter indicates the width of the circle, and the **height** parameter indicates the height of the circle. The diameter of the circle is determined by the minimum width and height.
Circle({ width: 150, height: 150 })

Viewport
viewPort{ x?: number|string, y?: number|string, width?: number|string, height?: number|string }
Creates a viewport, which is a rectangle in the user space that maps to the view boundary established for the associated SVG element. Among the four optional parameters, x and y represent the coordinates of the upper left corner of the viewport, and width and height represent the size of the viewport.
The following examples describe how to use the viewport:
- Zoom in or zoom out a graph through the shape viewport.
class tmp{
x:number = 0
y:number = 0
width:number = 75
height:number = 75
}
let viep:tmp = new tmp()
class tmp1{
x:number = 0
y:number = 0
width:number = 300
height:number = 300
}
let viep1:tmp1 = new tmp1()
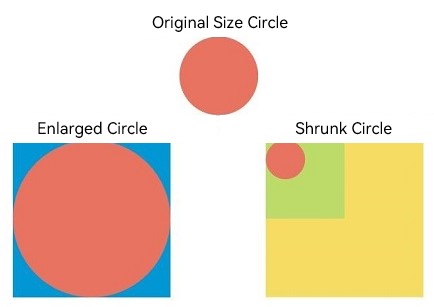
// Draw a circle whose width and height are both 75.
Text ('Original Size Circle')
Circle({width: 75, height: 75}).fill('#E87361')
Row({space:10}) {
Column() {
// Create a shape component whose width and height are both 150, the background color is yellow, and a viewport whose width and height are both 75. Fill the viewport with a blue rectangle and draw a circle with a diameter of 75 in the viewport.
// The drawing is complete. The viewport is zoomed in twice based on the width and height of the component.
Text ('Enlarged Circle')
Shape() {
Rect().width('100%').height('100%').fill('#0097D4')
Circle({width: 75, height: 75}).fill('#E87361')
}
.viewPort(viep)
.width(150)
.height(150)
.backgroundColor('#F5DC62')
}
Column() {
// Create a shape component whose width and height are both 150, the background color is yellow, and a viewport whose width and height are both 300. Fill the viewport with a green rectangle and draw a circle with a diameter of 75 in the viewport.
// After the drawing is complete, the viewport is zoomed out by twice based on the width and height of the component.
Text ('Shrunk Circle')
Shape() {
Rect().width('100%').height('100%').fill('#BDDB69')
Circle({width: 75, height: 75}).fill('#E87361')
}
.viewPort(viep1)
.width(150)
.height(150)
.backgroundColor('#F5DC62')
}
}
- Create a shape component whose width and height are both 300, with a yellow background and a viewport whose width and height are both 300. Fill the viewport with a blue rectangle and draw a circle with a radius of 75 in the viewport.
class tmp{
x:number = 0
y:number = 0
width:number = 300
height:number = 300
}
let viep:tmp = new tmp()
class tmp1{
x:number = -150
y:number = -150
width:number = 300
height:number = 300
}
let viep1:tmp1 = new tmp1()
Shape() {
Rect().width("100%").height("100%").fill("#0097D4")
Circle({ width: 150, height: 150 }).fill("#E87361")
}
.viewPort(viep)
.width(300)
.height(300)
.backgroundColor("#F5DC62")
.jpg)
- Create a shape component whose width and height are both 300, with a yellow background and a viewport whose width and height are both 300. Fill the viewport with a blue rectangle, draw a circle with a radius of 75 in the viewport, and move the viewport 150 to the right and below respectively.
Shape() {
Rect().width("100%").height("100%").fill("#0097D4")
Circle({ width: 150, height: 150 }).fill("#E87361")
}
.viewPort(viep1)
.width(300)
.height(300)
.backgroundColor("#F5DC62")
.jpg)
Setting Styles
The drawing component allows you to change the component style through various attributes.
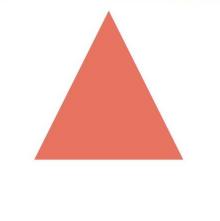
- You can use fill to set the color of the filling area of the component.
Path()
.width(100)
.height(100)
.commands('M150 0 L300 300 L0 300 Z')
.fill("#E87361")
 .jpg)
.jpg)
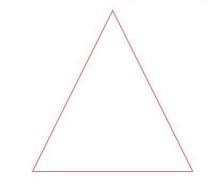
- You can use stroke to set the stroke color of a component.
Path()
.width(100)
.height(100)
.fillOpacity(0)
.commands('M150 0 L300 300 L0 300 Z')
.stroke(Color.Red)
- You can use strokeOpacity to set the stroke opacity.
Path()
.width(100)
.height(100)
.fillOpacity(0)
.commands('M150 0 L300 300 L0 300 Z')
.stroke(Color.Red)
.strokeWidth(10)
.strokeOpacity(0.2)

- You can use strokeLineJoin to set the join style of the stroke. Options include Bevel, Miter, and Round.
Polyline()
.width(100)
.height(100)
.fillOpacity(0)
.stroke(Color.Red)
.strokeWidth(8)
.points([[20, 0], [0, 100], [100, 90]])
// Set the join style of the stroke to Round.
.strokeLineJoin(LineJoinStyle.Round)

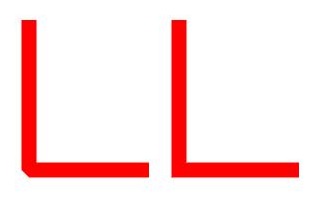
- strokeMiterLimit places a limit on the ratio of the miter length to the value of strokeWidth used to draw a miter join. The miter length indicates the distance from the outer tip to the inner corner of the miter. This attribute must be set to a value greater than or equal to 1 and takes effect when strokeLineJoin is set to LineJoinStyle.Miter.
Polyline()
.width(100)
.height(100)
.fillOpacity(0)
.stroke(Color.Red)
.strokeWidth(10)
.points([[20, 0], [20, 100], [100, 100]])
// Set the join style of the stroke to Miter.
.strokeLineJoin(LineJoinStyle.Miter)
// Set the limit on the ratio of the miter length to the value of strokeWidth used to draw a miter join.
.strokeMiterLimit(1/Math.sin(45))
Polyline()
.width(100)
.height(100)
.fillOpacity(0)
.stroke(Color.Red)
.strokeWidth(10)
.points([[20, 0], [20, 100], [100, 100]])
.strokeLineJoin(LineJoinStyle.Miter)
.strokeMiterLimit(1.42)
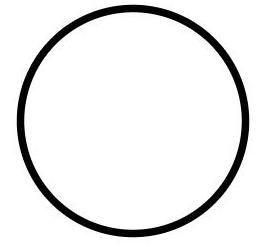
- Use the antiAlias attribute to set whether to enable anti-aliasing. The default value is true, indicating that anti-aliasing is enabled.
// Enable anti-aliasing.
Circle()
.width(150)
.height(200)
.fillOpacity(0)
.strokeWidth(5)
.stroke(Color.Black)
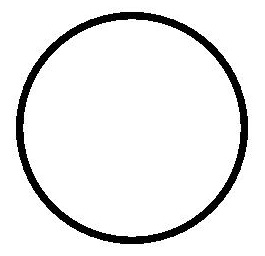
// Disable anti-aliasing.
Circle()
.width(150)
.height(200)
.fillOpacity(0)
.strokeWidth(5)
.stroke(Color.Black)
.antiAlias(false)
Example Scenario
- Draw a closed path at (-80, -5). The fill color is 0x317AF7, the stroke width is 10, the stroke color is red, and the stroke join style is miter (default value).
@Entry
@Component
struct ShapeExample {
build() {
Column({ space: 10 }) {
Shape() {
Path().width(200).height(60).commands('M0 0 L400 0 L400 150 Z')
}
.viewPort({ x: -80, y: -5, width: 500, height: 300 })
.fill(0x317AF7)
.stroke(Color.Red)
.strokeWidth(3)
.strokeLineJoin(LineJoinStyle.Miter)
.strokeMiterLimit(5)
}.width('100%').margin({ top: 15 })
}
}

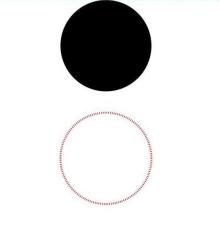
- Draw a circle with a diameter of 150 mm and a ring with a diameter of 150 mm and a red dotted line (use the shorter side as the diameter if the width and height are different).
@Entry
@Component
struct CircleExample {
build() {
Column({ space: 10 }) {
// Draw a circle whose diameter is 150.
Circle({ width: 150, height: 150 })
// Draw a ring with a diameter of 150 mm and a red dotted line.
Circle()
.width(150)
.height(200)
.fillOpacity(0)
.strokeWidth(3)
.stroke(Color.Red)
.strokeDashArray([1, 2])
}.width('100%')
}
}
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙Property Animation APIs
harmony 鸿蒙Property Animation Overview
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签:
热门推荐
-
2、 - 优质文章
-
3、 gate.io
-
8、 golang
-
9、 openharmony
-
10、 Vue中input框自动聚焦