harmony 鸿蒙Camera Development
Camera Development
When to Use
With the APIs provided by the Camera module, you can access and operate camera devices and develop new functions. Common operations include preview, photographing, and video recording. You can also implement flash control, exposure time control, focus mode control, zoom control, and much more.
Before calling camera APIs, be familiar with the following concepts:
- Static camera capabilities: A series of parameters used to describe inherent capabilities of a camera, such as orientation and supported resolution.
- Physical camera: An independent camera device. The physical camera ID is a string that uniquely identifies a physical camera.
- Asynchronous operation: A non-blocking operation that allows other operations to execute before it completes. To prevent the UI thread from being blocked, some Camera calls are asynchronous. Each asynchronous API provides the callback and promise functions.
How to Develop
Available APIs
For details about the APIs, see Camera Management.
Full-Process Scenario
The full process includes applying for permissions, creating an instance, setting parameters, managing sessions, taking photos, recording videos, and releasing resources.
Applying for Permissions
You must apply for the permissions for your application to access the camera device and other functions. The following table lists camera-related permissions.
| Permission | Attribute Value |
|---|---|
| Camera | ohos.permission.CAMERA |
| Call recording | ohos.permission.MICROPHONE |
| Storage | ohos.permission.WRITE_MEDIA |
| Read | ohos.permission.READ_MEDIA |
| Location | ohos.permission.MEDIA_LOCATION |
The code snippet is as follows:
const PERMISSIONS: Array<string> = [
'ohos.permission.CAMERA',
'ohos.permission.MICROPHONE',
'ohos.permission.MEDIA_LOCATION',
'ohos.permission.READ_MEDIA',
'ohos.permission.WRITE_MEDIA'
]
function applyPermission() {
console.info('[permission] get permission');
globalThis.abilityContext.requestPermissionFromUser(PERMISSIONS)
}
Creating an Instance
You must create an independent CameraManager instance before performing camera operations. If this operation fails, the camera may be occupied or unusable. If the camera is occupied, wait until it is released. You can call getSupportedCameras() to obtain the list of cameras supported by the current device. The list stores all camera IDs of the current device. Each of these IDs can be used to create an independent CameraManager instance. If the list is empty, no camera is available for the current device and subsequent operations cannot be performed. The camera has preview, shooting, video recording, and metadata output streams. You can use getSupportedOutputCapability() to obtain the output stream capabilities of the camera and configure them in the profile field in CameraOutputCapability. The procedure for creating a CameraManager instance is as follows:
import camera from '@ohos.multimedia.camera'
import image from '@ohos.multimedia.image'
import media from '@ohos.multimedia.media'
// Create a CameraManager instance.
context: any = getContext(this)
let cameraManager = camera.getCameraManager(this.context)
if (!cameraManager) {
console.error("camera.getCameraManager error")
return;
}
// Listen for camera state changes.
cameraManager.on('cameraStatus', (cameraStatusInfo) => {
console.log(`camera : ${cameraStatusInfo.camera.cameraId}`);
console.log(`status: ${cameraStatusInfo.status}`);
})
// Obtain the camera list.
let cameraArray = cameraManager.getSupportedCameras();
if (cameraArray.length <= 0) {
console.error("cameraManager.getSupportedCameras error")
return;
}
for (let index = 0; index < cameraArray.length; index++) {
console.log('cameraId : ' + cameraArray[index].cameraId); // Obtain the camera ID.
console.log('cameraPosition : ' + cameraArray[index].cameraPosition); // Obtain the camera position.
console.log('cameraType : ' + cameraArray[index].cameraType); // Obtain the camera type.
console.log('connectionType : ' + cameraArray[index].connectionType); // Obtain the camera connection type.
}
// Create a camera input stream.
let cameraInput
try {
cameraInput = cameraManager.createCameraInput(cameraArray[0]);
} catch () {
console.error('Failed to createCameraInput errorCode = ' + error.code);
}
// Listen for CameraInput errors.
let cameraDevice = cameraArray[0];
cameraInput.on('error', cameraDevice, (error) => {
console.log(`Camera input error code: ${error.code}`);
})
// Open the camera.
await cameraInput.open();
// Obtain the output stream capabilities supported by the camera.
let cameraOutputCap = cameraManager.getSupportedOutputCapability(cameraArray[0]);
if (!cameraOutputCap) {
console.error("cameraManager.getSupportedOutputCapability error")
return;
}
console.info("outputCapability: " + JSON.stringify(cameraOutputCap));
let previewProfilesArray = cameraOutputCap.previewProfiles;
if (!previewProfilesArray) {
console.error("createOutput previewProfilesArray == null||undefined")
}
let photoProfilesArray = cameraOutputCap.photoProfiles;
if (!photoProfilesArray) {
console.error("createOutput photoProfilesArray == null||undefined")
}
let videoProfilesArray = cameraOutputCap.videoProfiles;
if (!videoProfilesArray) {
console.error("createOutput videoProfilesArray == null||undefined")
}
let metadataObjectTypesArray = cameraOutputCap.supportedMetadataObjectTypes;
if (!metadataObjectTypesArray) {
console.error("createOutput metadataObjectTypesArray == null||undefined")
}
// Create a preview stream. For details about the surfaceId parameter, see the XComponent section. The preview stream is the surface provided by the XComponent.
let previewOutput
try {
previewOutput = cameraManager.createPreviewOutput(previewProfilesArray[0], surfaceId)
} catch (error) {
console.error("Failed to create the PreviewOutput instance.")
}
// Listen for PreviewOutput errors.
previewOutput.on('error', (error) => {
console.log(`Preview output error code: ${error.code}`);
})
// Create an ImageReceiver instance and set photo parameters. Wherein, the resolution must be one of the photographing resolutions supported by the current device, which are obtained by photoProfilesArray.
let imageReceiver = await image.createImageReceiver(1920, 1080, 4, 8)
// Obtain the surface ID for displaying the photos.
let photoSurfaceId = await imageReceiver.getReceivingSurfaceId()
// Create a photographing output stream.
let photoOutput
try {
photoOutput = cameraManager.createPhotoOutput(photoProfilesArray[0], photoSurfaceId)
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to createPhotoOutput errorCode = ' + error.code);
}
// Define video recording parameters.
let videoConfig = {
audioSourceType: 1,
videoSourceType: 1,
profile: {
audioBitrate: 48000,
audioChannels: 2,
audioCodec: 'audio/mp4v-es',
audioSampleRate: 48000,
durationTime: 1000,
fileFormat: 'mp4',
videoBitrate: 48000,
videoCodec: 'video/mp4v-es',
videoFrameWidth: 640,
videoFrameHeight: 480,
videoFrameRate: 30
},
url: 'file:///data/media/01.mp4',
orientationHint: 0,
maxSize: 100,
maxDuration: 500,
rotation: 0
}
// Create a video recording output stream.
let videoRecorder
media.createVideoRecorder().then((recorder) => {
console.log('createVideoRecorder called')
videoRecorder = recorder
})
// Set video recording parameters.
videoRecorder.prepare(videoConfig)
// Obtain the surface ID for video recording.
let videoSurfaceId
videoRecorder.getInputSurface().then((id) => {
console.log('getInputSurface called')
videoSurfaceId = id
})
// Create a VideoOutput instance.
let videoOutput
try {
videoOutput = cameraManager.createVideoOutput(videoProfilesArray[0], videoSurfaceId)
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to create the videoOutput instance. errorCode = ' + error.code);
}
// Listen for VideoOutput errors.
videoOutput.on('error', (error) => {
console.log(`Preview output error code: ${error.code}`);
})
Surfaces must be created in advance for the preview, shooting, and video recording stream. The preview stream is the surface provided by the XComponent, the shooting stream is the surface provided by ImageReceiver, and the video recording stream is the surface provided by VideoRecorder.
XComponent
mXComponentController: XComponentController = new XComponentController // Create an XComponentController.
build() {
Flex() {
XComponent({ // Create an XComponent.
id: '',
type: 'surface',
libraryname: '',
controller: this.mXComponentController
})
.onload(() => { // Set the onload callback.
// Set the surface width and height (1920 x 1080). For details about how to set the preview size, see the preview resolutions supported by the current device, which are obtained by previewProfilesArray.
this.mXComponentController.setXComponentSurfaceSize({surfaceWidth:1920,surfaceHeight:1080})
// Obtain the surface ID.
globalThis.surfaceId = mXComponentController.getXComponentSurfaceId()
})
.width('1920px') // Set the width of the XComponent.
.height('1080px') // Set the height of the XComponent.
}
}
ImageReceiver
function getImageReceiverSurfaceId() {
let receiver = image.createImageReceiver(640, 480, 4, 8)
console.log(TAG + 'before ImageReceiver check')
if (receiver !== undefined) {
console.log('ImageReceiver is ok')
surfaceId1 = receiver.getReceivingSurfaceId()
console.log('ImageReceived id: ' + JSON.stringify(surfaceId1))
} else {
console.log('ImageReceiver is not ok')
}
}
VideoRecorder
function getVideoRecorderSurface() {
await getFd('CameraManager.mp4');
mVideoConfig.url = mFdPath;
media.createVideoRecorder((err, recorder) => {
console.info('Entering create video receiver')
mVideoRecorder = recorder
console.info('videoRecorder is :' + JSON.stringify(mVideoRecorder))
console.info('videoRecorder.prepare called.')
mVideoRecorder.prepare(mVideoConfig, (err) => {
console.info('videoRecorder.prepare success.')
mVideoRecorder.getInputSurface((err, id) => {
console.info('getInputSurface called')
mVideoSurface = id
console.info('getInputSurface surfaceId: ' + JSON.stringify(mVideoSurface))
})
})
})
}
Managing Sessions
Creating a Session
// Create a session.
let captureSession
try {
captureSession = cameraManager.createCaptureSession()
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to create the CaptureSession instance. errorCode = ' + error.code);
}
// Listen for session errors.
captureSession.on('error', (error) => {
console.log(`Capture session error code: ${error.code}`);
})
// Start configuration for the session.
try {
captureSession.beginConfig()
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to beginConfig. errorCode = ' + error.code);
}
// Add the camera input stream to the session.
try {
captureSession.addInput(cameraInput)
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to addInput. errorCode = ' + error.code);
}
// Add the preview input stream to the session.
try {
captureSession.addOutput(previewOutput)
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to addOutput(previewOutput). errorCode = ' + error.code);
}
// Add the photographing output stream to the session.
try {
captureSession.addOutput(photoOutput)
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to addOutput(photoOutput). errorCode = ' + error.code);
}
// Commit the session configuration.
await captureSession.commitConfig()
// Start the session.
await captureSession.start().then(() => {
console.log('Promise returned to indicate the session start success.');
})
Switching a Session
// Stop the session.
await captureSession.stop()
// Start configuration for the session.
try {
captureSession.beginConfig()
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to beginConfig. errorCode = ' + error.code);
}
// Remove the photographing output stream from the session.
try {
captureSession.removeOutput(photoOutput)
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to removeOutput(photoOutput). errorCode = ' + error.code);
}
// Add a video recording output stream to the session.
try {
captureSession.addOutput(videoOutput)
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to addOutput(videoOutput). errorCode = ' + error.code);
}
// Commit the session configuration.
await captureSession.commitConfig()
// Start the session.
await captureSession.start().then(() => {
console.log('Promise returned to indicate the session start success.');
})
Setting Parameters
// Check whether the camera has flash.
let flashStatus
try {
flashStatus = captureSession.hasFlash()
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to hasFlash. errorCode = ' + error.code);
}
console.log('Promise returned with the flash light support status:' + flashStatus);
if (flashStatus) {
// Check whether the auto flash mode is supported.
let flashModeStatus
try {
let status = captureSession.isFlashModeSupported(camera.FlashMode.FLASH_MODE_AUTO)
flashModeStatus = status
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to check whether the flash mode is supported. errorCode = ' + error.code);
}
if(flashModeStatus) {
// Set the flash mode to auto.
try {
captureSession.setFlashMode(camera.FlashMode.FLASH_MODE_AUTO)
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to set the flash mode. errorCode = ' + error.code);
}
}
}
// Check whether the continuous auto focus is supported.
let focusModeStatus
try {
let status = captureSession.isFocusModeSupported(camera.FocusMode.FOCUS_MODE_CONTINUOUS_AUTO)
focusModeStatus = status
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to check whether the focus mode is supported. errorCode = ' + error.code);
}
if (focusModeStatus) {
// Set the focus mode to continuous auto focus.
try {
captureSession.setFocusMode(camera.FocusMode.FOCUS_MODE_CONTINUOUS_AUTO)
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to set the focus mode. errorCode = ' + error.code);
}
}
// Obtain the zoom ratio range supported by the camera.
let zoomRatioRange
try {
zoomRatioRange = captureSession.getZoomRatioRange()
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to get the zoom ratio range. errorCode = ' + error.code);
}
// Set a zoom ratio.
try {
captureSession.setZoomRatio(zoomRatioRange[0])
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to set the zoom ratio value. errorCode = ' + error.code);
}
Taking Photos
let settings = {
quality: camera.QualityLevel.QUALITY_LEVEL_HIGH, // Set the image quality to high.
rotation: camera.ImageRotation.ROTATION_0 // Set the image rotation angle to 0.
}
// Use the current photographing settings to take photos.
photoOutput.capture(settings, async (err) => {
if (err) {
console.error('Failed to capture the photo ${err.message}');
return;
}
console.log('Callback invoked to indicate the photo capture request success.');
});
Recording Videos
// Start the video recording output stream.
videoOutput.start(async (err) => {
if (err) {
console.error('Failed to start the video output ${err.message}');
return;
}
console.log('Callback invoked to indicate the video output start success.');
});
// Start video recording.
videoRecorder.start().then(() => {
console.info('videoRecorder start success');
}
// Stop video recording.
videoRecorder.stop().then(() => {
console.info('stop success');
}
// Stop the video recording output stream.
videoOutput.stop((err) => {
if (err) {
console.error('Failed to stop the video output ${err.message}');
return;
}
console.log('Callback invoked to indicate the video output stop success.');
});
For details about the APIs used for saving photos, see Image Processing.
Releasing Resources
// Stop the session.
captureSession.stop()
// Release the camera input stream.
cameraInput.close()
// Release the preview output stream.
previewOutput.release()
// Release the photographing output stream.
photoOutput.release()
// Release the video recording output stream.
videoOutput.release()
// Release the session.
captureSession.release()
// Set the session to null.
captureSession = null
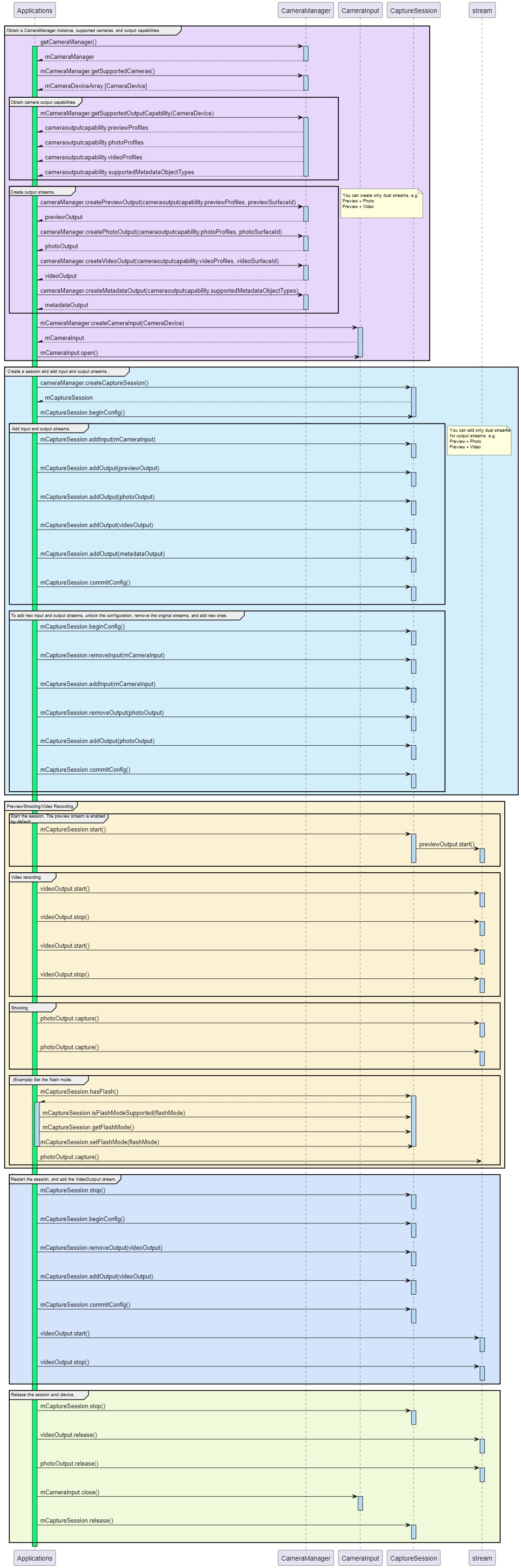
Process Flowchart
The following figure shows the process of using the camera.
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙Audio Capture Development
harmony 鸿蒙Audio Interruption Mode Development
harmony 鸿蒙Audio Playback Development
harmony 鸿蒙Audio Recording Development
harmony 鸿蒙Audio Rendering Development
harmony 鸿蒙Audio Routing and Device Management Development
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签:
热门推荐
-
2、 - 优质文章
-
3、 gate.io
-
8、 golang
-
9、 openharmony
-
10、 Vue中input框自动聚焦