harmony 鸿蒙Developing a JS Widget
Developing a JS Widget
The following describes how to develop JS widgets based on the web-like development paradigm.
Working Principles
Below shows the working principles of the widget framework.
Figure 1 Widget framework working principles in the stage model
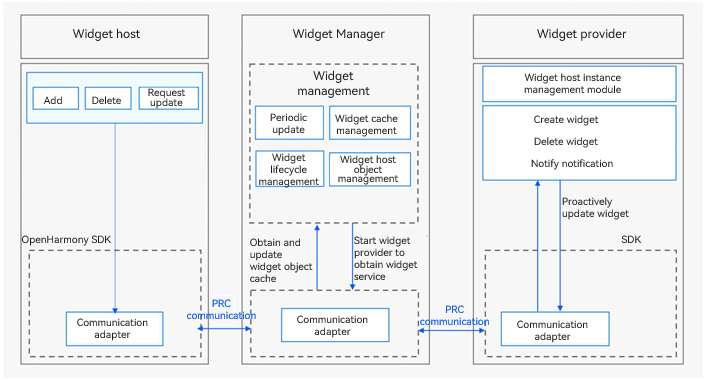
The widget host consists of the following modules:
Widget usage: provides operations such as creating, deleting, or updating a widget.
Communication adapter: provided by the SDK for communication with the Widget Manager. It sends widget-related operations to the Widget Manager.
The Widget Manager consists of the following modules:
Periodic updater: starts a scheduled task based on the update policy to periodically update a widget after it is added to the Widget Manager.
Cache manager: caches view information of a widget after it is added to the Widget Manager. This enables the cached data to be directly returned when the widget is obtained next time, greatly reducing the latency.
Lifecycle manager: suspends update when a widget is switched to the background or is blocked, and updates and/or clears widget data during upgrade and deletion.
Object manager: manages RPC objects of the widget host. It is used to verify requests from the widget host and process callbacks after the widget update.
Communication adapter: communicates with the widget host and provider through RPCs.
The widget provider consists of the following modules:
Widget service: implemented by the widget provider developer to process requests on widget creation, update, and deletion, and to provide corresponding widget services.
Instance manager: implemented by the widget provider developer for persistent management of widget instances allocated by the Widget Manager.
Communication adapter: provided by the SDK for communication with the Widget Manager. It pushes update data to the Widget Manager.
NOTE
You only need to develop the widget provider. The system automatically handles the work of the widget host and Widget Manager.
Available APIs
The FormExtensionAbility class has the following APIs. For details, see FormExtensionAbility.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| onAddForm(want: Want): formBindingData.FormBindingData | Called to notify the widget provider that a widget is being created. |
| onCastToNormalForm(formId: string): void | Called to notify the widget provider that a temporary widget is being converted to a normal one. |
| onUpdateForm(formId: string): void | Called to notify the widget provider that a widget is being updated. |
| onChangeFormVisibility(newStatus: { [key: string]: number }): void | Called to notify the widget provider that the widget visibility status is being changed. |
| onFormEvent(formId: string, message: string): void | Called to instruct the widget provider to process a widget event. |
| onRemoveForm(formId: string): void | Called to notify the widget provider that a widget is being destroyed. |
| onConfigurationUpdate(config: Configuration): void | Called when the configuration of the environment where the widget is running is being updated. |
| onShareForm?(formId: string): { [key: string]: Object } | Called to notify the widget provider that the widget host is sharing the widget data. |
The FormProvider class has the following APIs. For details, see FormProvider.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| setFormNextRefreshTime(formId: string, minute: number, callback: AsyncCallback<void>): void; | Sets the next refresh time for a widget. This API uses an asynchronous callback to return the result. |
| setFormNextRefreshTime(formId: string, minute: number): Promise<void>; | Sets the next refresh time for a widget. This API uses a promise to return the result. |
| updateForm(formId: string, formBindingData: FormBindingData, callback: AsyncCallback<void>): void; | Updates a widget. This API uses an asynchronous callback to return the result. |
| updateForm(formId: string, formBindingData: FormBindingData): Promise<void>; | Updates a widget. This API uses a promise to return the result. |
The FormBindingData class has the following APIs. For details, see FormBindingData.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| createFormBindingData(obj?: Object |string): FormBindingData | Creates a FormBindingData object. |
How to Develop
The widget provider development based on the stage model involves the following key steps:
Creating a FormExtensionAbility Instance: Develop the lifecycle callback functions of FormExtensionAbility.
Configuring the Widget Configuration Files: Configure the application configuration file module.json5 and profile configuration file.
Persistently Storing Widget Data: Manage widget data persistence.
Updating Widget Data: Call updateForm() to update the information displayed in a widget.
Developing the Widget UI Page: Use HML+CSS+JSON to develop a JS widget UI page.
Developing Widget Events: Add the router and message events for a widget.
Creating a FormExtensionAbility Instance
To create a widget in the stage model, you need to implement the lifecycle callbacks of FormExtensionAbility. Generate a widget template and then perform the following:
- Import related modules to EntryFormAbility.ets.
import FormExtensionAbility from '@ohos.app.form.FormExtensionAbility';
import formBindingData from '@ohos.app.form.formBindingData';
import formInfo from '@ohos.app.form.formInfo';
import formProvider from '@ohos.app.form.formProvider';
import dataPreferences from '@ohos.data.preferences';
import Want from '@ohos.app.ability.Want';
import Base from '@ohos.base';
- Implement the FormExtension lifecycle callbacks in EntryFormAbility.ets.
export default class EntryFormAbility extends FormExtensionAbility {
onAddForm(want: Want) {
console.info('[EntryFormAbility] onAddForm');
// Called when the widget is created. The widget provider should return the widget data binding class.
let obj: Record<string, string> = {
"title": "titleOnCreate",
"detail": "detailOnCreate"
};
let formData: formBindingData.FormBindingData = formBindingData.createFormBindingData(obj);
return formData;
}
onCastToNormalForm(formId: string) {
// Called when a temporary widget is being converted into a normal one. The widget provider should respond to the conversion.
console.info('[EntryFormAbility] onCastToNormalForm');
}
onUpdateForm(formId: string) {
// Override this method to support scheduled updates, periodic updates, or updates requested by the widget host.
console.info('[EntryFormAbility] onUpdateForm');
let obj: Record<string, string> = {
"title": "titleOnUpdate",
"detail": "detailOnUpdate"
};
let formData: formBindingData.FormBindingData = formBindingData.createFormBindingData(obj);
formProvider.updateForm(formId, formData).catch((error: Base.BusinessError) => {
console.info('[EntryFormAbility] updateForm, error:' + JSON.stringify(error));
});
}
onChangeFormVisibility(newStatus: Record<string, number>) {
// Called when the widget host initiates an event about visibility changes. The widget provider should do something to respond to the notification. This callback takes effect only for system applications.
console.info('[EntryFormAbility] onChangeFormVisibility');
}
onFormEvent(formId: string, message: string) {
// If the widget supports event triggering, override this method and implement the trigger.
console.info('[EntryFormAbility] onFormEvent');
}
onRemoveForm(formId: string) {
// Delete widget data.
console.info('[EntryFormAbility] onRemoveForm');
}
onAcquireFormState(want: Want) {
return formInfo.FormState.READY;
}
}
NOTE FormExtensionAbility cannot reside in the background. Therefore, continuous tasks cannot be processed in the widget lifecycle callbacks.
Configuring the Widget Configuration Files
- Configure ExtensionAbility information under extensionAbilities in the module.json5 file. For a FormExtensionAbility, you must specify metadata. Specifically, set name to ohos.extension.form (fixed), and set resource to the index of the widget configuration information. Example configuration:
{
"module": {
...
"extensionAbilities": [
{
"name": "EntryFormAbility",
"srcEntry": "./ets/entryformability/EntryFormAbility.ets",
"label": "$string:EntryFormAbility_label",
"description": "$string:EntryFormAbility_desc",
"type": "form",
"metadata": [
{
"name": "ohos.extension.form",
"resource": "$profile:form_config"
}
]
}
]
}
}
- Configure the widget configuration information. In the metadata configuration item of FormExtensionAbility, you can specify the resource index of specific configuration information of the widget. For example, if resource is set to $profile:form_config, form_config.json in the resources/base/profile/ directory of the development view is used as the profile configuration file of the widget. The following table describes the internal structure of the profile configuration file.
Table 1 Widget profile configuration file
|Field|Description|Data Type|Default Value Allowed|
|——–|——–|——–|——–|
|name|Class name of the widget. The value is a string with a maximum of 127 bytes.|String|No|
|description|Description of the widget. The value can be a string or a resource index to descriptions in multiple languages. The value is a string with a maximum of 255 bytes.|String|Yes (initial value: left empty)|
|src|Full path of the UI code corresponding to the widget.|String|No|
|window|Window-related configurations.|Object|Yes|
|isDefault|Whether the widget is a default one. Each UIAbility has only one default widget.
- true: The widget is the default one.
- false: The widget is not the default one.|Boolean|No|
|colorMode|Color mode of the widget.
- auto: auto-adaptive color mode
- dark: dark color mode
- light: light color mode|String|Yes (initial value: auto)|
|supportDimensions|Grid styles supported by the widget.
- 1 * 2: indicates a grid with one row and two columns.
- 2 * 2: indicates a grid with two rows and two columns.
- 2 * 4: indicates a grid with two rows and four columns.
- 4 * 4: indicates a grid with four rows and four columns.|String array|No|
|defaultDimension|Default grid style of the widget. The value must be available in the supportDimensions array of the widget.|String|No|
|updateEnabled|Whether the widget can be updated periodically.
- true: The widget can be updated at a specified interval (updateDuration) or at the scheduled time (scheduledUpdateTime). updateDuration takes precedence over scheduledUpdateTime.
- false: The widget cannot be updated periodically.|Boolean|No|
|scheduledUpdateTime|Scheduled time to update the widget. The value is in 24-hour format and accurate to minute.
updateDuration takes precedence over scheduledUpdateTime. If both are specified, the value specified by updateDuration is used.|String|Yes (initial value: 0:0)|
|updateDuration|Interval to update the widget. The value is a natural number, in the unit of 30 minutes.
If the value is 0, this field does not take effect.
If the value is a positive integer N, the interval is calculated by multiplying N and 30 minutes.
updateDuration takes precedence over scheduledUpdateTime. If both are specified, the value specified by updateDuration is used.|Number|Yes (initial value: 0)|
|formConfigAbility|Link to a specific page of the application. The value is a URI.|String|Yes (initial value: left empty)|
|formVisibleNotify|Whether the widget is allowed to use the widget visibility notification.|String|Yes (initial value: left empty)|
|metaData|Metadata of the widget. This field contains the array of the customizeData field.|Object|Yes (initial value: left empty)|
Example configuration:
{
"forms": [
{
"name": "widget",
"description": "This is a service widget.",
"src": "./js/widget/pages/index/index",
"window": {
"designWidth": 720,
"autoDesignWidth": true
},
"colorMode": "auto",
"isDefault": true,
"updateEnabled": true,
"scheduledUpdateTime": "10:30",
"updateDuration": 1,
"defaultDimension": "2*2",
"supportDimensions": [
"2*2"
]
}
]
}
Persistently Storing Widget Data
A widget provider is usually started when it is needed to provide information about a widget. The Widget Manager supports multi-instance management and uses the widget ID to identify an instance. If the widget provider supports widget data modification, it must persistently store the data based on the widget ID, so that it can access the data of the target widget when obtaining, updating, or starting a widget.
import FormExtensionAbility from '@ohos.app.form.FormExtensionAbility';
import formBindingData from '@ohos.app.form.formBindingData';
import dataPreferences from '@ohos.data.preferences';
import Want from '@ohos.app.ability.Want';
import Base from '@ohos.base';
import common from '@ohos.app.ability.common'
const DATA_STORAGE_PATH: string = "/data/storage/el2/base/haps/form_store";
let storeFormInfo = async (formId: string, formName: string, tempFlag: boolean, context: common.FormExtensionContext): Promise<void> => {
// Only the widget ID (formId), widget name (formName), and whether the widget is a temporary one (tempFlag) are persistently stored.
let formInfo: Record<string, string|boolean|number> = {
"formName": formName,
"tempFlag": tempFlag,
"updateCount": 0
};
try {
const storage: dataPreferences.Preferences = await dataPreferences.getPreferences(context, DATA_STORAGE_PATH);
// put form info
await storage.put(formId, JSON.stringify(formInfo));
console.info(`[EntryFormAbility] storeFormInfo, put form info successfully, formId: ${formId}`);
await storage.flush();
} catch (err) {
console.error(`[EntryFormAbility] failed to storeFormInfo, err: ${JSON.stringify(err as Base.BusinessError)}`);
}
}
export default class EntryFormAbility extends FormExtensionAbility {
onAddForm(want: Want) {
console.info('[EntryFormAbility] onAddForm');
if (want.parameters) {
let formId = JSON.stringify(want.parameters["ohos.extra.param.key.form_identity"]);
let formName = JSON.stringify(want.parameters["ohos.extra.param.key.form_name"]);
let tempFlag = want.parameters["ohos.extra.param.key.form_temporary"] as boolean;
// Persistently store widget data for subsequent use, such as instance acquisition and update.
// Implement this API based on project requirements.
storeFormInfo(formId, formName, tempFlag, this.context);
}
let obj: Record<string, string> = {
"title": "titleOnCreate",
"detail": "detailOnCreate"
};
let formData: formBindingData.FormBindingData = formBindingData.createFormBindingData(obj);
return formData;
}
}
You should override onRemoveForm to implement widget data deletion.
import FormExtensionAbility from '@ohos.app.form.FormExtensionAbility';
import dataPreferences from '@ohos.data.preferences';
import Base from '@ohos.base';
import common from '@ohos.app.ability.common'
const DATA_STORAGE_PATH: string = "/data/storage/el2/base/haps/form_store";
let deleteFormInfo = async (formId: string, context: common.FormExtensionContext): Promise<void> => {
try {
const storage: dataPreferences.Preferences = await dataPreferences.getPreferences(context, DATA_STORAGE_PATH);
// Delete the widget information.
await storage.delete(formId);
console.info(`[EntryFormAbility] deleteFormInfo, del form info successfully, formId: ${formId}`);
await storage.flush();
} catch (err) {
console.error(`[EntryFormAbility] failed to deleteFormInfo, err: ${JSON.stringify(err as Base.BusinessError)}`);
}
}
export default class EntryFormAbility extends FormExtensionAbility {
onRemoveForm(formId: string) {
console.info('[EntryFormAbility] onRemoveForm');
// Delete the persistent widget instance data.
// Implement this API based on project requirements.
deleteFormInfo(formId, this.context);
}
}
For details about how to implement data persistence, see Application Data Persistence Overview.
The Want object passed in by the widget host to the widget provider contains a flag that specifies whether the requested widget is normal or temporary.
Normal widget: a widget persistently used by the widget host
Temporary widget: a widget temporarily used by the widget host
Data of a temporary widget will be deleted on the Widget Manager if the widget framework is killed and restarted. The widget provider, however, is not notified of the deletion and still keeps the data. Therefore, the widget provider needs to clear the data of temporary widgets proactively if the data has been kept for a long period of time. If the widget host has converted a temporary widget into a normal one, the widget provider should change the widget data from temporary storage to persistent storage. Otherwise, the widget data may be deleted by mistake.
Updating Widget Data
When an application initiates a scheduled or periodic update, the application obtains the latest data and calls updateForm() to update the widget.
import FormExtensionAbility from '@ohos.app.form.FormExtensionAbility';
import formBindingData from '@ohos.app.form.formBindingData';
import formProvider from '@ohos.app.form.formProvider';
import Base from '@ohos.base';
export default class EntryFormAbility extends FormExtensionAbility {
onUpdateForm(formId: string) {
// Override this method to support scheduled updates, periodic updates, or updates requested by the widget host.
console.info('[EntryFormAbility] onUpdateForm');
let obj: Record<string, string> = {
"title": "titleOnUpdate",
"detail": "detailOnUpdate"
};
let formData: formBindingData.FormBindingData = formBindingData.createFormBindingData(obj);
// Call the updateForm() method to update the widget. Only the data passed through the input parameter is updated. Other information remains unchanged.
formProvider.updateForm(formId, formData).catch((error: Base.BusinessError) => {
console.info('[EntryFormAbility] updateForm, error:' + JSON.stringify(error));
});
}
}
Developing the Widget UI Page
You can use the web-like paradigm (HML+CSS+JSON) to develop JS widget pages. This section describes how to develop a page shown below.

- HML: uses web-like paradigm components to describe the widget page information.
<div class="container">
<stack>
<div class="container-img">
<image src="/common/widget.png" class="bg-img"></image>
</div>
<div class="container-inner">
<text class="title">{{title}}</text>
<text class="detail_text" onclick="routerEvent">{{detail}}</text>
</div>
</stack>
</div>
- CSS: defines style information about the web-like paradigm components in HML.
.container {
flex-direction: column;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
.bg-img {
flex-shrink: 0;
height: 100%;
}
.container-inner {
flex-direction: column;
justify-content: flex-end;
align-items: flex-start;
height: 100%;
width: 100%;
padding: 12px;
}
.title {
font-size: 19px;
font-weight: bold;
color: white;
text-overflow: ellipsis;
max-lines: 1;
}
.detail_text {
font-size: 16px;
color: white;
opacity: 0.66;
text-overflow: ellipsis;
max-lines: 1;
margin-top: 6px;
}
- JSON: defines data and event interaction on the widget UI page.
{
"data": {
"title": "TitleDefault",
"detail": "TextDefault"
},
"actions": {
"routerEvent": {
"action": "router",
"abilityName": "EntryAbility",
"params": {
"message": "add detail"
}
}
}
}
Developing Widget Events
You can set router and message events for components on a widget. The router event applies to UIAbility redirection, and the message event applies to custom click events.
The key steps are as follows:
Set the onclick field in the HML file to routerEvent or messageEvent, depending on the actions settings in the JSON file.
Set the router event.
- action: “router”, which indicates a router event.
- abilityName: name of the UIAbility to redirect to (PageAbility component in the FA model and UIAbility component in the stage model). For example, the default UIAbility name of the stage model created by DevEco Studio is EntryAbility.
- params: custom parameters passed to the target UIAbility. Set them as required. The value can be obtained from parameters in want used for starting the target UIAbility. For example, in the lifecycle function onCreate of the MainAbility in the stage model, you can obtain want and its parameters field.
Set the message event.
- action: “message”, which indicates a message event.
- params: custom parameters of the message event. Set them as required. The value can be obtained from message in the widget lifecycle function onFormEvent().
The following are examples:
- HML file:
<div class="container">
<stack>
<div class="container-img">
<image src="/common/widget.png" class="bg-img"></image>
</div>
<div class="container-inner">
<text class="title" onclick="routerEvent">{{title}}</text>
<text class="detail_text" onclick="messageEvent">{{detail}}</text>
</div>
</stack>
</div>
- CSS file:
.container {
flex-direction: column;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
.bg-img {
flex-shrink: 0;
height: 100%;
}
.container-inner {
flex-direction: column;
justify-content: flex-end;
align-items: flex-start;
height: 100%;
width: 100%;
padding: 12px;
}
.title {
font-size: 19px;
font-weight: bold;
color: white;
text-overflow: ellipsis;
max-lines: 1;
}
.detail_text {
font-size: 16px;
color: white;
opacity: 0.66;
text-overflow: ellipsis;
max-lines: 1;
margin-top: 6px;
}
- JSON file:
{
"data": {
"title": "TitleDefault",
"detail": "TextDefault"
},
"actions": {
"routerEvent": {
"action": "router",
"abilityName": "EntryAbility",
"params": {
"info": "router info",
"message": "router message"
}
},
"messageEvent": {
"action": "message",
"params": {
"detail": "message detail"
}
}
}
}
Note:
JSON Value in data supports multi-level nested data. When updating data, ensure that complete data is carried.
Assume that a widget is displaying the course information of Mr. Zhang on July 18, as shown in the following code snippet.
"data": {
"Day": "07.18",
"teacher": {
"name": "Mr.Zhang",
"course": "Math"
}
}
To update the widget content to the course information of Mr. Li on July 18, you must pass the complete data as follows, instead of only a single date item such as name or course:
"teacher": {
"name": "Mr.Li",
"course": "English"
}
- Receive the router event in UIAbility and obtain parameters.
import UIAbility from '@ohos.app.ability.UIAbility';
import AbilityConstant from '@ohos.app.ability.AbilityConstant';
import Want from '@ohos.app.ability.Want';
export default class EntryAbility extends UIAbility {
onCreate(want: Want, launchParam: AbilityConstant.LaunchParam) {
if (want.parameters) {
let params: Record<string, Object> = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(want.parameters.params));
// Obtain the info parameter passed in the router event.
if (params.info === "router info") {
// do something
// console.info("router info:" + params.info)
}
// Obtain the message parameter passed in the router event.
if (params.message === "router message") {
// do something
// console.info("router message:" + params.message)
}
}
}
};
- Receive the message event in FormExtensionAbility and obtain parameters.
import FormExtension from '@ohos.app.form.FormExtensionAbility';
export default class FormAbility extends FormExtension {
onFormEvent(formId: string, message: string) {
// Obtain the detail parameter passed in the message event.
let msg: Record<string, string> = JSON.parse(message)
if (msg.detail === "message detail") {
// do something
// console.info("message info:" + msg.detail)
}
}
};
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙Using Explicit Want to Start an Application Component
harmony 鸿蒙Using Implicit Want to Open a Website
harmony 鸿蒙AbilityStage Component Container
harmony 鸿蒙Accessing a DataAbility
harmony 鸿蒙Accessing a DataShareExtensionAbility from the FA Model
harmony 鸿蒙AccessibilityExtensionAbility
harmony 鸿蒙Common action and entities Values
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签:
热门推荐
-
2、 - 优质文章
-
3、 gate.io
-
8、 golang
-
9、 openharmony
-
10、 Vue中input框自动聚焦