harmony 鸿蒙Device Driver Porting
Device Driver Porting
This section describes how to port device drivers.
LCD Driver Porting
To port an LCD driver, write the driver, create an instance of the corresponding model in the driver, and complete the registration.
The LCD drivers are stored in //drivers/hdf_core/framework/model/display/driver/panel.
Create a panel driver.
Create an HDF driver and call the RegisterPanel method to register a model instance during driver initialization.
int32_t LCDxxEntryInit(struct HdfDeviceObject *object) { struct PanelData *panel = CreateYourPanel(); // Register a model instance. if (RegisterPanel(panel) != HDF_SUCCESS) { HDF_LOGE("%s: RegisterPanel failed", __func__); return HDF_FAILURE; } return HDF_SUCCESS; } struct HdfDriverEntry g_xxxxDevEntry = { .moduleVersion = 1, .moduleName = "LCD_XXXX", .Init = LCDxxEntryInit, }; HDF_INIT(g_xxxxDevEntry);Configure and load the panel driver.
Modify the source code file //vendor/vendor_name/product_name/config/device_info/device_info.hcs. Add configurations for the device named device_lcd for the display host.
 CAUTION
CAUTIONMake sure the value of moduleName is the same as that of moduleName in the panel driver.
root { ... display :: host { device_lcd :: device { deviceN :: deviceNode { policy = 0; priority = 100; preload = 2; moduleName = "LCD_XXXX"; } } } }
Touchscreen Driver Porting
This section describes how to port a touchscreen driver. The touchscreen drivers are stored in the source code directory //drivers/hdf_core/framework/model/input/driver/touchscreen. To port a touchscreen driver, register a ChipDevice model instance with the system.
For details about how to develop a touchscreen driver, see Touchscreen Development Guidelines.
Create a touchscreen driver.
Create the touch_ic_name.c file in the touchscreen directory. Write the following content:
#include "hdf_touch.h" static int32_t HdfXXXXChipInit(struct HdfDeviceObject *device) { ChipDevice *tpImpl = CreateXXXXTpImpl(); if(RegisterChipDevice(tpImpl) != HDF_SUCCESS) { // Register the ChipDevice model instance. ReleaseXXXXTpImpl(tpImpl); return HDF_FAILURE; } return HDF_SUCCESS; } struct HdfDriverEntry g_touchXXXXChipEntry = { .moduleVersion = 1, .moduleName = "HDF_TOUCH_XXXX", // Make sure the value is the same as that in the subsequent configuration. .Init = HdfXXXXChipInit, }; HDF_INIT(g_touchXXXXChipEntry);The following methods need to be implemented in ChipDevice.
|Method|Description| |——–|——–| |int32_t (*Init)(ChipDevice *device)|Initializes the device.| |int32_t (*Detect)(ChipDevice *device)|Detects the device.| |int32_t (*Suspend)(ChipDevice *device)|Places the device in sleep mode.| |int32_t (*Resume)(ChipDevice *device)|Wakes up the device.| |int32_t (*DataHandle)(ChipDevice *device)|Reads data from the device and writes touch point data to device > driver > frameData.| |int32_t (*UpdateFirmware)(ChipDevice *device)|Updates the firmware.|
Configure the product and load the driver.
All device information of the product is defined in the source code file //vendor/vendor_name/product_name/config/device_info/device_info.hcs. Modify the file and add configurations to the device named device_touch_chip in the host of the input command.
 NOTE
NOTEMake sure the value of moduleName is the same as that of moduleName in the touchscreen driver.
deviceN :: deviceNode { policy = 0; priority = 130; preload = 0; permission = 0660; moduleName = "HDF_TOUCH_XXXX"; deviceMatchAttr = "touch_XXXX_configs"; }
WLAN Driver Porting
The WLAN driver is divided into two parts. One of the parts manages WLAN devices, and the other part manages WLAN traffic.
Figure 1 OpenHarmony WLAN driver architecture
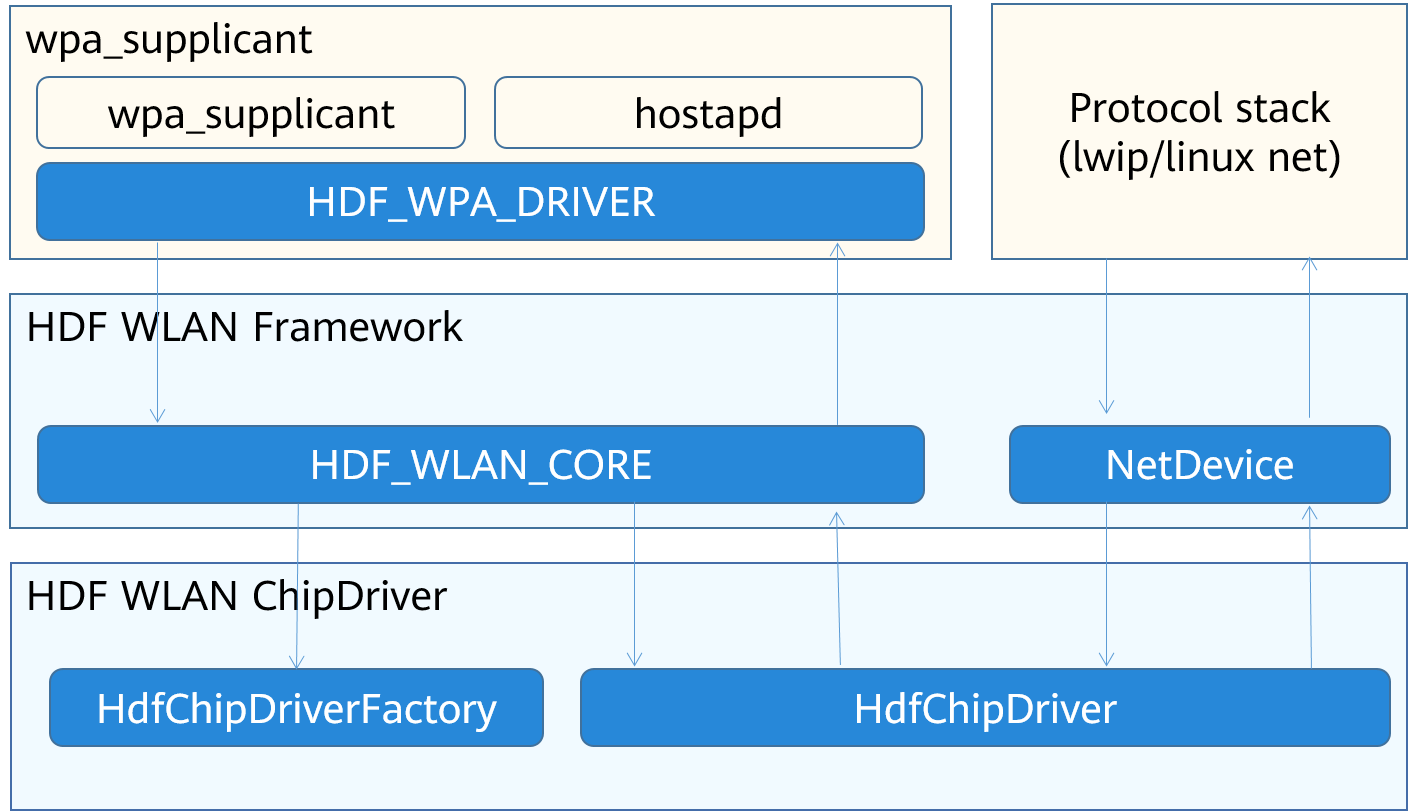
As shown in Figure 1, the part on the left manages WLAN devices, and the part on the right manages WLAN traffic. The HDF WLAN framework abstracts these two parts. The porting process of the driver can be considered as the implementation of the APIs required by the two parts. These APIs are described in the table below.
| API | Header File | Description |
|---|---|---|
| HdfChipDriverFactory | drivers\hdf_core\framework\include\wifi\hdf_wlan_chipdriver_manager.h | Factory of the ChipDriver, which is used to support multiple WLAN interfaces of a chip. |
| HdfChipDriver | drivers\hdf_core\framework\include\wifi\wifi_module.h | Manages a specific WLAN interface. |
| NetDeviceInterFace | drivers\hdf_core\framework\include\wifi\net_device.h | Communicates with the protocol stack, such as sending data and setting the status of network interfaces. |
NOTE
For details about the API development, see WLAN Development Guidelines.
The porting procedure is as follows:
Create a WLAN chip driver.
Create the hdf_wlan_chip_name.c file in /device/vendor_name/peripheral/wifi/chip_name/. The sample code is as follows:
static int32_t HdfWlanXXXChipDriverInit(struct HdfDeviceObject *device) { static struct HdfChipDriverFactory factory = CreateChipDriverFactory(); // Implement the method. struct HdfChipDriverManager *driverMgr = HdfWlanGetChipDriverMgr(); if (driverMgr->RegChipDriver(&factory) != HDF_SUCCESS) { // Register the driver factory. HDF_LOGE("%s fail: driverMgr is NULL!", __func__); return HDF_FAILURE; } return HDF_SUCCESS; } struct HdfDriverEntry g_hdfXXXChipEntry = { .moduleVersion = 1, .Init = HdfWlanXXXChipDriverInit, .Release = HdfWlanXXXChipRelease, .moduleName = "HDF_WIFI_CHIP_XXX" // Make sure the name is the same as the configured one. }; HDF_INIT(g_hdfXXXChipEntry);In the CreateChipDriverFactory method, create an object of the HdfChipDriverFactory type. This object provides the methods listed below.
|Method|Description| |——–|——–| |const char *driverName|Indicates the driver name.| |int32_t (*InitChip)(struct HdfWlanDevice *device)|Initializes the chip.| |int32_t (*DeinitChip)(struct HdfWlanDevice *device)|Deinitializes the chip.| |void (*ReleaseFactory)(struct HdfChipDriverFactory *factory)|Releases the HdfChipDriverFactory object.| |struct HdfChipDriver *(*Build)(struct HdfWlanDevice *device, uint8_t ifIndex)|Creates an HdfChipDriver. In the input parameters, device indicates the device information, and ifIndex indicates the sequence number of this interface in the chip.| |void (*Release)(struct HdfChipDriver *chipDriver)|Releases the chip driver.| |uint8_t (*GetMaxIFCount)(struct HdfChipDriverFactory *factory)|Obtains the maximum number of interfaces supported by the current chip.|
The Build method creates an HdfChipDriver object that manages the specified network interface. This object needs to provide the following methods:
|Method|Description| |——–|——–| |int32_t (*init)(struct HdfChipDriver *chipDriver, NetDevice *netDev)|Initializes the current network interface. The NetDeviceInterFace needs to be provided for the netDev.| |int32_t (*deinit)(struct HdfChipDriver *chipDriver, NetDevice *netDev)|Deinitializes the current network interface.| |struct HdfMac80211BaseOps *ops|Provides the WLAN basic capability interface set.| |struct HdfMac80211STAOps *staOps|Provides the interface set required for supporting the STA mode.| |struct HdfMac80211APOps *apOps|Provides the interface set required for supporting the AP mode.|
Create a configuration file to describe the chips supported by the driver.
Create a chip configuration file in the product configuration directory and save it to the source code path //vendor/vendor_name/product_name/config/wifi/wlan_chip_chip_name.hcs.
root { wlan_config { chip_name :& chipList { chip_name :: chipInst { match_attr = "hdf_wlan_chips_chip_name"; /* Indicates the configuration matching attribute, which is used to provide the configuration root of the driver. */ driverName = "driverName"; /* Indicates the driver name, which must be the same as that of driverName in HdfChipDriverFactory.*/ sdio { vendorId = 0xXXXX; /* your vendor id */ deviceId = [0xXXXX]; /*your supported devices */ } } } } } NOTE
NOTEReplace the values of vendor_name, product_name, and chip_name in the path and file with the actual names.
Set vendorId and deviceId to the actual vendor ID and chip ID, respectively.
Edit the configuration file and load the driver.
All device information of the product is defined in the source code file //vendor/vendor_name/product_name/config/device_info/device_info.hcs. Modify the file and add configurations to the device named device_wlan_chips in the host of the network command. The sample code is as follows:
deviceN :: deviceNode { policy = 0; preload = 2; moduleName = "HDF_WLAN_CHIPS"; deviceMatchAttr = "hdf_wlan_chips_chip_name"; serviceName = "driverName"; } NOTE
NOTEMake sure the value of moduleName is the same as that of moduleName in the WLAN driver.
Modify the Kconfig file to make the ported WLAN driver appear in the kernel configuration.
Add configurations to device/vendor_name/drivers/Kconfig. The sample code is as follows:
config DRIVERS_HDF_WIFI_chip_name bool "Enable chip_name Host driver" default n depends on DRIVERS_HDF_WLAN help Answer Y to enable chip_name Host driver. NOTE
NOTEReplace chip_name with the actual chip name.
Modify the build script to enable the driver to participate in the kernel build.
Add the following content to the end of the source code file //device/vendor_name/drivers/lite.mk:
ifeq ($(LOSCFG_DRIVERS_HDF_WIFI_chip_name), y) # After the build is complete, an object named hdf_wlan_chipdriver_chip_name needs to be linked. You are advised to use this name to prevent conflicts. LITEOS_BASELIB += -lhdf_wlan_chipdriver_chip_name # Add the build directory gpio. LIB_SUBDIRS += ../peripheral/wifi/chip_name endif NOTE
NOTEReplace chip_name with the actual chip name.
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙Combo Solution – ASR Chip Porting Case
harmony 鸿蒙Mini-System Devices with Screens – Bestechnic SoC Porting Case
harmony 鸿蒙IoT Solution - Chipsea CST85 Chip Porting Case
harmony 鸿蒙Standard System Solution – Rockchip RK3568 Porting Case
harmony 鸿蒙A Method for Rapidly Porting the OpenHarmony Linux Kernel
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签:
热门推荐
-
2、 - 优质文章
-
3、 gate.io
-
8、 golang
-
9、 openharmony
-
10、 Vue中input框自动聚焦