harmony 鸿蒙Video Playback
Video Playback
OpenHarmony provides two solutions for video playback development:
AVPlayer class: provides ArkTS and JS APIs to implement audio and video playback. It also supports parsing streaming media and local assets, decapsulating media assets, decoding video, and rendering video. It is applicable to end-to-end playback of media assets and can be used to play video files in MP4 and MKV formats.
<Video> component: encapsulates basic video playback capabilities. It can be used to play video files after the data source and basic information are set. However, its scalability is poor. This component is provided by ArkUI. For details about how to use this component for video playback development, see Video Component.
In this topic, you will learn how to use the AVPlayer to develop a video playback service that plays a complete video file. If you want the application to continue playing the video in the background or when the screen is off, you must use the AVSession and continuous task to prevent the playback from being forcibly interrupted by the system.
Development Guidelines
The full playback process includes creating an AVPlayer instance, setting the media asset to play and the window to display the video, setting playback parameters (volume, speed, and scale type), controlling playback (play, pause, seek, and stop), resetting the playback configuration, and releasing the instance. During application development, you can use the state attribute of the AVPlayer to obtain the AVPlayer state or call on(‘stateChange’) to listen for state changes. If the application performs an operation when the AudioPlayer is not in the given state, the system may throw an exception or generate other undefined behavior.
Figure 1 Playback state transition
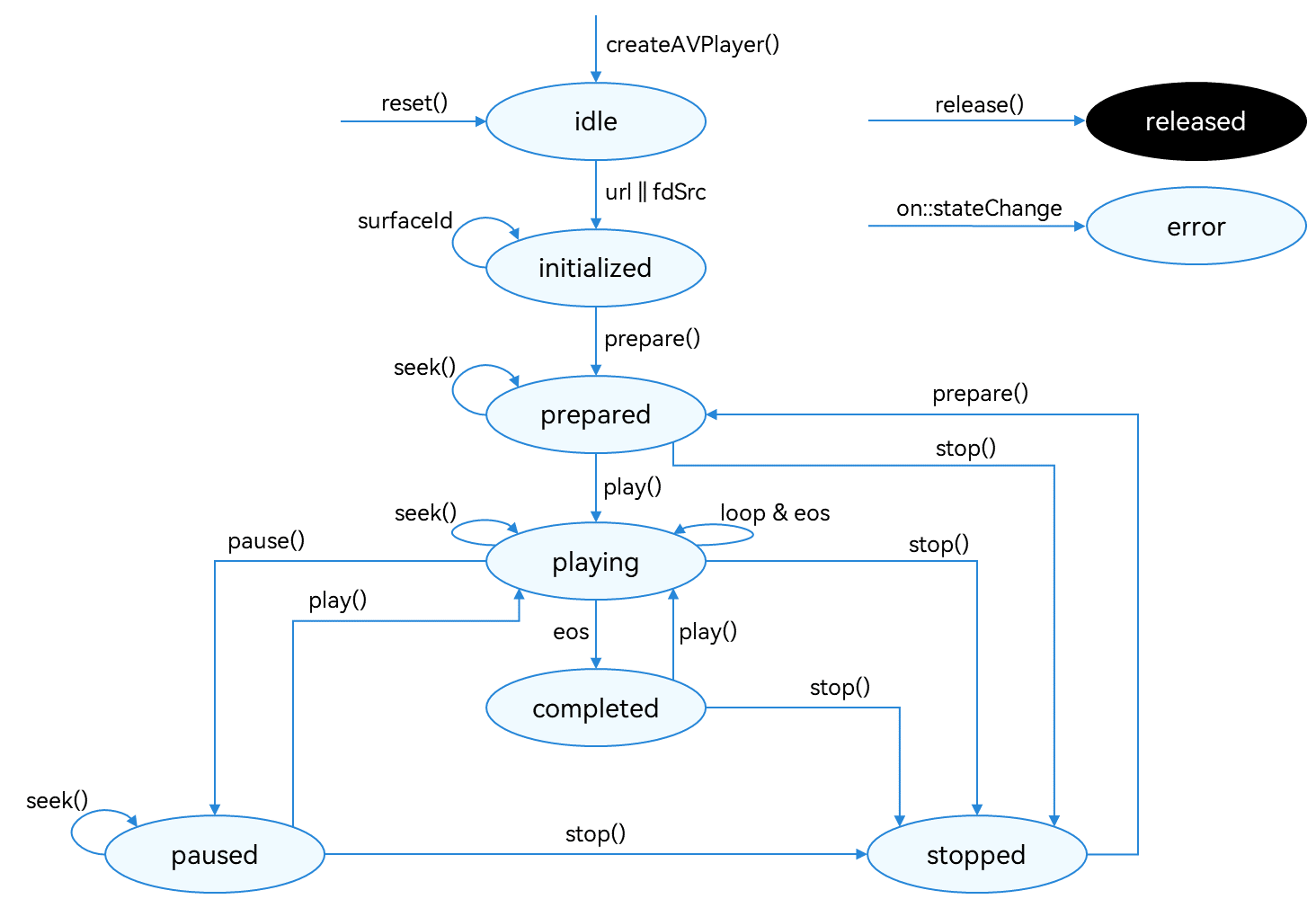
For details about the state, see AVPlayerState. When the AVPlayer is in the prepared, playing, paused, or completed state, the playback engine is working and a large amount of RAM is occupied. If your application does not need to use the AVPlayer, call reset() or release() to release the instance.
How to Develop
Read AVPlayer for the API reference.
Call createAVPlayer() to create an AVPlayer instance. The AVPlayer is the idle state.
Set the events to listen for, which will be used in the full-process scenario. The table below lists the supported events. |Event Type|Description| |——–|——–| |stateChange|Mandatory; used to listen for changes of the state attribute of the AVPlayer.| |error|Mandatory; used to listen for AVPlayer errors.| |durationUpdate|Used to listen for progress bar updates to refresh the media asset duration.| |timeUpdate|Used to listen for the current position of the progress bar to refresh the current time.| |seekDone|Used to listen for the completion status of the seek() request.
This event is reported when the AVPlayer seeks to the playback position specified in seek().| |speedDone|Used to listen for the completion status of the setSpeed() request.
This event is reported when the AVPlayer plays video at the speed specified in setSpeed().| |volumeChange|Used to listen for the completion status of the setVolume() request.
This event is reported when the AVPlayer plays video at the volume specified in setVolume().| |bitrateDone|Used to listen for the completion status of the setBitrate() request, which is used for HTTP Live Streaming (HLS) streams.
This event is reported when the AVPlayer plays video at the bit rate specified in setBitrate().| |availableBitrates|Used to listen for available bit rates of HLS resources. The available bit rates are provided for setBitrate().| |bufferingUpdate|Used to listen for network playback buffer information.| |startRenderFrame|Used to listen for the rendering time of the first frame during video playback.| |videoSizeChange|Used to listen for the width and height of video playback and adjust the window size and ratio.| |audioInterrupt|Used to listen for audio interruption. This event is used together with the audioInterruptMode attribute.
This event is reported when the current audio playback is interrupted by another (for example, when a call is coming), so the application can process the event in time.|Set the media asset URL. The AVPlayer enters the initialized state. > NOTE > > The URL in the code snippet below is for reference only. You need to check the media asset validity and set the URL based on service requirements. > > - If local files are used for playback, ensure that the files are available and the application sandbox path is used for access. For details about how to obtain the application sandbox path, see Obtaining Application File Paths. For details about the application sandbox and how to push files to the application sandbox, see File Management. > > - If a network playback path is used, you must request the ohos.permission.INTERNET permission. > > - You can also use ResourceManager.getRawFd to obtain the file descriptor of a file packed in the HAP file. For details, see ResourceManager API Reference. > > - The playback formats and protocols in use must be those supported by the system.
Obtain and set the surface ID of the window to display the video. The application obtains the surface ID from the XComponent. For details about the process, see XComponent.
Call prepare() to switch the AVPlayer to the prepared state. In this state, you can obtain the duration of the media asset to play and set the scale type and volume.
Call play(), pause(), seek(), and stop() to perform video playback control as required.
(Optional) Call reset() to reset the AVPlayer. The AVPlayer enters the idle state again and you can change the media asset URL.
Call release() to switch the AVPlayer to the released state. Now your application exits the playback.
Sample Code
import media from '@ohos.multimedia.media';
import fs from '@ohos.file.fs';
import common from '@ohos.app.ability.common';
import { BusinessError } from '@ohos.base';
export class AVPlayerDemo {
private count: number = 0;
private surfaceID: string = ''; // The surfaceID parameter specifies the window used to display the video. Its value is obtained through the XComponent.
private isSeek: boolean = true; // Specify whether the seek operation is supported.
private fileSize: number = -1;
private fd: number = 0;
// Set AVPlayer callback functions.
setAVPlayerCallback(avPlayer: media.AVPlayer) {
// Callback function for the seek operation.
avPlayer.on('seekDone', (seekDoneTime: number) => {
console.info(`AVPlayer seek succeeded, seek time is ${seekDoneTime}`);
})
// Callback function for errors. If an error occurs during the operation on the AVPlayer, reset() is called to reset the AVPlayer.
avPlayer.on('error', (err: BusinessError) => {
console.error(`Invoke avPlayer failed, code is ${err.code}, message is ${err.message}`);
avPlayer.reset(); // Call reset() to reset the AVPlayer, which enters the idle state.
})
// Callback function for state changes.
avPlayer.on('stateChange', async (state: string, reason: media.StateChangeReason) => {
switch (state) {
case 'idle': // This state is reported upon a successful callback of reset().
console.info('AVPlayer state idle called.');
avPlayer.release(); // Call release() to release the instance.
break;
case 'initialized': // This state is reported when the AVPlayer sets the playback source.
console.info('AVPlayer state initialized called.');
avPlayer.surfaceId = this.surfaceID; // Set the window to display the video. This setting is not required when a pure audio asset is to be played.
avPlayer.prepare();
break;
case 'prepared': // This state is reported upon a successful callback of prepare().
console.info('AVPlayer state prepared called.');
avPlayer.play(); // Call play() to start playback.
break;
case 'playing': // This state is reported upon a successful callback of play().
console.info('AVPlayer state playing called.');
if (this.count !== 0) {
if (this.isSeek) {
console.info('AVPlayer start to seek.');
avPlayer.seek(avPlayer.duration); // Call seek() to seek to the end of the video clip.
} else {
// When the seek operation is not supported, the playback continues until it reaches the end.
console.info('AVPlayer wait to play end.');
}
} else {
avPlayer.pause(); // Call pause() to pause the playback.
}
this.count++;
break;
case 'paused': // This state is reported upon a successful callback of pause().
console.info('AVPlayer state paused called.');
avPlayer.play(); // Call play() again to start playback.
break;
case 'completed': // This state is reported upon the completion of the playback.
console.info('AVPlayer state completed called.');
avPlayer.stop(); // Call stop() to stop the playback.
break;
case 'stopped': // This state is reported upon a successful callback of stop().
console.info('AVPlayer state stopped called.');
avPlayer.reset(); // Call reset() to reset the AVPlayer state.
break;
case 'released':
console.info('AVPlayer state released called.');
break;
default:
console.info('AVPlayer state unknown called.');
break;
}
})
}
// The following demo shows how to use the file system to open the sandbox address, obtain the media file address, and play the media file using the URL attribute.
async avPlayerUrlDemo() {
// Create an AVPlayer instance.
let avPlayer: media.AVPlayer = await media.createAVPlayer();
// Set a callback function for state changes.
this.setAVPlayerCallback(avPlayer);
let fdPath = 'fd://';
let context = getContext(this) as common.UIAbilityContext;
// Obtain the sandbox address filesDir through UIAbilityContext. The stage model is used as an example.
let pathDir = context.filesDir;
let path = pathDir + '/H264_AAC.mp4';
// Open the corresponding file address to obtain the file descriptor and assign a value to the URL to trigger the reporting of the initialized state.
let file = await fs.open(path);
fdPath = fdPath + '' + file.fd;
this.isSeek = true; // The seek operation is supported.
avPlayer.url = fdPath;
}
// The following demo shows how to use resourceManager to obtain the media file packed in the HAP file and play the media file by using the fdSrc attribute.
async avPlayerFdSrcDemo() {
// Create an AVPlayer instance.
let avPlayer: media.AVPlayer = await media.createAVPlayer();
// Set a callback function for state changes.
this.setAVPlayerCallback(avPlayer);
// Call getRawFd of the resourceManager member of UIAbilityContext to obtain the media asset URL.
// The return type is {fd,offset,length}, where fd indicates the file descriptor address of the HAP file, offset indicates the media asset offset, and length indicates the duration of the media asset to play.
let context = getContext(this) as common.UIAbilityContext;
let fileDescriptor = await context.resourceManager.getRawFd('H264_AAC.mp4');
let avFileDescriptor: media.AVFileDescriptor =
{ fd: fileDescriptor.fd, offset: fileDescriptor.offset, length: fileDescriptor.length };
this.isSeek = true; // The seek operation is supported.
// Assign a value to fdSrc to trigger the reporting of the initialized state.
avPlayer.fdSrc = avFileDescriptor;
}
// The following demo shows how to use the file system to open the sandbox address, obtain the media file address, and play the media file with the seek operation using the dataSrc attribute.
async avPlayerDataSrcSeekDemo() {
// Create an AVPlayer instance.
let avPlayer: media.AVPlayer = await media.createAVPlayer();
// Set a callback function for state changes.
this.setAVPlayerCallback(avPlayer);
// dataSrc indicates the playback source address. When the seek operation is supported, fileSize indicates the size of the file to be played. The following describes how to assign a value to fileSize.
let src: media.AVDataSrcDescriptor = {
fileSize: -1,
callback: (buf: ArrayBuffer, length: number, pos: number|undefined) => {
let num = 0;
if (buf == undefined||length == undefined||pos == undefined) {
return -1;
}
num = fs.readSync(this.fd, buf, { offset: pos, length: length });
if (num > 0 && (this.fileSize >= pos)) {
return num;
}
return -1;
}
}
let context = getContext(this) as common.UIAbilityContext;
// Obtain the sandbox address filesDir through UIAbilityContext. The stage model is used as an example.
let pathDir = context.filesDir;
let path = pathDir + '/H264_AAC.mp4';
await fs.open(path).then((file: fs.File) => {
this.fd = file.fd;
})
// Obtain the size of the file to be played.
this.fileSize = fs.statSync(path).size;
src.fileSize = this.fileSize;
this.isSeek = true; // The seek operation is supported.
avPlayer.dataSrc = src;
}
// The following demo shows how to use the file system to open the sandbox address, obtain the media file address, and play the media file without the seek operation using the dataSrc attribute.
async avPlayerDataSrcNoSeekDemo() {
// Create an AVPlayer instance.
let avPlayer: media.AVPlayer = await media.createAVPlayer();
// Set a callback function for state changes.
this.setAVPlayerCallback(avPlayer);
let context = getContext(this) as common.UIAbilityContext;
let src: media.AVDataSrcDescriptor = {
fileSize: -1,
callback: (buf: ArrayBuffer, length: number) => {
let num = 0;
if (buf == undefined||length == undefined) {
return -1;
}
num = fs.readSync(this.fd, buf);
if (num > 0) {
return num;
}
return -1;
}
}
// Obtain the sandbox address filesDir through UIAbilityContext. The stage model is used as an example.
let pathDir = context.filesDir;
let path = pathDir + '/H264_AAC.mp4';
await fs.open(path).then((file: fs.File) => {
this.fd = file.fd;
})
this.isSeek = false; // The seek operation is not supported.
avPlayer.dataSrc = src;
}
// The following demo shows how to play live streams by setting the network address through the URL.
async avPlayerLiveDemo() {
// Create an AVPlayer instance.
let avPlayer: media.AVPlayer = await media.createAVPlayer();
// Set a callback function for state changes.
this.setAVPlayerCallback(avPlayer);
this.isSeek = false; // The seek operation is not supported.
avPlayer.url = 'http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:xx/xx/index.m3u8'; // Play live webcasting streams using HLS.
}
}
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙Developing Audio Call
harmony 鸿蒙Audio Call Development
harmony 鸿蒙Audio Effect Management
harmony 鸿蒙Audio Input Device Management
harmony 鸿蒙Audio Output Device Management
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签:
热门推荐
-
2、 - 优质文章
-
3、 gate.io
-
8、 golang
-
9、 openharmony
-
10、 Vue中input框自动聚焦