harmony 鸿蒙USB
USB
Introduction
Function Overview
The universal serial bus (USB) consists of a USB host and multiple USB devices. The USB host implement data transfer and port management in the USB bus, and the USB device can connect to various peripherals. Therefore, USB driver development is divided into USB host driver development and USB device driver development.
The USB module of OpenHarmony supports the development of USB services, provides USB-related functions, provides interfaces to read and write USB device data of third-party function drivers in user mode, creates and deletes USB devices, obtains notification events, enables or disables event listening, implements non-isochronous and isochronous data transfer over USB pipes, and sets custom USB attributes.
The USB DriverDevelop Kit (DDK) is the USB driver development kit provided by the Framework of the OpenHarmony Driver Foundation (HDF). This kit consists of the USB Host DDK and USB Device DDK. It supports the development of USB device drivers based on the user mode and provides rich USB driver development capabilities that help you to efficiently develop USB drivers.
Basic Concepts
- Pipe
A pipe is a model for data transfer between the USB host and a device endpoint. Once a USB device is powered on, a pipe, that is, the default control pipe, is established. The USB host obtains the description, configuration, and status of the USB device through the pipe, and configures the device as requested. Pipes and endpoints are associated and share the same attributes, such as the supported transfer type, maximum packet length, and data transfer direction.
- Endpoint
The minimum unit that transfers and receives data in a USB device. It supports unidirectional or bidirectional data transfer. One USB device may include several endpoints, and different endpoints are distinguished by endpoint numbers and directions. Different endpoints can support different data transfer types, access intervals, and maximum packet sizes. All endpoints except endpoint 0 support data transfer in only one direction. Endpoint 0 is a special endpoint that supports bidirectional control transfer.
- Interface
The application implements device control and data transfer through exchanging data with the device. Because a pipe supports only one data transfer type, multiple pipes are usually required to complete data exchange in this process. A collection of pipes that are used together to control a device is called an interface.
- Descriptor
A data structure used to describe device attributes. The first byte indicates the descriptor size (number of bytes), and the second byte indicates the descriptor type.
Working Principles
USB Host DDK
The USB Host DDK provides the capability of developing USB drivers on the host. Based on functions, APIs of the USB Host DDK are classified into three types: DDK initialization, interface object operation, and request object operation.
Figure 1 USB host driver model
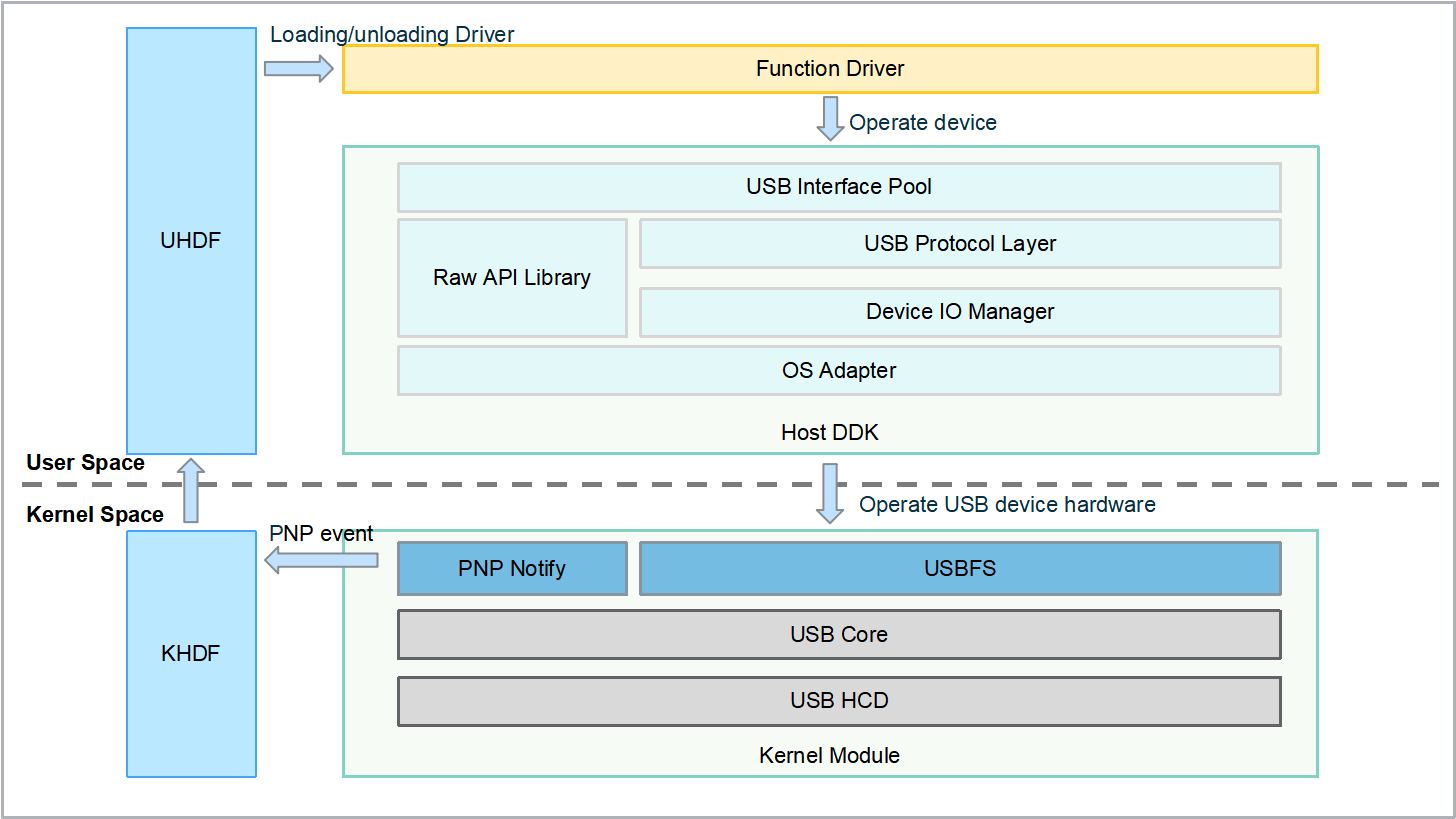
The USB Interface Pool module manages USB interfaces. It applies for and reclaims USB interface objects, which are used to record device port information and resources. The module manages USB interfaces by USB port. In addition, it provides USB DDK APIs to read and write USB data.
The USB Protocol Layer module provides USB protocol encapsulation, translates and parses device I/O and control commands based on the USB protocol, manages device descriptors, and matches descriptors based on the enum information reported by the USB device. This module creates the corresponding USB interface objects and adds them to the USB Interface Pool module for management.
The Device I/O Manager module manages USB I/O requests and provides synchronous and asynchronous I/O management mechanisms. For the asynchronous I/O management mechanism, the module records the asynchronous I/O requests and processes the requests to be sent through the APIs provided by the Raw API Library module. After receiving the processing result from the USB controller, the I/O request receiving thread parses the processing result and reports it to the upper-layer caller.
The Raw API Library module abstracts underlying OS capabilities, defines unified OS capability APIs, and provides the USB RAW APIs needed to implement more complex driver functions.
The OS Adapter module encapsulates operations related to platforms (Linux and LiteOS). It compiles encapsulation APIs depending on the configuration of the specific platform. On the Linux platform, all USB FS access operations are encapsulated in this module. On the LiteOS platform, all device access operations based on the FreeBSD USB framework are encapsulated in this module.
The PNP Notify module dynamically monitors USB status changes. This module updates the device information when a device is added or removed. Meanwhile, it reports all USB device information to the PNP Notify Manager module on the UHDF side through the KHDF to load or uninstall third-party function drivers.
USB Device DDK
The USB Device DDK provides the capability of developing USB drivers on the device side. For example, with the dynamic registration and deregistration capabilities, you can dynamically add and combine USB ports based on the actual requirement; with the dynamic instantiation capability, you can create device instances and transmission channels based on dynamically delivered device, configuration, interface, and endpoint descriptors. In addition, the following functions are supported: sending and receiving data in user mode, isolating multiple logical devices from each other on a physical device, and accessing different logical devices from different application processes at the same time.
Figure 2 USB device driver model
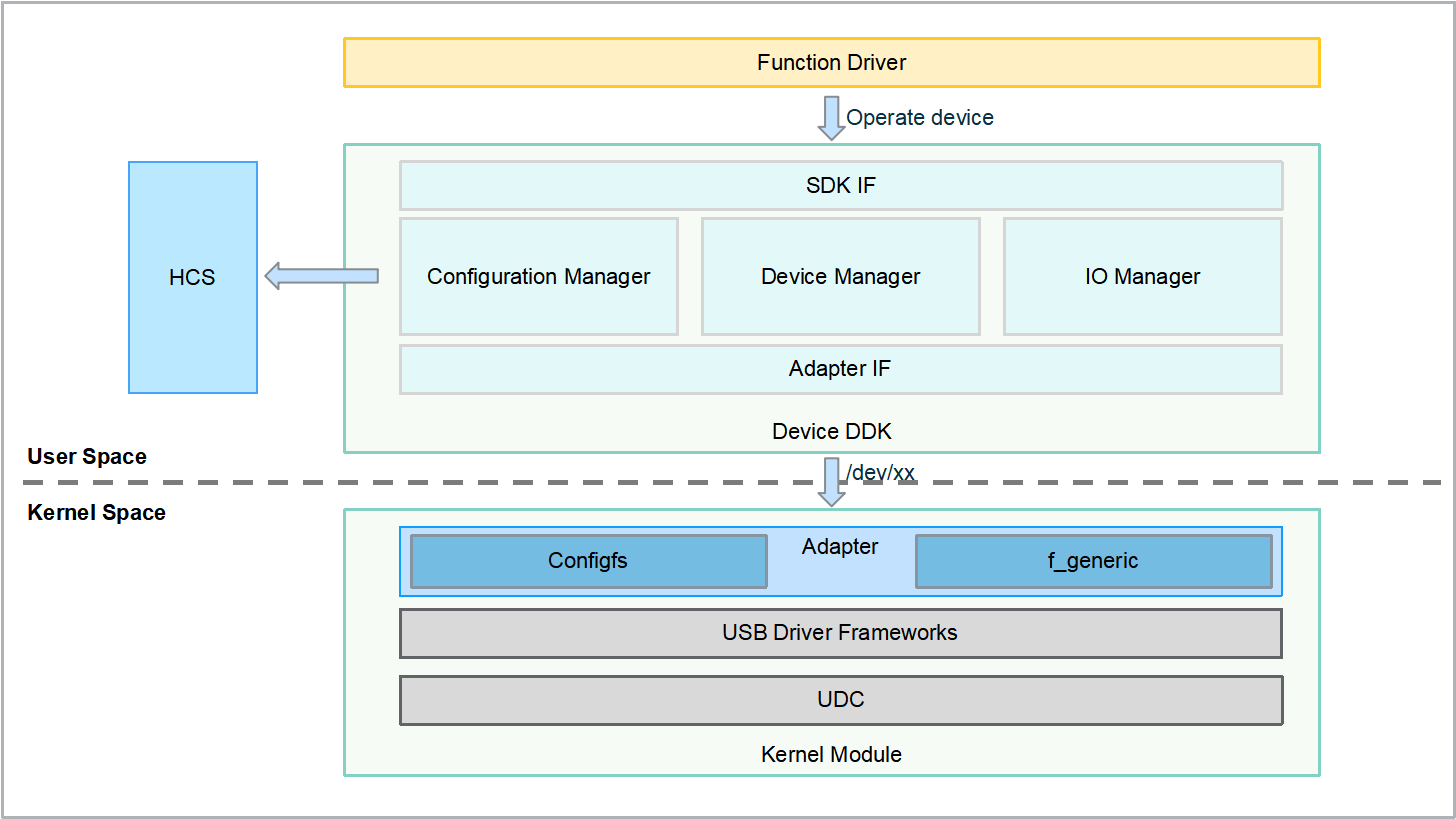
The SDK IF module divides USB devices logically by device, interface, and pipe, and encapsulates functions including configuration management, device management, and I/O management. This module also provides APIs for device driver development, such as creating and obtaining devices, receiving events, and sending and receiving data.
The Configuration Manager module parses the .hcs file for the USB descriptor information, which will be used for creating USB devices. In addition, the module provides operations such as reading, creating, deleting, and modifying custom USB attributes.
The Device Manager module parses USB descriptor information and creates USB devices accordingly. It also provides functions such as adding or deleting USB devices, obtaining USB device status, and obtaining USB device interface information.
The IO Manager module reads and writes data, including common events and data read and write events. It supports data read and write in synchronous and asynchronous modes.
The Adapter IF module encapsulates device node operations of composite device configuration drivers and common function drivers to provide unified device management APIs for the upper layer.
The Adapter module is provided by the composite device configuration driver and common function driver.
Development Guidelines
The USB driver development in kernel mode is complex. Therefore, you need to have a deep understanding of the USB protocol. The USB DDK is introduced to help you to develop USB drivers in user mode more conveniently.
When to Use
The USB Host DDK comes with two modes, namely, common mode and expert mode. In common mode, you can directly read and write USB data by using USB DDK APIs without knowing details about data transfer at the bottom layer. In expert mode, you can use USB RAW APIs to directly access the USB channel interfaces provided by the OS platform to implement more complex functions. The USB Device DDk provides functions such as USB device management, interface definition, and USB data request.
Available APIs
The following table lists the APIs related to USB host driver development (common mode). For details about the API definitions, see the source code.
Table 1 APIs for USB host driver development (common mode)
| API | Description |
|---|---|
| int32_t UsbInitHostSdk(struct UsbSession **session); | Initializes the USB host driver DDK. |
| const struct UsbInterface *UsbClaimInterface(const struct UsbSession *session, uint8_t busNum, uint8_t usbAddr, uint8_t interfaceIndex); |
Obtains a USB interface. |
| UsbInterfaceHandle *UsbOpenInterface(const struct UsbInterface *interfaceObj); |
Opens a USB interface. |
| int32_t UsbGetPipeInfo(const UsbInterfaceHandle *interfaceHandle, uint8_t settingIndex, uint8_t pipeId, struct UsbPipeInfo *pipeInfo); |
Obtains USB pipe information. |
| struct UsbRequest *UsbAllocRequest(const UsbInterfaceHandle *interfaceHandle, int32_t isoPackets , int32_t length); |
Allocates a request object. |
| int32_t UsbFillRequest(const struct UsbRequest *request, const UsbInterfaceHandle *interfaceHandle, const struct UsbRequestParams *params); |
Fills in a request. |
| int32_t UsbSubmitRequestSync(const struct UsbRequest *request); |
Sends a synchronous request. |
The following table lists the APIs related to USB host driver development (expert mode). For details about the API definitions, see the source code.
Table 2 APIs for USB host driver development (expert mode)
| API | Description |
|---|---|
| int32_t UsbRawInit(struct UsbSession **session); | Initializes the USB raw APIs. |
| UsbRawHandle *UsbRawOpenDevice(const struct UsbSession *session, uint8_t busNum, uint8_t usbAddr); |
Opens a USB device. |
| int32_t UsbRawSendControlRequest(const struct UsbRawRequest *request, const UsbRawHandle *devHandle, const struct UsbControlRequestData *requestData); |
Performs a control transfer synchronously. |
| int32_t UsbRawSendBulkRequest(const struct UsbRawRequest *request, const UsbRawHandle *devHandle, const struct UsbRequestData *requestData); |
Performs a bulk transfer synchronously. |
| int32_t UsbRawSendInterruptRequest(const struct UsbRawRequest *request, const UsbRawHandle *devHandle, const struct UsbRequestData *requestData); |
Performs an interrupt transfer synchronously. |
| int32_t UsbRawGetConfigDescriptor(const UsbRawDevice *rawDev, uint8_t configIndex, struct UsbRawConfigDescriptor **config); |
Obtains the configuration descriptor of a device. |
| int32_t UsbRawFillInterruptRequest(const struct UsbRawRequest *request, const UsbRawHandle *devHandle, const struct UsbRawFillRequestData *fillData); |
Fills in an interrupt transfer request. |
| int32_t UsbRawFillIsoRequest(const struct UsbRawRequest *request, const UsbRawHandle *devHandle, const struct UsbRawFillRequestData *fillData); |
Fills in an isochronous transfer request. |
| int32_t UsbRawSubmitRequest(const struct UsbRawRequest *request); |
Submits a transfer request. |
| int32_t UsbRawCancelRequest(const struct UsbRawRequest *request); |
Cancels a transfer request. |
| int32_t UsbRawHandleRequests(const UsbRawHandle *devHandle); |
Handles a transfer request event. |
The following table lists the APIs for USB device management on the device side. For details about the API definitions, see the source code.
Table 3 APIs for USB device management on the device side
| API | Description |
|---|---|
| const struct UsbFnDevice *UsbFnCreateDevice(const char *udcName, const struct UsbFnDescriptorData *descriptor); |
Creates a USB device. |
| int32_t UsbFnRemoveDevice(struct UsbFnDevice *fnDevice); |
Deletes a USB device. |
| const struct UsbFnDevice *UsbFnGetDevice(const char *udcName); |
Obtains a USB device. |
The following table lists the APIs for USB interface definition on the device side. For details about the API definitions, see the source code.
Table 4 APIs for USB interface definition on the device side
| API | Description |
|---|---|
| int32_t UsbFnStartRecvInterfaceEvent(struct UsbFnInterface *interface, uint32_t eventMask, UsbFnEventCallback callback, void *context); |
Starts receiving events. |
| int32_t UsbFnStopRecvInterfaceEvent(struct UsbFnInterface *interface); |
Stops receiving events. |
| UsbFnInterfaceHandle UsbFnOpenInterface(struct UsbFnInterface *interface); | Opens an interface. |
| int32_t UsbFnCloseInterface(UsbFnInterfaceHandle handle); | Closes an interface. |
| int32_t UsbFnGetInterfacePipeInfo(struct UsbFnInterface *interface, uint8_t pipeId, struct UsbFnPipeInfo *info); |
Obtains pipe information. |
| int32_t UsbFnSetInterfaceProp(const struct UsbFnInterface *interface, const char *name, const char *value); |
Sets custom properties. |
The following table lists the APIs for USB data request on the device side. For details about the API definitions, see the source code.
Table 5 APIs for USB data request on the device side
| API | Description |
|---|---|
| struct UsbFnRequest *UsbFnAllocCtrlRequest(UsbFnInterfaceHandle handle, uint32_t len); |
Allocates a control transfer request. |
| struct UsbFnRequest *UsbFnAllocRequest(UsbFnInterfaceHandle handle, uint8_t pipe, uint32_t len); |
Allocates a data request. |
| int32_t UsbFnFreeRequest(struct UsbFnRequest *req); | Releases a request. |
| int32_t UsbFnSubmitRequestAsync(struct UsbFnRequest *req); |
Sends an asynchronous request. |
| int32_t UsbFnSubmitRequestSync(struct UsbFnRequest *req, uint32_t timeout); |
Sends a synchronous request. |
| int32_t UsbFnCancelRequest(struct UsbFnRequest *req); | Cancels a request. |
How to Develop
USB drivers are developed based on the Hardware Driver Foundation (HDF), platform, and Operating System Abstraction Layer (OSAL) APIs. A unified driver model is provided for USB devices, irrespective of the operating system and chip architecture. This section uses the serial port as an example to describe how to develop USB host and USB device drivers.
Developing Driver Using Host DDK APIs
Configure USB host driver information in the .hcs file of private device data.
root { module = "usb_pnp_device"; usb_pnp_config { match_attr = "usb_pnp_match"; usb_pnp_device_id = "UsbPnpDeviceId"; UsbPnpDeviceId { idTableList = [ "host_acm_table" ]; host_acm_table { // Driver module name, which must be the same as the value of moduleName in the driver entry structure. moduleName = "usbhost_acm"; // Service name of the driver, which must be unique. serviceName = "usbhost_acm_pnp_service"; // Keyword for matching private driver data. deviceMatchAttr = "usbhost_acm_pnp_matchAttr"; // Data length starting from this field, in bytes. length = 21; // USB driver matching rule: vendorId+productId+interfaceSubClass+interfaceProtocol+interfaceNumber. matchFlag = 0x0303; // Vendor ID. vendorId = 0x12D1; // Product ID. productId = 0x5000; // The least significant 16 bits of the device sequence number. bcdDeviceLow = 0x0000; // The most significant 16 bits of the device sequence number. bcdDeviceHigh = 0x0000; // Device class code allocated by the USB. deviceClass = 0; // Child class code allocated by the USB. deviceSubClass = 0; // Device protocol code allocated by the USB. deviceProtocol = 0; // Interface type. You can enter multiple types as needed. interfaceClass = [0]; // Interface subtype. You can enter multiple subtypes as needed. interfaceSubClass = [2, 0]; // Protocol that the interface complies with. You can enter multiple protocols as needed. interfaceProtocol = [1, 2]; // Interface number. You can enter multiple interface numbers as needed. interfaceNumber = [2, 3]; } } } }Initialize the USB host driver DDK.
int32_t UsbInitHostSdk(struct UsbSession **session);Obtain the UsbInterface object after initialization.
const struct UsbInterface *UsbClaimInterface(const struct UsbSession *session, uint8_t busNum, uint8_t usbAddr, uint8_t interfaceIndex);Open the UsbInterface object to obtain the UsbInterfaceHandle object.
UsbInterfaceHandle *UsbOpenInterface(const struct UsbInterface *interfaceObj);Obtain pipe information of the specified pipeIndex based on the UsbInterfaceHandle object.
int32_t UsbGetPipeInfo(const UsbInterfaceHandle *interfaceHandle, uint8_t settingIndex, uint8_t pipeId, struct UsbPipeInfo *pipeInfo);Pre-allocate an I/O request for the UsbInterfaceHandle object.
struct UsbRequest *UsbAllocRequest(const UsbInterfaceHandle *interfaceHandle, int32_t isoPackets, int32_t length);Fill in the I/O request based on the input parameters.
int32_t UsbFillRequest(const struct UsbRequest *request, const UsbInterfaceHandle *interfaceHandle, const struct UsbRequestParams *params);Submit the I/O request in synchronous or asynchronous mode.
int32_t UsbSubmitRequestSync(const struct UsbRequest *request); // Send a synchronous I/O request. int32_t UsbSubmitRequestAsync(const struct UsbRequest *request); // Send an asynchronous I/O request.
Developing Driver Using Host Raw APIs
Configure USB host driver information in the .hcs file of private device data. For details, see step 1 in the previous section.
Initialize the host raw data, open the USB device, obtain the descriptor, and then obtain interface and endpoint information based on the descriptor.
int32_t UsbRawInit(struct UsbSession **session);Open the USB device.
UsbRawHandle *UsbRawOpenDevice(const struct UsbSession *session, uint8_t busNum, uint8_t usbAddr);Obtain the device descriptor, and obtain the interface and endpoint information based on the descriptor.
int32_t UsbRawGetConfigDescriptor(const UsbRawDevice *rawDev, uint8_t configIndex, struct UsbRawConfigDescriptor **config);Allocate a request and fill in the request based on the transfer type.
int32_t UsbRawFillBulkRequest(const struct UsbRawRequest *request, const UsbRawHandle *devHandle, const struct UsbRawFillRequestData *fillData); // Populate the request for bulk transfer. int32_t UsbRawFillControlSetup(const unsigned char *setup, const struct UsbControlRequestData *requestData); int32_t UsbRawFillControlRequest(const struct UsbRawRequest *request, const UsbRawHandle *devHandle, const struct UsbRawFillRequestData *fillData); // Populate the request for control transfer. int32_t UsbRawFillInterruptRequest(const struct UsbRawRequest *request, const UsbRawHandle *devHandle, const struct UsbRawFillRequestData *fillData); // Populate the request for interrupt transfer. int32_t UsbRawFillIsoRequest(const struct UsbRawRequest *request, const UsbRawHandle *devHandle, const struct UsbRawFillRequestData *fillData); // Populate the request for isochronous transfer.Submit the I/O request in synchronous or asynchronous mode.
int32_t UsbRawSendControlRequest(const struct UsbRawRequest *request, const UsbRawHandle *devHandle, const struct UsbControlRequestData *requestData); // Send a synchronous request for control transfer. int32_t UsbRawSendBulkRequest(const struct UsbRawRequest *request, const UsbRawHandle *devHandle, const struct UsbRequestData *requestData); // Send a synchronous request for bulk transfer. int32_t UsbRawSendInterruptRequest(const struct UsbRawRequest *request, const UsbRawHandle *devHandle, const struct UsbRequestData *requestData); // Send a synchronous request for interrupt transfer. int32_t UsbRawSubmitRequest(const struct UsbRawRequest *request); // Send an asynchronous I/O request.
Developing Driver Using Device DDK APIs
Construct a descriptor in the device function code.
static struct UsbFnFunction g_acmFunction = { // Function descriptor .enable = true, .funcName = "f_generic.a", .strings = g_acmStrings, .fsDescriptors = g_acmFsFunction, .hsDescriptors = g_acmHsFunction, .ssDescriptors = g_acmSsFunction, .sspDescriptors = NULL, }; struct UsbFnFunction *g_functions[] = { #ifdef CDC_ECM &g_ecmFunction, #endif #ifdef CDC_ACM &g_acmFunction, #endif NULL }; static struct UsbFnConfiguration g_masterConfig = { // Configuration descriptor .configurationValue = 1, .iConfiguration = USB_FUNC_CONFIG_IDX, .attributes = USB_CFG_BUS_POWERED, .maxPower = POWER, .functions = g_functions, }; static struct UsbFnConfiguration *g_configs[] = { &g_masterConfig, NULL, }; static struct UsbDeviceDescriptor g_cdcMasterDeviceDesc = { // Device descriptor .bLength = sizeof(g_cdcMasterDeviceDesc), .bDescriptorType = USB_DDK_DT_DEVICE, .bcdUSB = CpuToLe16(BCD_USB), .bDeviceClass = 0, .bDeviceSubClass = 0, .bDeviceProtocol = 0, .bMaxPacketSize0 = USB_MAX_PACKET_SIZE, .idVendor = CpuToLe16(DEVICE_VENDOR_ID), .idProduct = CpuToLe16(DEVICE_PRODUCT_ID), .bcdDevice = CpuToLe16(DEVICE_VERSION), .iManufacturer = USB_FUNC_MANUFACTURER_IDX, .iProduct = USB_FUNC_PRODUCT_IDX, .iSerialNumber = USB_FUNC_SERIAL_IDX, .bNumConfigurations = 1, }; static struct UsbFnDeviceDesc g_masterFuncDevice = { // Descriptor entry .deviceDesc = &g_cdcMasterDeviceDesc, .deviceStrings = g_devStrings, .configs = g_configs, };Create a USB device. Call UsbFnDeviceCreate and pass in the UDC controller and UsbFnDescriptorData structure to create a USB device.
if (useHcs == 0) { // Descriptor written in the code. descData.type = USBFN_DESC_DATA_TYPE_DESC; descData.descriptor = &g_acmFuncDevice; } else { // Descriptor compiled by using the .hcs file. descData.type = USBFN_DESC_DATA_TYPE_PROP; descData.property = acm->device->property; } // Create a USB device. fnDev = (struct UsbFnDevice *) UsbFnCreateDevice(acm->udcName, &descData);Call UsbFnGetInterface to obtain a UsbInterface object, and call UsbFnGetInterfacePipeInfo to obtain the USB pipe information.
// Obtain an interface. fnIface = (struct UsbFnInterface *)UsbFnGetInterface(fnDev, i); // Obtain the pipe information. UsbFnGetInterfacePipeInfo(fnIface, i, &pipeInfo); // Obtain a handle. handle = UsbFnOpenInterface(fnIface); // Obtain a control (EP0) request. req = UsbFnAllocCtrlRequest(acm->ctrlIface.handle, sizeof(struct UsbCdcLineCoding) + sizeof(struct UsbCdcLineCoding)); // Obtain the request. req = UsbFnAllocCtrlRequest(acm->ctrlIface.handle, sizeof(struct UsbCdcLineCoding) + sizeof(struct UsbCdcLineCoding));Call UsbFnStartRecvInterfaceEvent to receive events, and call UsbFnEventCallback to respond to the events.
// Start receiving events. ret = UsbFnStartRecvInterfaceEvent(acm->ctrlIface.fn, 0xff, UsbAcmEventCallback, acm); // Process the event in the callback. static void UsbAcmEventCallback(struct UsbFnEvent *event) { struct UsbAcmDevice *acm = NULL; if (event == NULL||event->context == NULL) { HDF_LOGE("%s: event is null", __func__); return; } acm = (struct UsbAcmDevice *)event->context; switch (event->type) { case USBFN_STATE_BIND: HDF_LOGI("%s: receive bind event", __func__); break; case USBFN_STATE_UNBIND: HDF_LOGI("%s: receive unbind event", __func__); break; case USBFN_STATE_ENABLE: HDF_LOGI("%s: receive enable event", __func__); AcmEnable(acm); break; case USBFN_STATE_DISABLE: HDF_LOGI("%s: receive disable event", __func__); AcmDisable(acm); acm->enableEvtCnt = 0; break; case USBFN_STATE_SETUP: HDF_LOGI("%s: receive setup event", __func__); if (event->setup != NULL) { AcmSetup(acm, event->setup); } break; case USBFN_STATE_SUSPEND: HDF_LOGI("%s: receive suspend event", __func__); AcmSuspend(acm); break; case USBFN_STATE_RESUME: HDF_LOGI("%s: receive resume event", __func__); AcmResume(acm); break; default: break; } }Send and receive data in synchronously or asynchronously.
notify = (struct UsbCdcNotification *)req->buf; ... if (memcpy_s((void *)(notify + 1), length, data, length) != EOK) { return HDF_FAILURE; } ret = UsbFnSubmitRequestAsync(req); // Send data asynchronously.
Development Example
The following example helps you better understand the development of the USB serial port driver.
Developing Driver Using Host DDK APIs
#include "usb_serial.h"
#include "hdf_base.h"
#include "hdf_log.h"
#include "osal_mem.h"
#include "osal_time.h"
#include "securec.h"
#include "usb_ddk_interface.h"
#include "hdf_usb_pnp_manage.h"
#define HDF_LOG_TAG USB_HOST_ACM
#define STR_LEN 512
static struct UsbRequest *g_syncRequest = NULL; // Define a USB request.
static struct UsbRequest *g_ctrlCmdRequest = NULL;
static bool g_acmReleaseFlag = false;
static uint8_t *g_acmReadBuffer = NULL;
...
static int32_t SerialCtrlMsg(struct AcmDevice *acm, uint8_t request,
uint16_t value, void *buf, uint16_t len)
{
int32_t ret;
uint16_t index = acm->intPipe->interfaceId;
struct UsbControlParams controlParams;
struct UsbRequestParams params; // Define a UsbRequestParams object.
if (acm == NULL||buf == NULL) {
return HDF_ERR_IO;
}
if (acm->ctrlReq == NULL) {
// Pre-allocate the IO Request object to be sent to UsbInterfaceHandle.
acm->ctrlReq = UsbAllocRequest(acm->ctrDevHandle, 0, len);
if (acm->ctrlReq == NULL) {
return HDF_ERR_IO;
}
}
controlParams.request = request;
controlParams.target = USB_REQUEST_TARGET_INTERFACE; // Interface object
controlParams.reqType = USB_REQUEST_TYPE_CLASS; // Request type
controlParams.direction = USB_REQUEST_DIR_TO_DEVICE; // Data transfer from the host to the device
controlParams.value = value;
controlParams.index = index;
controlParams.data = buf;
controlParams.size = len;
params.interfaceId = USB_CTRL_INTERFACE_ID; // Define the default ID of the USB control interface.
params.pipeAddress = acm->ctrPipe->pipeAddress;
params.pipeId = acm->ctrPipe->pipeId;
params.requestType = USB_REQUEST_PARAMS_CTRL_TYPE; // Control type.
params.timeout = USB_CTRL_SET_TIMEOUT; // Set the timeout interval.
params.ctrlReq = UsbControlSetUp(&controlParams);
// Fill in the pre-allocated I/O request based on UsbRequestParams.
ret = UsbFillRequest(acm->ctrlReq, acm->ctrDevHandle, ¶ms);
if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) {
return ret;
}
// Send an I/O request synchronously.
ret = UsbSubmitRequestSync(acm->ctrlReq);
if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) {
return ret;
}
if (!acm->ctrlReq->compInfo.status) {
HDF_LOGE("%s status=%d ", __func__, acm->ctrlReq->compInfo.status);
}
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
...
static struct UsbInterface *GetUsbInterfaceById(const struct AcmDevice *acm,
uint8_t interfaceIndex)
{
struct UsbInterface *tmpIf = NULL;
// Obtain a UsbInterface object.
tmpIf = (struct UsbInterface *)UsbClaimInterface(acm->session, acm->busNum, acm->devAddr, interfaceIndex);
return tmpIf;
}
...
static struct UsbPipeInfo *EnumePipe(const struct AcmDevice *acm,
uint8_t interfaceIndex, UsbPipeType pipeType, UsbPipeDirection pipeDirection)
{
uint8_t i;
int32_t ret;
struct UsbInterfaceInfo *info = NULL; // Define a UsbInterfaceInfo object.
UsbInterfaceHandle *interfaceHandle = NULL; // Define a USB interface operation handle (that is, the void * type).
if (pipeType == USB_PIPE_TYPE_CONTROL)
{
info = &acm->ctrIface->info;
interfaceHandle = acm->ctrDevHandle;
}
else
{
info = &acm->iface[interfaceIndex]->info;
// Obtain the device handle based on interfaceIndex.
interfaceHandle = InterfaceIdToHandle(acm, info->interfaceIndex);
}
for (i = 0; i <= info->pipeNum; i++) {
struct UsbPipeInfo p;
// Obtain the pipeInfo object whose index is i.
ret = UsbGetPipeInfo(interfaceHandle, info->curAltSetting, i, &p);
if (ret < 0) {
continue;
}
if ((p.pipeDirection == pipeDirection) && (p.pipeType == pipeType)) {
struct UsbPipeInfo *pi = OsalMemCalloc(sizeof(*pi)); // Allocate and initialize the memory.
if (pi == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
p.interfaceId = info->interfaceIndex;
*pi = p;
return pi;
}
}
return NULL;
}
static struct UsbPipeInfo *GetPipe(const struct AcmDevice *acm,
UsbPipeType pipeType, UsbPipeDirection pipeDirection)
{
uint8_t i;
if (acm == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
for (i = 0; i < acm->interfaceCnt; i++) {
struct UsbPipeInfo *p = NULL;
if (!acm->iface[i]) {
continue;
}
// Obtain pipe information of the control pipe.
p = EnumePipe(acm, i, pipeType, pipeDirection);
if (p == NULL) {
continue;
}
return p;
}
return NULL;
}
/* HdfDriverEntry implementations */
static int32_t UsbSerialDriverBind(struct HdfDeviceObject *device)
{
struct UsbPnpNotifyServiceInfo *info = NULL;
errno_t err;
struct AcmDevice *acm = NULL;
if (device == NULL) {
return HDF_ERR_INVALID_OBJECT;
}
acm = (struct AcmDevice *)OsalMemCalloc(sizeof(*acm));
if (acm == NULL) {
return HDF_FAILURE;
}
// Initialize the mutex. &acm->lock indicates the pointer pointing to the mutex.
if (OsalMutexInit(&acm->lock) != HDF_SUCCESS) {
goto error;
}
info = (struct UsbPnpNotifyServiceInfo *)device->priv;
if (info != NULL) {
acm->busNum = info->busNum;
acm->devAddr = info->devNum;
acm->interfaceCnt = info->interfaceLength;
err = memcpy_s((void *)(acm->interfaceIndex), USB_MAX_INTERFACES,
(const void*)info->interfaceNumber, info->interfaceLength);
if (err != EOK) {
goto lock_error;
}
} else {
goto lock_error;
}
acm->device = device;
device->service = &(acm->service);
acm->device->service->Dispatch = UsbSerialDeviceDispatch;
return HDF_SUCCESS;
lock_error:
if (OsalMutexDestroy(&acm->lock)) {
HDF_LOGE("%s:%d OsalMutexDestroy failed", __func__, __LINE__);
}
error:
OsalMemFree(acm);
acm = NULL;
return HDF_FAILURE;
}
...
static int32_t AcmAllocReadRequests(struct AcmDevice *acm)
{
int32_t ret;
struct UsbRequestParams readParams;
for (int32_t i = 0; i < ACM_NR; i++) {
// Allocate the readReq I/O request to be sent.
acm->readReq[i] = UsbAllocRequest(InterfaceIdToHandle(acm, acm->dataInPipe->interfaceId), 0, acm->readSize);
if (!acm->readReq[i]) {
goto error;
}
readParams.userData = (void *)acm;
readParams.pipeAddress = acm->dataInPipe->pipeAddress;
readParams.pipeId = acm->dataInPipe->pipeId;
readParams.interfaceId = acm->dataInPipe->interfaceId;
readParams.callback = AcmReadBulk;
readParams.requestType = USB_REQUEST_PARAMS_DATA_TYPE; /* Data type */
readParams.timeout = USB_CTRL_SET_TIMEOUT;
readParams.dataReq.numIsoPackets = 0;
readParams.dataReq.direction = (acm->dataInPipe->pipeDirection >> USB_PIPE_DIR_OFFSET) & 0x1;
readParams.dataReq.length = acm->readSize;
// Fill in the readReq IO Request object to be sent based on readParams.
ret = UsbFillRequest(acm->readReq[i], InterfaceIdToHandle(acm, acm->dataInPipe->interfaceId), &readParams);
if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) {
goto error;
}
}
return HDF_SUCCESS;
error:
AcmFreeReadRequests(acm);
return HDF_ERR_MALLOC_FAIL;
}
static int32_t AcmAllocNotifyRequest(struct AcmDevice *acm)
{
int32_t ret;
struct UsbRequestParams intParams = {};
// Allocate the interrupt I/O request to be sent.
acm->notifyReq = UsbAllocRequest(InterfaceIdToHandle(acm, acm->intPipe->interfaceId), 0, acm->intSize);
if (!acm->notifyReq) {
return HDF_ERR_MALLOC_FAIL;
}
intParams.userData = (void *)acm;
intParams.pipeAddress = acm->intPipe->pipeAddress;
intParams.pipeId = acm->intPipe->pipeId;
intParams.interfaceId = acm->intPipe->interfaceId;
intParams.callback = AcmCtrlIrq;
intParams.requestType = USB_REQUEST_PARAMS_DATA_TYPE;
intParams.timeout = USB_CTRL_SET_TIMEOUT;
intParams.dataReq.numIsoPackets = 0;
intParams.dataReq.direction = (acm->intPipe->pipeDirection >> USB_PIPE_DIR_OFFSET) & DIRECTION_MASK;
intParams.dataReq.length = acm->intSize;
// Fill in the interrupt I/O request.
ret = UsbFillRequest(acm->notifyReq, InterfaceIdToHandle(acm, acm->intPipe->interfaceId), &intParams);
if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) {
goto error;
}
return HDF_SUCCESS;
error:
AcmFreeNotifyRequest(acm);
return ret;
}
static void AcmReleaseInterfaces(struct AcmDevice *acm)
{
for (int32_t i = 0; i < acm->interfaceCnt; i++) {
if (acm->iface[i]) {
// Release a USB interface object.
UsbReleaseInterface(acm->iface[i]);
acm->iface[i] = NULL;
}
}
if (acm->ctrIface) {
UsbReleaseInterface(acm->ctrIface);
acm->ctrIface = NULL;
}
}
static int32_t AcmClaimInterfaces(struct AcmDevice *acm)
{
for (int32_t i = 0; i < acm->interfaceCnt; i++) {
// Obtain a UsbInterface object.
acm->iface[i] = GetUsbInterfaceById((const struct AcmDevice *)acm, acm->interfaceIndex[i]);
if (acm->iface[i] == NULL) {
goto error;
}
}
// Obtain the UsbInterface object corresponding to the control interface.
acm->ctrIface = GetUsbInterfaceById((const struct AcmDevice *)acm, USB_CTRL_INTERFACE_ID);
if (acm->ctrIface == NULL) {
goto error;
}
return HDF_SUCCESS;
error:
// Release the UsbInterface object cyclically based on acm->interfaceCnt.
AcmReleaseInterfaces(acm);
return HDF_FAILURE;
}
static void AcmCloseInterfaces(struct AcmDevice *acm)
{
for (int32_t i = 0; i < acm->interfaceCnt; i++) {
if (acm->devHandle[i]) {
// Close a USB device object.
UsbCloseInterface(acm->devHandle[i]);
acm->devHandle[i] = NULL;
}
}
if (acm->ctrDevHandle) {
UsbCloseInterface(acm->ctrDevHandle);
acm->ctrDevHandle = NULL;
}
}
static int32_t AcmOpenInterfaces(struct AcmDevice *acm)
{
for (int32_t i = 0; i < acm->interfaceCnt; i++) {
if (acm->iface[i]) {
// Open the UsbInterface object obtained.
acm->devHandle[i] = UsbOpenInterface(acm->iface[i]);
if (acm->devHandle[i] == NULL) {
goto error;
}
}
}
acm->ctrDevHandle = UsbOpenInterface(acm->ctrIface);
if (acm->ctrDevHandle == NULL) {
goto error;
}
return HDF_SUCCESS;
error:
// Disable all UsbInterface objects.
AcmCloseInterfaces(acm);
return HDF_FAILURE;
}
static int32_t AcmGetPipes(struct AcmDevice *acm)
{
// Obtain pipe information of dataInPipe.
acm->dataInPipe = GetPipe(acm, USB_PIPE_TYPE_BULK, USB_PIPE_DIRECTION_IN);
if (acm->dataInPipe == NULL) {
goto error;
}
// Obtain pipe information of dataOutPipe.
acm->dataOutPipe = GetPipe(acm, USB_PIPE_TYPE_BULK, USB_PIPE_DIRECTION_OUT);
if (acm->dataOutPipe == NULL) {
goto error;
}
// Obtain pipe information of the control pipe.
acm->ctrPipe = EnumePipe(acm, acm->ctrIface->info.interfaceIndex, USB_PIPE_TYPE_CONTROL, USB_PIPE_DIRECTION_OUT);
if (acm->ctrPipe == NULL) {
goto error;
}
//Obtain pipe information of the interrupt pipe.
acm->intPipe = GetPipe(acm, USB_PIPE_TYPE_INTERRUPT, USB_PIPE_DIRECTION_IN);
if (acm->intPipe == NULL) {
goto error;
}
acm->readSize = acm->dataInPipe->maxPacketSize;
acm->writeSize = acm->dataOutPipe->maxPacketSize;
acm->ctrlSize = acm->ctrPipe->maxPacketSize;
acm->intSize = acm->intPipe->maxPacketSize;
return HDF_SUCCESS;
error:
// Release all pipe information on the device.
AcmFreePipes(acm);
return HDF_FAILURE;
}
static void AcmFreeRequests(struct AcmDevice *acm)
{
if (g_syncRequest != NULL) {
UsbFreeRequest(g_syncRequest);
g_syncRequest = NULL;
}
AcmFreeReadRequests(acm);
AcmFreeNotifyRequest(acm);
AcmFreeWriteRequests(acm);
AcmWriteBufFree(acm);
}
static int32_t AcmAllocRequests(struct AcmDevice *acm)
{
int32_t ret;
if (AcmWriteBufAlloc(acm) < 0) {
return HDF_ERR_MALLOC_FAIL;
}
for (int32_t i = 0; i < ACM_NW; i++) {
struct AcmWb *snd = &(acm->wb[i]);
// Allocate the I/O request to be sent.
snd->request = UsbAllocRequest(InterfaceIdToHandle(acm, acm->dataOutPipe->interfaceId), 0, acm->writeSize);
snd->instance = acm;
if (snd->request == NULL) {
goto error_alloc_write_req;
}
}
ret = AcmAllocNotifyRequest(acm); // Allocate and fill in the interrupt I/O request.
if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) {
goto error_alloc_int_req;
}
ret = AcmAllocReadRequests(acm); // Allocate and fill in the readReq I/O request.
if (ret) {
goto error_alloc_read_req;
}
return HDF_SUCCESS;
error_alloc_read_req:
AcmFreeNotifyRequest(acm);
error_alloc_int_req:
AcmFreeWriteRequests(acm);
error_alloc_write_req:
AcmWriteBufFree(acm);
return HDF_FAILURE;
}
static int32_t AcmInit(struct AcmDevice *acm)
{
int32_t ret;
struct UsbSession *session = NULL;
if (acm->initFlag == true) {
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
// Initialize the USB Host DDK.
ret = UsbInitHostSdk(NULL);
if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) {
return HDF_ERR_IO;
}
acm->session = session;
// Obtain UsbInterface objects based on acm->interfaceIndex[i].
ret = AcmClaimInterfaces(acm);
if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) {
goto error_claim_interfaces;
}
// Open UsbInterface objects based on acm->iface[i].
ret = AcmOpenInterfaces(acm);
if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) {
goto error_open_interfaces;
}
// Obtain the pointer to the pipe information.
ret = AcmGetPipes(acm);
if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) {
goto error_get_pipes;
}
ret = AcmAllocRequests(acm);
if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) {
goto error_alloc_reqs;
}
acm->lineCoding.dwDTERate = CpuToLe32(DATARATE); // Convert to little-endian data.
acm->lineCoding.bCharFormat = CHARFORMAT; // 8
acm->lineCoding.bParityType = USB_CDC_NO_PARITY;
acm->lineCoding.bDataBits = USB_CDC_1_STOP_BITS;
acm->initFlag = true;
return HDF_SUCCESS;
error_alloc_reqs:
AcmFreePipes(acm);
error_get_pipes:
// Disable all UsbInterface objects.
AcmCloseInterfaces(acm);
error_open_interfaces:
// Release all UsbInterface objects.
AcmReleaseInterfaces(acm);
error_claim_interfaces:
// Exit the USB DDK on the host. acm->session indicates the pointer pointing to the session context.
UsbExitHostSdk(acm->session);
acm->session = NULL;
return ret;
}
static void AcmRelease(struct AcmDevice *acm)
{
if (acm->initFlag == false) {
return;
}
AcmFreeRequests(acm);
AcmFreePipes(acm);
AcmCloseInterfaces(acm);
AcmReleaseInterfaces(acm);
// Exit the USB DDK on the host.
UsbExitHostSdk(acm->session);
acm->session = NULL;
acm->initFlag = false;
}
static int32_t UsbSerialDriverInit(struct HdfDeviceObject *device)
{
int32_t ret;
struct AcmDevice *acm = NULL;
if (device == NULL) {
return HDF_ERR_INVALID_OBJECT;
}
acm = (struct AcmDevice *)device->service;
// Initialize the mutex. &acm->readLock indicates the pointer pointing to the mutex.
OsalMutexInit(&acm->readLock);
OsalMutexInit(&acm->writeLock);
HDF_LOGD("%s:%d busNum=%d,devAddr=%d", __func__, __LINE__, acm->busNum, acm->devAddr);
// Allocate space for the USB serial port device information and assign a value.
ret = UsbSerialDeviceAlloc(acm);
if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) {
HDF_LOGE("%s: Serial Device alloc failed", __func__);
}
acm->initFlag = false;
g_acmReleaseFlag = false;
return ret;
}
static void UsbSerialDriverRelease(struct HdfDeviceObject *device)
{
struct AcmDevice *acm = NULL;
if (device == NULL) {
return;
}
acm = (struct AcmDevice *)device->service;
if (acm == NULL) {
return;
}
g_acmReleaseFlag = true;
if (acm->initFlag == true) {
AcmRelease(acm);
}
// Release the USB serial port device information.
UsbSeriaDevicelFree(acm);
// Release the mutex.
OsalMutexDestroy(&acm->writeLock);
OsalMutexDestroy(&acm->readLock);
OsalMutexDestroy(&acm->lock);
OsalMemFree(acm);
acm = NULL;
}
// Perform Bind, Init, and Release operations on the driver.
struct HdfDriverEntry g_usbSerialDriverEntry = {
.moduleVersion = 1,
.moduleName = "usbhost_acm", // Driver module name, which must be the same as that configured in the .hcs file.
.Bind = UsbSerialDriverBind,
.Init = UsbSerialDriverInit,
.Release = UsbSerialDriverRelease,
};
HDF_INIT(g_usbSerialDriverEntry); // Driver entry.
Developing Driver Using Host Raw APIs
root {
module = "usb_pnp_device";
usb_pnp_config {
match_attr = "usb_pnp_match";
usb_pnp_device_id = "UsbPnpDeviceId";
UsbPnpDeviceId {
idTableList = [
"host_acm_rawapi_table"
];
host_acm_rawapi_table { // Driver mapping table information.
// Driver module name, which must be the same as the value of moduleName in the driver entry structure.
moduleName = "usbhost_acm_rawapi";
// Service name of the driver, which must be unique.
serviceName = "usbhost_acm_rawapi_service";
// Keyword for matching private driver data.
deviceMatchAttr = "usbhost_acm_rawapi_matchAttr";
// Data length starting from this field, in bytes.
length = 21;
// USB driver matching rule: vendorId+productId+interfaceSubClass+interfaceProtocol+interfaceNumber.
matchFlag = 0x0303;
// Vendor ID.
vendorId = 0x12D1;
// Product ID.
productId = 0x5000;
// The least significant 16 bits of the device sequence number.
bcdDeviceLow = 0x0000;
// The most significant 16 bits of the device sequence number.
bcdDeviceHigh = 0x0000;
// Device class code allocated by the USB.
deviceClass = 0;
// Child class code allocated by the USB.
deviceSubClass = 0;
// Device protocol code allocated by the USB.
deviceProtocol = 0;
// Interface type. You can enter multiple types as needed.
interfaceClass = [0];
// Interface subtype. You can enter multiple subtypes as needed.
interfaceSubClass = [2, 0];
// Protocol that the interface complies with. You can enter multiple protocols as needed.
interfaceProtocol = [1, 2];
// Interface number. You can enter multiple interface numbers as needed.
interfaceNumber = [2, 3];
}
}
}
}
#include "usb_serial_rawapi.h"
#include <unistd.h>
#include "osal_mem.h"
#include "osal_time.h"
#include "securec.h"
#include "hdf_base.h"
#include "hdf_log.h"
#include "hdf_usb_pnp_manage.h"
#define HDF_LOG_TAG USB_HOST_ACM_RAW_API // Labels that can be queried in logs.
#define USB_CTRL_REQ_SIZE 64
#define USB_IO_THREAD_STACK_SIZE 8192
#define USB_RAW_IO_SLEEP_MS_TIME 100
#define USB_RAW_IO_STOP_WAIT_MAX_TIME 3
static struct UsbRawRequest *g_syncRequest = NULL;
static UsbRawIoProcessStatusType g_stopIoStatus = USB_RAW_IO_PROCESS_RUNNING;
struct OsalMutex g_stopIoLock;
static bool g_rawAcmReleaseFlag = false;
......
static int32_t UsbGetConfigDescriptor(UsbRawHandle *devHandle, struct UsbRawConfigDescriptor **config)
{
UsbRawDevice *dev = NULL;
int32_t activeConfig;
int32_t ret;
if (devHandle == NULL) {
return HDF_ERR_INVALID_PARAM;
}
// Obtain the configuration of the active device.
ret = UsbRawGetConfiguration(devHandle, &activeConfig);
if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) {
return HDF_FAILURE;
}
// Obtain the device pointer based on the specified device handle.
dev = UsbRawGetDevice(devHandle);
if (dev == NULL) {
return HDF_FAILURE;
}
// Obtain the device configuration descriptor based on the specified device ID.
ret = UsbRawGetConfigDescriptor(dev, activeConfig, config);
if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) {
HDF_LOGE("UsbRawGetConfigDescriptor failed, ret=%d\n", ret);
}
return ret;
}
...
static int32_t UsbAllocWriteRequests(struct AcmDevice *acm)
{
int32_t i;
for (i = 0; i < ACM_NW; i++) {
struct AcmWb *snd = &acm->wb[i];
// Allocate a transfer request with the specified number of sync packet descriptors.
snd->request = UsbRawAllocRequest(acm->devHandle, 0, acm->dataOutEp->maxPacketSize);
snd->instance = acm;
if (snd->request == NULL) {
return HDF_ERR_MALLOC_FAIL;
}
}
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
...
/* HdfDriverEntry implementations */
static int32_t UsbSerialDriverBind(struct HdfDeviceObject *device)
{
struct AcmDevice *acm = NULL;
struct UsbPnpNotifyServiceInfo *info = NULL;
errno_t err;
if (device == NULL) {
return HDF_ERR_INVALID_OBJECT;
}
acm = (struct AcmDevice *)OsalMemCalloc(sizeof(*acm));
if (acm == NULL) {
return HDF_FAILURE;
}
if (OsalMutexInit(&acm->lock) != HDF_SUCCESS) {
goto error;
}
info = (struct UsbPnpNotifyServiceInfo *)device->priv;
if (info != NULL) {
acm->busNum = info->busNum;
acm->devAddr = info->devNum;
acm->interfaceCnt = info->interfaceLength;
err = memcpy_s((void *)(acm->interfaceIndex), USB_MAX_INTERFACES,
(const void*)info->interfaceNumber, info->interfaceLength);
if (err != EOK) {
goto lock_error;
}
} else {
goto lock_error;
}
device->service = &(acm->service);
device->service->Dispatch = UsbSerialDeviceDispatch;
acm->device = device;
return HDF_SUCCESS;
lock_error:
if (OsalMutexDestroy(&acm->lock)) {
HDF_LOGE("%s:%d OsalMutexDestroy failed", __func__, __LINE__);
}
error:
OsalMemFree(acm);
acm = NULL;
return HDF_FAILURE;
}
...
static int32_t UsbAllocReadRequests(struct AcmDevice *acm)
{
struct UsbRawFillRequestData reqData;
int32_t size = acm->dataInEp->maxPacketSize;
int32_t ret;
for (int32_t i = 0; i < ACM_NR; i++) {
// Allocate a transfer request with the specified number of sync packet descriptors.
acm->readReq[i] = UsbRawAllocRequest(acm->devHandle, 0, size);
if (!acm->readReq[i]) {
return HDF_ERR_MALLOC_FAIL;
}
reqData.endPoint = acm->dataInEp->addr;
reqData.numIsoPackets = 0;
reqData.callback = AcmReadBulkCallback;
reqData.userData = (void *)acm;
reqData.timeout = USB_CTRL_SET_TIMEOUT;
reqData.length = size;
// Fill the required information in the bulk transfer request.
ret = UsbRawFillBulkRequest(acm->readReq[i], acm->devHandle, &reqData);
if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) {
return HDF_FAILURE;
}
}
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
...
static int32_t UsbAllocNotifyRequest(struct AcmDevice *acm)
{
struct UsbRawFillRequestData fillRequestData;
int32_t size = acm->notifyEp->maxPacketSize;
int32_t ret;
// Allocate a transfer request with the specified number of sync packet descriptors.
acm->notifyReq = UsbRawAllocRequest(acm->devHandle, 0, size);
if (!acm->notifyReq) {
return HDF_ERR_MALLOC_FAIL;
}
fillRequestData.endPoint = acm->notifyEp->addr;
fillRequestData.length = size;
fillRequestData.numIsoPackets = 0;
fillRequestData.callback = AcmNotifyReqCallback;
fillRequestData.userData = (void *)acm;
fillRequestData.timeout = USB_CTRL_SET_TIMEOUT;
// Fill the required information in the interrupt transfer request.
ret = UsbRawFillInterruptRequest(acm->notifyReq, acm->devHandle, &fillRequestData);
if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) {
return HDF_FAILURE;
}
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
...
static int32_t UsbSerialInit(struct AcmDevice *acm)
{
struct UsbSession *session = NULL;
UsbRawHandle *devHandle = NULL;
int32_t ret;
if (acm->initFlag == true) {
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
// Initialize the USB DDK in expert mode.
ret = UsbRawInit(NULL);
if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) {
return HDF_ERR_IO;
}
acm->session = session;
// Open a USB device object.
devHandle = UsbRawOpenDevice(session, acm->busNum, acm->devAddr);
if (devHandle == NULL) {
ret = HDF_FAILURE;
goto err_open_device;
}
acm->devHandle = devHandle;
// Obtain the configuration of the active device, device pointer, and configuration descriptor.
ret = UsbGetConfigDescriptor(devHandle, &acm->config);
if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) {
ret = HDF_FAILURE;
goto err_get_desc;
}
ret = UsbParseConfigDescriptor(acm, acm->config);
if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) {
ret = HDF_FAILURE;
goto err_parse_desc;
}
ret = AcmWriteBufAlloc(acm);
if (ret < 0) {
ret = HDF_FAILURE;
goto err_alloc_write_buf;
}
ret = UsbAllocWriteRequests(acm);
if (ret < 0) {
ret = HDF_FAILURE;
goto err_alloc_write_reqs;
}
ret = UsbAllocNotifyRequest(acm);
if (ret) {
goto err_alloc_notify_req;
}
ret = UsbAllocReadRequests(acm);
if (ret) {
goto err_alloc_read_reqs;
}
ret = UsbStartIo(acm);
if (ret) {
goto err_start_io;
}
acm->lineCoding.dwDTERate = CpuToLe32(DATARATE);
acm->lineCoding.bCharFormat = CHARFORMAT;
acm->lineCoding.bParityType = USB_CDC_NO_PARITY;
acm->lineCoding.bDataBits = USB_CDC_1_STOP_BITS;
ret = UsbRawSubmitRequest(acm->notifyReq);
if (ret) {
goto err_submit_req;
}
acm->initFlag = true;
return HDF_SUCCESS;
err_submit_req:
UsbStopIo(acm); // Stop the I/O thread and release all resources.
err_start_io:
UsbFreeReadRequests(acm);
err_alloc_read_reqs:
UsbFreeNotifyRequest(acm);
err_alloc_notify_req:
UsbFreeWriteRequests(acm);
err_alloc_write_reqs:
AcmWriteBufFree(acm);
err_alloc_write_buf:
UsbReleaseInterfaces(acm);
err_parse_desc:
UsbRawFreeConfigDescriptor(acm->config);
acm->config = NULL;
err_get_desc:
(void)UsbRawCloseDevice(devHandle); // Close the USB device object.
err_open_device:
UsbRawExit(acm->session); // Exit the expert mode of the USB DDK.
return ret;
}
static void UsbSerialRelease(struct AcmDevice *acm)
{
if (acm->initFlag == false) {
return;
}
/* stop io thread and release all resources */
UsbStopIo(acm);
if (g_syncRequest != NULL) {
UsbRawFreeRequest(g_syncRequest);
g_syncRequest = NULL;
}
UsbFreeReadRequests(acm);
UsbFreeNotifyRequest(acm);
UsbFreeWriteRequests(acm);
AcmWriteBufFree(acm);
(void)UsbRawCloseDevice(acm->devHandle);
UsbReleaseInterfaces(acm);
UsbRawFreeConfigDescriptor(acm->config);
acm->config = NULL;
// Exit the expert mode of the USB DDK.
UsbRawExit(acm->session);
acm->initFlag = false;
}
static int32_t UsbSerialDriverInit(struct HdfDeviceObject *device)
{
struct AcmDevice *acm = NULL;
int32_t ret;
if (device == NULL) {
return HDF_ERR_INVALID_OBJECT;
}
acm = (struct AcmDevice *)device->service;
OsalMutexInit(&acm->readLock);
OsalMutexInit(&acm->writeLock);
ret = UsbSerialDeviceAlloc(acm);
if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) {
HDF_LOGE("%s:%d UsbSerialDeviceAlloc failed", __func__, __LINE__);
}
acm->initFlag = false;
g_rawAcmReleaseFlag = false;
return ret;
}
static void UsbSerialDriverRelease(struct HdfDeviceObject *device)
{
struct AcmDevice *acm = NULL;
if (device == NULL) {
return;
}
acm = (struct AcmDevice *)device->service;
if (acm == NULL) {
return;
}
g_rawAcmReleaseFlag = true;
if (acm->initFlag == true) {
UsbSerialRelease(acm);
}
UsbSeriaDevicelFree(acm);
OsalMutexDestroy(&acm->writeLock);
OsalMutexDestroy(&acm->readLock);
OsalMutexDestroy(&acm->lock);
OsalMemFree(acm);
acm = NULL;
}
struct HdfDriverEntry g_usbSerialRawDriverEntry = {
.moduleVersion = 1,
.moduleName = "usbhost_acm_rawapi", // Driver module name, which must be the same as that configured in the .hcs file.
.Bind = UsbSerialDriverBind,
.Init = UsbSerialDriverInit,
.Release = UsbSerialDriverRelease,
};
HDF_INIT(g_usbSerialRawDriverEntry);
Developing Driver Using Device DDK APIs
The core code of the USB ACM device is stored in drivers\peripheral\usb\gadget\function\acm\cdcacm.c. The following sample code implements driver development by using the Device DDK APIs. To develop a driver, you must create a device based on the descriptor, obtain the interface, open the interface to obtain the pipe information, receive events, and then perform USB communication (such as read and write). When the device is uninstalled, you need to close the interface, stop receiving events, and remove the device.
Create a USB device.
static int32_t AcmCreateFuncDevice(struct UsbAcmDevice *acm, struct DeviceResourceIface *iface) { struct UsbFnDevice *fnDev = NULL; struct UsbFnDescriptorData descData; uint8_t useHcs; ... if (useHcs == 0) { // The descriptor is sourced from the code. descData.type = USBFN_DESC_DATA_TYPE_DESC; descData.descriptor = &g_masterFuncDevice; } else {// The descriptor is sourced from the .hcs file. descData.type = USBFN_DESC_DATA_TYPE_PROP; descData.property = device->property; } /* Create a device. */ fnDev = (struct UsbFnDevice *)UsbFnDeviceCreate(acm->udcName, &descData); if (fnDev == NULL) { return HDF_FAILURE; } ... }Obtain an interface and open the interface to obtain the pipe information.
static int32_t AcmParseEachPipe(struct UsbAcmDevice *acm, struct UsbAcmInterface *iface) { ... for (i = 0; i < fnIface->info.numPipes; i++) { struct UsbFnPipeInfo pipeInfo; /* Obtain pipe information. */ ret = UsbFnInterfaceGetPipeInfo(fnIface, i, &pipeInfo); ... } return HDF_SUCCESS; } /* Obtain an interface and open the interface to obtain the handle. */ static int32_t AcmParseEachIface(struct UsbAcmDevice *acm, struct UsbFnDevice *fnDev) { ... for (i = 0; i < fnDev->numInterfaces; i++) { /* Obtain an interface.*/ fnIface = (struct UsbFnInterface *)UsbFnGetInterface(fnDev, i); ... /* Open the interface. */ handle = UsbFnInterfaceOpen(fnIface); ... } return HDF_SUCCESS; }Receive events (EP0 control transfer).
static int32_t AcmAllocCtrlRequests(struct UsbAcmDevice *acm, int32_t num) { ... req = UsbFnCtrlRequestAlloc(acm->ctrlIface.handle, sizeof(struct UsbCdcLineCoding) + sizeof(struct UsbCdcLineCoding)); ... } static int32_t AcmDriverInit(struct HdfDeviceObject *device) { ... /* Start to receive events.*/ ret = UsbFnInterfaceStartRecvEvent(acm->ctrlIface.fn, 0xff, UsbAcmEventCallback, acm); ... }Perform USB communication (read and write).
static int32_t AcmSendNotifyRequest(struct UsbAcmDevice *acm, uint8_t type, uint16_t value, void *data, uint32_t length) { ... /* Send an asynchronous request.*/ ret = UsbFnRequestSubmitAsync(req); ... }Close the interface, stop receiving events, and delete the device.
static int32_t AcmReleaseFuncDevice(struct UsbAcmDevice *acm) { int32_t ret; /* Close the interface. */ (void)UsbFnInterfaceClose(acm->ctrlIface.handle); (void)UsbFnInterfaceClose(acm->dataIface.handle); /* Stop receiving the Event EP0 control transfer. */ (void)UsbFnInterfaceStopRecvEvent(acm->ctrlIface.fn); /* Delete the device. */ ret = UsbFnDeviceRemove(acm->fnDev); if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) { HDF_LOGE("%s: remove usb function device failed", __func__); } return ret; }
References
- Code repositories:
- Code paths:
USB driver model adaptation for LiteOS: //drivers/hdf_core/adapter/khdf/liteos/model/usb
USB DDK driver loading: //drivers/hdf_core/framework/model/usb
USB HDI server implementation: //drivers/peripheral/usb/hdi_service
USB HDI external APIs: //out/{product_name}/gen/drivers/interface/usb/v1_0
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙HDF Driver Development Process
harmony 鸿蒙Facial Authentication
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签:
热门推荐
-
2、 - 优质文章
-
3、 gate.io
-
8、 golang
-
9、 openharmony
-
10、 Vue中input框自动聚焦