harmony 鸿蒙HDMI
HDMI
Overview
HDMI
High Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) is an audio and video transmission protocol jointly released by Hitachi, Panasonic, Philips, Silicon Image, Sony, Thomson and Toshiba. It is used to transmit audio and video data from a source device, such as a DVD player or set-top box (STB), to a sink device, such as a TV or display. The transmission process complies with the Transition-minimized Differential Signaling (TMDS).
Basic Concepts
TMDS
Transmits audio, video, and various auxiliary data.Display data channel (DDC)
Allows the TX and RX ends to obtain the transmitting and receiving capabilities. However, HDMI only needs to unidirectionally obtain the capabilities of the RX end (display).Consumer Electronics Control (CEC)
Enables interaction between the HDMI TX and RX devices.Fixed rate link (FRL)
Allows the maximum TMDS bandwidth to be increased from 18 Gbit/s to 48 Gbit/s.High-bandwidth Digital Content Protection (HDCP)
Prevents copying of digital audio and video content being transmitted across devices.
Working Principles
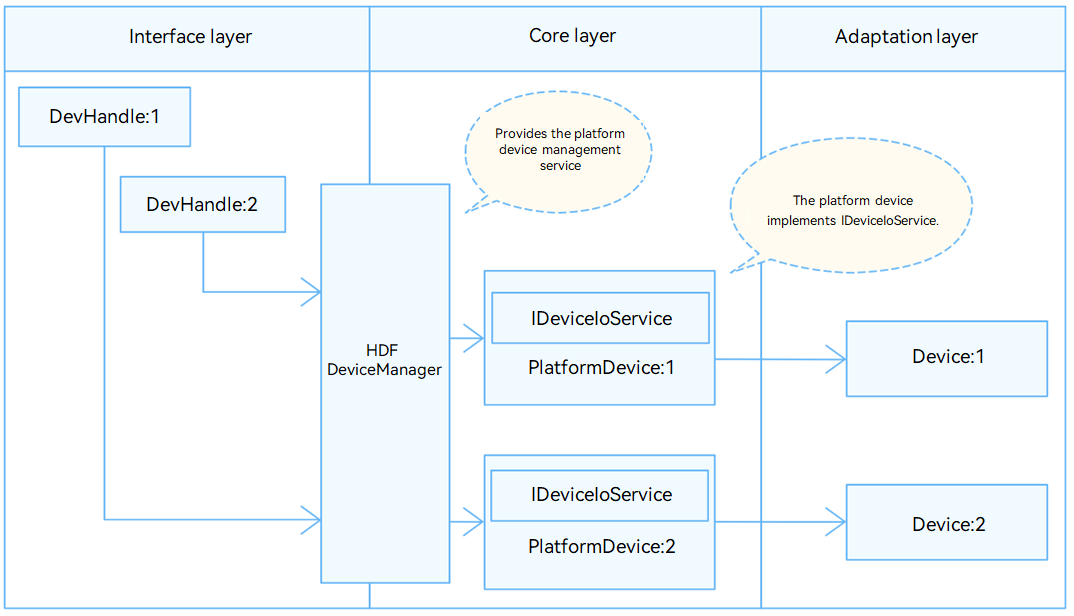
In the HDF, the HDMI module uses the independent service mode for API adaptation. In this mode, each device independently publishes a service to process external access requests. When receiving an access request, the HDF DeviceManager extracts parameters from the request to call the internal APIs of the target device. In the independent service mode, the HDF DeviceManager provides service management capabilities. However, you need to configure a node for each device, which increases memory usage.
Figure 1 Independent service mode
Constraints
Currently, the HDMI module supports only the kernels (LiteOS) of mini and small systems.
Development Guidelines
When to Use
HDMI features high transmission rate, wide transmission bandwidth, high compatibility, and can transmit uncompressed audio and video signals. Compared with the traditional full analog interface, HDMI simplifies connection between devices and provides HDMI-specific intelligent features, which are ideal for high-quality audio and video transmission of small-sized devices.
Available APIs
HdmiCntlrOps:
struct HdmiCntlrOps {
void (*hardWareInit)(struct HdmiCntlr *cntlr);
void (*hardWareStatusGet)(struct HdmiCntlr *cntlr, struct HdmiHardwareStatus *status);
void (*controllerReset)(struct HdmiCntlr *cntlr);
bool (*hotPlugStateGet)(struct HdmiCntlr *cntlr);
bool (*hotPlugInterruptStateGet)(struct HdmiCntlr *cntlr);
void (*lowPowerSet)(struct HdmiCntlr *cntlr, bool enable);
void (*tmdsModeSet)(struct HdmiCntlr *cntlr, enum HdmiTmdsModeType mode);
int32_t (*tmdsConfigSet)(struct HdmiCntlr *cntlr, struct HdmiTmdsConfig mode);
void (*infoFrameEnable)(struct HdmiCntlr *cntlr, enum HdmiPacketType infoFrameType, bool enable);
int32_t (*infoFrameSend)(struct HdmiCntlr *cntlr, enum HdmiPacketType infoFrameType, uint8_t *data, uint32_t len);
int32_t (*infoFrameDataSet)(struct HdmiCntlr *cntlr, uint32_t type, uint8_t *data, uint32_t len);
int32_t (*cecMsgSend)(struct HdmiCntlr *cntlr, struct HdmiCecMsg *msg);
void (*audioPathEnable)(struct HdmiCntlr *cntlr, bool enable);
void (*audioPathSet)(struct HdmiCntlr *cntlr, struct HdmiAudioConfigInfo *config);
void (*phyOutputEnable)(struct HdmiCntlr *cntlr, bool enable);
void (*phyOutputSet)(struct HdmiCntlr *cntlr, struct HdmiPhyCfg *cfg);
void (*blackDataSet)(struct HdmiCntlr *cntlr, bool enable);
void (*videoMuteEnable)(struct HdmiCntlr *cntlr, bool enable);
void (*videoPathSet)(struct HdmiCntlr *cntlr, struct HdmiVideoAttr *attr);
void (*audioMuteEnable)(struct HdmiCntlr *cntlr, bool enable);
void (*avmuteSet)(struct HdmiCntlr *cntlr, bool enable);
int32_t (*ddcTransfer)(struct HdmiCntlr *cntlr, struct HdmiDdcCfg *ddcCfg);
bool (*scdcSourceScrambleGet)(struct HdmiCntlr *cntlr);
int32_t (*scdcSourceScrambleSet)(struct HdmiCntlr *cntlr, bool enable);
void (*frlSet)(struct HdmiCntlr *cntlr);
int32_t (*frlEnable)(struct HdmiCntlr *cntlr, bool enable);
int32_t (*audioNctsSet)(struct HdmiCntlr *cntlr, struct HdmiFrlAudioNctsConfig *cfg);
void (*frlTrainingConfigSet)(struct HdmiCntlr *cntlr, struct HdmiFrlTrainConfig *cfg);
void (*frlTrainingStart)(struct HdmiCntlr *cntlr);
void (*frlGetTriningRslt)(struct HdmiCntlr *cntlr, struct HdmiFrlTrainRslt *rslt);
void (*hdcpRegInit)(struct HdmiCntlr *cntlr);
int32_t (*hdcpGenerateAksvAndAn)(struct HdmiCntlr *cntlr);
int32_t (*hdcpOptReg)(struct HdmiCntlr *cntlr, enum HdmiHdcpRegOptType type, uint8_t *data, uint32_t len);
void (*hdrTimerSet)(struct HdmiCntlr *cntlr, struct HdmiHdrTimerConfig *config);
};
Table 1 Description of the callback functions in HdmiCntlrOps
| Function | Input Parameter | Output Parameter | Return Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hardWareInit | cntlr: structure pointer to an HDMI controller at the core layer. | – | – | Initializes the HDMI hardware. |
| hardWareStatusGet | cntlr: structure pointer to an HDMI controller at the core layer. |
status: pointer to the HDMI hardware status. | – | Obtains the HDMI hardware status. |
| controllerReset | cntlr: structure pointer to an HDMI controller at the core layer. | – | – | Resets an HDMI controller. |
| hotPlugStateGet | cntlr: structure pointer to an HDMI controller at the core layer. | – | bool: HDMI hot-plug status. | Obtains the HDMI hot-plug status. |
| hotPlugInterruptStateGet | cntlr: structure pointer to an HDMI controller at the core layer. | – | bool: HDMI hot-plug interrupt status. | Obtains the HDMI hot-plug interrupt status. |
| lowPowerSet | cntlr: structure pointer to an HDMI controller at the core layer. enable: whether to enable low power consumption. |
– | – | Enables or disables low power consumption. |
| tmdsModeSet | cntlr: structure pointer to an HDMI controller at the core layer. mode: TMDS mode. |
– | – | Sets the TMDS mode. |
| tmdsConfigSet | cntlr: structure pointer to an HDMI controller at the core layer. mode: TMDS parameters. |
– | HDF_STATUS | Sets TMDS parameters. |
| infoFrameEnable | cntlr: structure pointer to an HDMI controller at the core layer. infoFrameType: packet type. enable: whether to enable infoFrame. |
– | – | Enables or disables infoFrame. |
| infoFrameSend | cntlr: structure pointer to an HDMI controller at the core layer. infoFrameType: packet type. data: pointer to infoFrame data. len: data length. |
– | HDF_STATUS | Sends an infoFrame. |
| cecMsgSend | cntlr: structure pointer to an HDMI controller at the core layer. msg: pointer to the CEC message |
– | HDF_STATUS | Sends a CEC message. |
| audioPathEnable | cntlr: structure pointer to an HDMI controller at the core layer. enable: whether to enable the audio path. |
– | – | Enables or disables the audio path. |
| audioPathSet | cntlr: structure pointer to an HDMI controller at the core layer. config: pointer to the audio path configuration. |
– | – | Sets the audio path. |
| phyOutputEnable | cntlr: structure pointer to an HDMI controller at the core layer. enable: whether to enable the physical layer output. |
– | – | Enables or disables the physical layer output. |
| phyOutputSet | cntlr: structure pointer to an HDMI controller at the core layer. cfg: pointer to the physical layer configuration. |
– | – | Sets the physical layer information. |
| blackDataSet | cntlr: structure pointer to an HDMI controller at the core layer. enable: whether to enable the black screen. |
– | – | Sets the black screen. |
| videoMuteEnable | cntlr: structure pointer to an HDMI controller at the core layer. enable: whether to enable the video mute feature. |
– | – | Enables or disables the video mute feature. |
| videoPathSet | cntlr: structure pointer to an HDMI controller at the core layer. attr: pointer to the video path configuration. |
– | – | Sets the video path. |
| audioMuteEnable | cntlr: structure pointer to an HDMI controller at the core layer. enable: whether to enable the audio mute feature. |
– | – | Enables or disables the audio mute feature. |
| avmuteSet | cntlr: structure pointer to an HDMI controller at the core layer. enable: whether to enable the AV mute feature. |
– | – | Enables or disables the AV mute feature. |
| ddcTransfer | cntlr: structure pointer to an HDMI controller at the core layer. ddcCfg: pointer to the DDC configuration. |
ddcCfg: DDC configuration. | HDF_STATUS | Reads and writes data through the DDC. |
| scdcSourceScrambleGet | cntlr: structure pointer to an HDMI controller at the core layer. | – | Scrambling status of the source. | Obtains the scrambling status of the source. |
| scdcSourceScrambleSet | cntlr: structure pointer to an HDMI controller at the core layer. enable: whether to enable the scrambling for the source. |
– | HDF_STATUS | Enables or disable scrambling for the source. |
| frlEnable | cntlr: structure pointer to an HDMI controller at the core layer. enable: whether to enable the FRL. |
– | HDF_STATUS | Enables or disables the FRL. |
| audioNctsSet | cntlr: structure pointer to an HDMI controller at the core layer. cfg: pointer to the N/CTS configuration. |
– | HDF_STATUS | Sets the audio N/CTS information. |
| frlTrainingConfigSet | cntlr: structure pointer to an HDMI controller at the core layer. cfg: pointer to the FRL training configuration. |
– | – | Sets FRL training information. |
| frlTrainingStart | cntlr: structure pointer to an HDMI controller at the core layer. | – | – | Starts FRL training. |
| frlGetTriningRslt | cntlr: structure pointer to an HDMI controller at the core layer. | rslt: FRL training result. | – | Obtains the FRL training result. |
| hdcpRegInit | cntlr: structure pointer to an HDMI controller at the core layer. | – | – | Initializes registers related to the High-bandwidth Digital Content Protection (HDCP) process. |
| hdcpGenerateAksvAndAn | cntlr: structure pointer to an HDMI controller at the core layer. | – | HDF_STATUS | Generates the Aksv and An in the HDCP process. |
| hdcpOptReg | cntlr: structure pointer to an HDMI controller at the core layer. type: operation type. data: register data. len: data length. |
data: register data. | HDF_STATUS | Reads or writes the registers during the HDCP process. |
| hdrTimerSet | cntlr: structure pointer to an HDMI controller at the core layer. config: pointer to the timer configuration |
– | – | Sets the HDR-related timer. |
How to Develop
The HDMI module adaptation involves the following steps:
- Instantiate the driver entry.
- Instantiate the HdfDriverEntry structure.
- Call HDF_INIT to register the HdfDriverEntry instance with the HDF.
- Configure attribute files.
- Add the deviceNode information to the device_info.hcs file.
- (Optional) Add the hdmi_config.hcs file.
- Instantiate the HDMI controller object.
- Initialize HdmiCntlr.
- Instantiate HdmiCntlrOps in HdmiCntlr.
Development Example
Instantiate the driver entry.
The driver entry must be a global variable of the HdfDriverEntry type (which is defined in hdf_device_desc.h), and the value of moduleName must be the same as that in device_info.hcs. In the HDF, the start address of each HdfDriverEntry object of all loaded drivers is collected to form a segment address space similar to an array for the upper layer to invoke.
Generally, the HDF calls the Bind function and then the Init function to load a driver. If Init fails to be called, the HDF calls Release to release driver resources and exit.
HDMI driver entry example:
struct HdfDriverEntry g_hdmiDriverEntry = { .moduleVersion = 1, .Bind = HdmiAdapterBind, .Init = HdmiAdapterInit, .Release = HdmiAdapterRelease, .moduleName = "adapter_hdmi_driver",// (mandatory) The value must be the same as that in the .hcs file. }; HDF_INIT(g_hdmiDriverEntry); // Call HDF_INIT to register the driver entry with the HDF.Configure attribute files.
Add deviceNode to the device_info.hcs file, and configure the device attributes in the hdmi_config.hcs file. The deviceNode information is related to registration of the driver entry. The device attribute values are closely related to the driver implementation and the default values or restriction ranges of the HdmiCntlr members at the core layer.
Configure HDMI controller information from the first node. This node specifies a type of HDMI controllers rather than a specific HDMI controller. In this example, there is only one HDMI controller. If there are multiple HDMI controllers, you need to add the deviceNode information to the device_info file and add the corresponding device attributes to the hdmi_config file.
device_info.hcs configuration example
root { platform :: host { device_hdmi :: device { device0 :: deviceNode { policy = 2; // Publish services. priority = 20; // Driver startup priority. permission = 0644; // Permission to create device nodes for the driver. serviceName = "HDF_PLATFORM_HDMI_0"; // (Mandatory) Unique name of the service published by the driver. moduleName = "hdmi_driver"; // (Mandatory) Driver name, which must be the same as moduleName in the driver entry. deviceMatchAttr = "adapter_hdmi_driver"; // (Mandatory) Controller private data, which must be same as that of the corresponding controller in hdmi_config.hcs. } // The specific controller information is in hdmi_config.hcs. } } }hdmi_config.hcs configuration example
root { platform { hdmi_config { template hdmi_controller { // Template configuration. In the template, you can configure the common parameters shared by device nodes. match_attr = ""; // (Mandatory) The value must be the same as that of deviceMatchAttr in device_info.hcs. index = 0; // (Mandatory) HDMI controller number. regBasePhy = 0x10100000; // (Mandatory) Physical base address of the register. regSize = 0xd1; // (Mandatory) Register bit width. irqNum = 100; //(Mandatory) Interrupt request (IRQ) number. maxTmdsClock = 300; videoTiming = 10; quantization = 1; colorSpace = 0; colorimetry = 0; audioIfType = 0; audioBitDepth = 1; audioSampleRate = 2; audioChannels = 1; hdrColorimetry = 4; hdrUserMode = 1; cap = 0xd001e045; } controller_0x10100000 :: hdmi_controller { match_attr = "adapter_hdmi_driver"; index = 0; regBasePhy = 0x10100000; irqNum = 100; maxTmdsClock = 400; defTmdsClock = 300; maxFrlRate = 600; videoTiming = 10; quantization = 1; colorSpace = 0; colorimetry = 0; audioIfType = 0; audioSampleRate = 2; audioChannels = 1; hdrColorimetry = 4; hdrUserMode = 1; cap = 0xd001e045; } } } }
Instantiate the HdmiCntlr object.
Initialize the HdmiCntlr object at the core layer, including defining a custom structure (to pass parameters and data) and implementing the HdfDriverEntry member functions (Bind, Init and Release) to instantiate HdmiCntlrOps in HdmiCntlr (so that the underlying driver functions can be called).
Defining the custom structure
 NOTE
NOTETo the driver, the custom structure holds parameters and data. The DeviceResourceIface method provided by the HDF reads the values in the hdmi_config.hcs file to initialize the members in the custom structure and passes important parameters, such as the device number and bus number, to the HdmiCntlr object at the core layer.
struct HdmiAdapterHost { struct HdmiCntlr *cntlr; // (Mandatory) Control object at the core layer. The details are as follows: volatile unsigned char *regBase;// (Mandatory) Register base address. uint32_t regBasePhy; // (Mandatory) Physical base address of the register. uint32_t regSize; // (Mandatory) Register bit width. uint32_t irqNum; // (Mandatory) IRQ number. }; /* HdmiCntlr is the controller structure at the core layer. The Init function assigns values to the members of HdmiCntlr. */ struct HdmiCntlr { struct IDeviceIoService service; struct HdfDeviceObject *hdfDevObj; struct PlatformDevice device; struct OsalMutex mutex; struct PlatformQueue *msgQueue; struct HdmiCntlrCap cap; struct HdmiAttr attr; struct HdmiCntlrOps *ops; uint32_t deviceIndex; uint32_t state; // Controller status. enum HdmiTmdsModeType tmdsMode; struct HdmiDevice *hdmi; struct HdmiInfoframe infoframe; struct HdmiScdc *scdc; struct HdmiDdc ddc; struct HdmiFrl *frl; struct HdmiHdcp *hdcp; struct HdmiCec *cec; struct HdmiEvent event; struct HdmiHdr *hdr; void *priv; };Instantiating HdmiCntlrOps in HdmiCntlr
static struct HdmiCntlrOps g_hdmiAdapterHostOps = { .hardWareInit = HdmiAdapterHardWareInit, .hardWareStatusGet = HdmiAdapterHardWareStatusGet, .controllerReset = HdmiAdapterControllerReset, .hotPlugStateGet = HdmiAdapterHotPlugStateGet, .hotPlugInterruptStateGet = HdmiAdapterHotPlugInterruptStateGet, .lowPowerSet = HdmiAdapterLowPowerSet, .tmdsModeSet = HdmiAdapterTmdsModeSet, .tmdsConfigSet = HdmiAdapterTmdsConfigSet, .infoframeEnable = HdmiAdapterInfoframeEnable, .infoframeSend = HdmiAdapterInfoframeSend, .infoframeDataSet = HdmiAdapterInfoframeDataSet, .cecMsgSend = HdmiAdapterCecMsgSend, .audioPathEnable = HdmiAdapterAudioPathEnable, .audioPathSet = HdmiAdapterAudioPathSet, .phyOutputEnable = HdmiAdapterPhyOutputEnable, .phyOutputSet = HdmiAdapterPhyOutputSet, .blackDataSet = HdmiAdapterBlackDataSet, .videoMuteEnable = HdmiAdapterVideoMuteEnable, .videoPathSet = HdmiAdapterVideoPathSet, .audioMuteEnable = HdmiAdapterAudioMuteEnable, .avmuteSet = HdmiAdapterAvmuteSet, .ddcTransfer = HdmiAdapterDdcTransfer, .scdcSourceScrambleGet = HdmiAdapterScdcSourceScrambleGet, .scdcSourceScrambleSet = HdmiAdapterScdcSourceScrambleSet, .frlSet = HdmiAdapterFrlSet, .frlEnable = HdmiAdapterFrlEnable, .audioNctsSet = HdmiAdapterAudioNctsSet, .frlTrainingConfigSet = HdmiAdapterFrlTrainingConfigSet, .frlTrainingStart = HdmiAdapterFrlTrainingStart, .frlGetTriningRslt = HdmiAdapterFrlGetTriningRslt, .hdcpRegInit = HdmiAdapterHdcpRegInit, .hdcpGenerateAksvAndAn = HdmiAdapterHdcpGenerateAksvAndAn, .hdcpOptReg = HdmiAdapterHdcpOptReg, .hdrTimerSet = HdmiAdapterHdrTimerSet, };Bind function
Input parameter:
HdfDeviceObject, an interface parameter exposed by the driver, contains the .hcs information.
Return value:
HDF_STATUS
The table below describes some status. For more information, see HDF_STATUS in the /drivers/framework/include/utils/hdf_base.h file.
|Status|Description| |:-|:-| |HDF_ERR_INVALID_OBJECT|Invalid controller object.| |HDF_ERR_INVALID_PARAM|Invalid parameter.| |HDF_ERR_MALLOC_FAIL |Failed to allocate memory.| |HDF_ERR_IO |I/O error.| |HDF_SUCCESS |Transmission successful.| |HDF_FAILURE |Transmission failed.|
**Function description**: Initializes the custom structure object **HdmiAdapterHost** and **HdmiCntlr**, and calls the **HdmiCntlrAdd** function to add the HDMI controller to the core layer. The **HdmiCntlr**, **HdmiAdapterHost**, and **HdfDeviceObject** assign values with each other so that other functions can be converted successfully. ```c static int32_t HdmiAdapterBind(struct HdfDeviceObject *obj) { struct HdmiCntlr *cntlr = NULL; struct HimciAdapterHost *host = NULL; int32_t ret; cntlr = (struct HdmiCntlr *)OsalMemCalloc(sizeof(struct HdmiCntlr)); if (cntlr == NULL) { HDF_LOGE("%s: malloc cntlr failed!", __func__); return HDF_ERR_MALLOC_FAIL; } host = (struct HimciAdapterHost *)OsalMemCalloc(sizeof(struct HimciAdapterHost)); if (host == NULL) { HDF_LOGE("%s: malloc host failed!", __func__); return HDF_ERR_MALLOC_FAIL; } cntlr->priv = (void *)host; // (Mandatory) Store host to the private data of cntlr. cntlr->ops = &g_hdmiHostOps; // (Mandatory) Connect to the HdmiCntlrOps instance. cntlr->hdfDevObj = obj; // (Mandatory) Prerequisites for conversion between HdfDeviceObject and HdmiCntlr. obj->service = &cntlr->service; // (Mandatory) Prerequisites for conversion between HdfDeviceObject and HdmiCntlr. ret = HdmiAdapterCntlrParse(cntlr, obj); // (Mandatory) Initialize cntlr. If the operation fails, execute goto __ERR. ... ret = HdmiAdapterHostParse(host, obj); // (Mandatory) Initialize the attributes of the host object. If the operation fails, execute goto__ERR. ... ret = HdmiAdapterHostInit(host, cntlr); // Initialize the custom structure. If the operation fails, execute goto __ERR. ... ret = HdmiCntlrAdd(cntlr); // Call the functions at the core layer. If the operation fails, execute goto__ERR. ... HDF_LOGD("HdmiAdapterBind: success."); return HDF_SUCCESS; __ERR: HdmiAdapterDeleteHost(host); HDF_LOGD("HdmiAdapterBind: fail, err = %d.", ret); return ret; } ```Init function
Input parameter:
HdfDeviceObject, an interface parameter exposed by the driver, contains the .hcs information.
Return value:
HDF_STATUS
Function description:
Implements the HdmiAdapterInit function.
static int32_t HdmiAdapterInit(struct HdfDeviceObject *obj) { return HDF_SUCCESS; }Release function
Input parameter:
HdfDeviceObject, an interface parameter exposed by the driver, contains the .hcs information.
**Return value**: No value is returned. **Function description**: Releases the memory and deletes the controller. This function assigns values to the **Release** callback in the driver entry structure. If the HDF fails to call the **Init** function to initialize the driver, the **Release** function can be called to release driver resources. >  **NOTE**<br> > All forced conversion operations for obtaining the corresponding object can be successful only when the **Init** function has the corresponding value assignment operations. ```c static void HdmiAdapterRelease(struct HdfDeviceObject *obj) { struct HdmiCntlr *cntlr = NULL; ... cntlr = (struct HdmiCntlr *)obj->service;// Forcibly convert HdfDeviceObject to HdmiCntlr by using service. For details about the value assignment, see the Bind function. ... HimciDeleteHost((struct HimciAdapterHost *)cntlr->priv);// Customized memory release function. A forced conversion from HdmiCntlr to HimciAdapterHost is involved in the process. } ```
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙HDF Driver Development Process
harmony 鸿蒙Facial Authentication
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签:
热门推荐
-
2、 - 优质文章
-
3、 gate.io
-
8、 golang
-
9、 openharmony
-
10、 Vue中input框自动聚焦