harmony(鸿蒙)Context Usage
Context Usage
Context Overview
Context provides the capability of obtaining contextual information of an application.
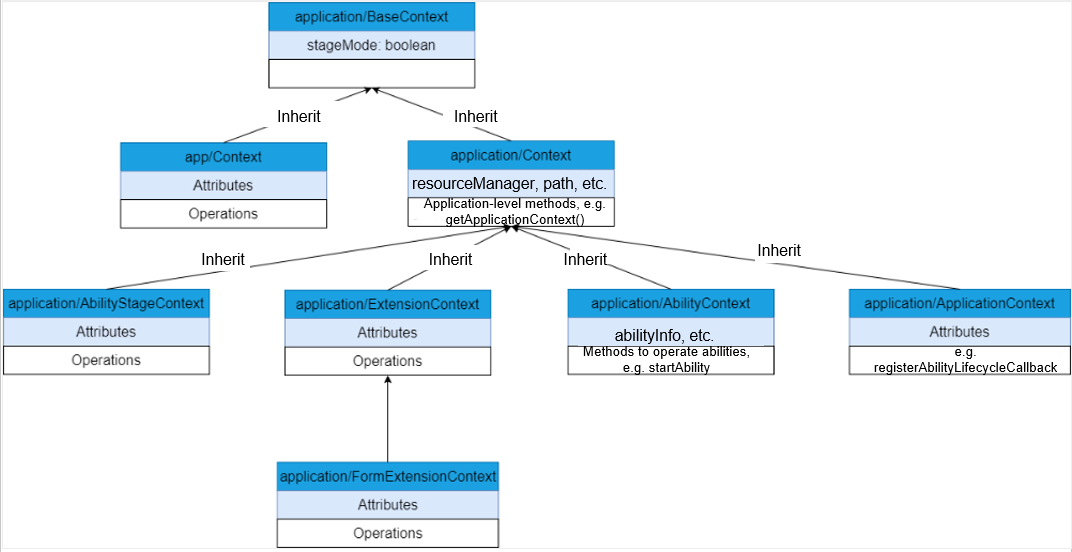
The OpenHarmony application framework has two models: Feature Ability (FA) model and stage model. Correspondingly, there are two sets of context mechanisms. application/BaseContext is a common context base class. It uses the stageMode attribute to specify whether the context is used for the stage model.
- FA model
Only the methods in app/Context can be used for the context in the FA model. Both the application-level context and ability-level context are instances of this type. If an ability-level method is invoked in the application-level context, an error occurs. Therefore, you must pay attention to the actual meaning of the Context instance.
- Stage model
The stage model has the following types of contexts: application/Context, application/ApplicationContext, application/AbilityStageContext, application/ExtensionContext, application/AbilityContext, and application/FormExtensionContext. For details about these contexts and how to use them, see Context in the Stage Model.
Context in the FA Model
Only the methods in app/Context can be used for the context in the FA model.
The FA model has only one context definition. All capabilities in the context are provided through methods. The context uses these methods to extend the capabilities of the FA.
d.ts statement
https://gitee.com/openharmony/interface_sdk-js/blob/master/api/app/context.d.ts
Example
import featureAbility from '@ohos.ability.featureAbility'
export default {
onCreate() {
// Obtain the context and call related APIs.
let context = featureAbility.getContext();
context.getBundleName((data, bundleName)=>{
console.info("ability bundleName:" + bundleName)
});
console.info('Application onCreate')
},
onDestroy() {
console.info('Application onDestroy')
},
}
Common Context-related Methods in the FA Model
The following context-related methods are available in the FA model:
setDisplayOrientation(orientation: bundle.DisplayOrientation, callback: AsyncCallback<void>): void
setDisplayOrientation(orientation: bundle.DisplayOrientation): Promise<void>;
The methods are used to set the display orientation of the current ability.
Example
import featureAbility from '@ohos.ability.featureAbility'
import bundle from '@ohos.bundle';
export default {
onCreate() {
// Obtain the context and call related APIs.
let context = featureAbility.getContext();
context.setDisplayOrientation(bundle.DisplayOrientation.LANDSCAPE).then(() => {
console.log("Set display orientation.")
})
console.info('Application onCreate')
},
onDestroy() {
console.info('Application onDestroy')
},
}
Context in the Stage Model
The following describes the contexts provided by the stage model in detail.
application/Context
application/Context is the base class context. It provides basic application information, such as resourceManager, applicationInfo, cacheDir, and area. It also provides basic application methods such as createModuleContext.
d.ts statement
https://gitee.com/openharmony/interface_sdk-js/blob/master/api/application/Context.d.ts
application/ApplicationContext
application/ApplicationContext is an application-level context. In addition to the capabilities provided by the base class context, the application-level context provides registerAbilityLifecycleCallback and unregisterAbilityLifecycleCallback to monitor the ability lifecycle in a process.
How to Obtain
Obtain the context by calling context.getApplicationContext() in Ability.
Example
import Ability from "@ohos.application.Ability";
var lifecycleid;
export default class MainAbility extends Ability {
onCreate() {
console.log("MainAbility onCreate")
let AbilityLifecycleCallback = {
onAbilityCreate(ability){
console.log("AbilityLifecycleCallback onAbilityCreate ability:" + JSON.stringify(ability));
},
onWindowStageCreate(ability, windowStage){
console.log("AbilityLifecycleCallback onWindowStageCreate ability:" + JSON.stringify(ability));
console.log("AbilityLifecycleCallback onWindowStageCreate windowStage:" + JSON.stringify(windowStage));
},
onWindowStageActive(ability, windowStage){
console.log("AbilityLifecycleCallback onWindowStageActive ability:" + JSON.stringify(ability));
console.log("AbilityLifecycleCallback onWindowStageActive windowStage:" + JSON.stringify(windowStage));
},
onWindowStageInactive(ability, windowStage){
console.log("AbilityLifecycleCallback onWindowStageInactive ability:" + JSON.stringify(ability));
console.log("AbilityLifecycleCallback onWindowStageInactive windowStage:" + JSON.stringify(windowStage));
},
onWindowStageDestroy(ability, windowStage){
console.log("AbilityLifecycleCallback onWindowStageDestroy ability:" + JSON.stringify(ability));
console.log("AbilityLifecycleCallback onWindowStageDestroy windowStage:" + JSON.stringify(windowStage));
},
onAbilityDestroy(ability){
console.log("AbilityLifecycleCallback onAbilityDestroy ability:" + JSON.stringify(ability));
},
onAbilityForeground(ability){
console.log("AbilityLifecycleCallback onAbilityForeground ability:" + JSON.stringify(ability));
},
onAbilityBackground(ability){
console.log("AbilityLifecycleCallback onAbilityBackground ability:" + JSON.stringify(ability));
},
onAbilityContinue(ability){
console.log("AbilityLifecycleCallback onAbilityContinue ability:" + JSON.stringify(ability));
}
}
// 1. Obtain applicationContext through the context attribute.
let applicationContext = this.context.getApplicationContext();
// 2. Use applicationContext to register and listen for the ability lifecycle in the application.
lifecycleid = applicationContext.registerAbilityLifecycleCallback(AbilityLifecycleCallback);
console.log("registerAbilityLifecycleCallback number: " + JSON.stringify(lifecycleid));
},
onDestroy() {
let applicationContext = this.context.getApplicationContext();
applicationContext.unregisterAbilityLifecycleCallback(lifecycleid, (error, data) => {
console.log("unregisterAbilityLifecycleCallback success, err: " + JSON.stringify(error));
});
}
}
d.ts statement
https://gitee.com/openharmony/interface_sdk-js/blob/master/api/application/ApplicationContext.d.ts
application/AbilityStageContext
application/AbilityStageContext is the context for the HAP file. In addition to those provided by the base class application/Context, this context contains HapModuleInfo and Configuration.
How to Obtain
Obtain the context from the context attribute in AbilityStage.
Example
export default class MyAbilityStage extends AbilityStage {
onCreate() {
// The context attribute is of the AbilityStageContext type.
console.log('HapModuleInfo is ' + this.context.currentHapModuleInfo);
}
}
d.ts statement
https://gitee.com/openharmony/interface_sdk-js/blob/master/api/application/AbilityStageContext.d.ts
application/AbilityContext
In the stage model, each ability has a context attribute.
Ability provides methods to manage the ability lifecycle, and AbilityContext provides methods to operate abilities (such as startAbility and connectAbility).
How to Obtain
Obtain the context from the context attribute in Ability.
Example
import Ability from '@ohos.application.Ability'
export default class MainAbility extends Ability {
onCreate(want, launchParam) {
console.log("[Demo] MainAbility onCreate")
globalThis.abilityWant = want;
}
onDestroy() {
console.log("[Demo] MainAbility onDestroy")
}
onWindowStageCreate(windowStage) {
// Set the main page for this ability when the main window is created.
console.log("[Demo] MainAbility onWindowStageCreate")
// Obtain AbilityContext and print the ability information.
let context = this.context;
console.log("[Demo] MainAbility bundleName " + context.abilityInfo.bundleName)
windowStage.loadContent("pages/index", (err, data) => {
if (err.code) {
console.error('Failed to load the content. Cause:' + JSON.stringify(err));
return;
}
console.info('Succeeded in loading the content. Data: ' + JSON.stringify(data))
});
}
onWindowStageDestroy() {
// Release the UI related resources when the main window is destroyed.
console.log("[Demo] MainAbility onWindowStageDestroy")
}
onForeground() {
// The ability is switched to run in the foreground.
console.log("[Demo] MainAbility onForeground")
}
onBackground() {
// The ability is switched to run in the background.
console.log("[Demo] MainAbility onBackground")
}
};
application/FormExtensionContext
For details, see FormExtensionContext.
Obtaining the Context on an ArkTS Page
In the stage model, in the onWindowStageCreate lifecycle of an ability, you can call SetUIContent of WindowStage to load an ArkTS page. In some scenarios, you need to obtain the context on the page to call related APIs.
How to Obtain
Use the API described in the table below to obtain the context associated with an ArkTS page.
| API | Description |
|---|---|
| getContext(component: Object): Object | Obtains the Context object associated with a component on the page. |
Example
// MainAbility.ts
import Ability from '@ohos.application.Ability'
export default class MainAbility extends Ability {
onCreate(want, launchParam) {
console.log("[Demo] MainAbility onCreate")
}
onDestroy() {
console.log("[Demo] MainAbility onDestroy")
}
onWindowStageCreate(windowStage) {
// Load the index page and pass the current Context object.
windowStage.setUIContent(this.context, "pages/index", null)
}
onWindowStageDestroy() {}
onForeground() {}
onBackground() {}
};
// pages/index.ets
import context from '@ohos.application.context'
type Context = context.Context
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
build() {
Row() {
Column() {
Text('GetContext')
.fontSize(50)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.onClick(() => {
// Obtain the Context object associated with the current component.
var context : Context = getContext(this) as Context
console.info("CacheDir:" + context.cacheDir)
})
}
.width('100%')
}
.height('100%')
}
}
Common Incorrect Usage
Error 1: Use globalThis to obtain the context in the stage model.
Reason
In the FA model, each ability instance has a JS VM instance. Therefore, a global ability instance can be obtained from the global object of the JS engine. In the stage model, where all the processes of an application share a JS VM instance, there is no global ability instance, and using globalThis may cause an error or crash.
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony(鸿蒙)Ability Development
harmony(鸿蒙)Ability Assistant Usage
harmony(鸿蒙)Ability Framework Overview
harmony(鸿蒙)Test Framework Usage
harmony(鸿蒙)ContinuationManager Development
harmony(鸿蒙)Data Ability Development
harmony(鸿蒙)FA Widget Development
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签: