harmony 鸿蒙HUKS Development
HUKS Development
Overview
HUKS
OpenHarmony Universal KeyStore (HUKS) provides lifecycle key management capabilities, including generating, storing, and destroying keys, and provides attestation for the keys stored in the HUKS. In the HUKS hierarchical architecture, the HUKS core layer (HUKS Core) at the bottom implements key management functions and runs in a secure hardware environment, such as a Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) or secure chipset. The implementation of the HUKS core layer varies depending on the secure hardware environment of the vendor. To ensure consistency of the architecture and interfaces between the service layer and application layer, the HUKS core layer defines a set of Hardware Device Interface (HDI) APIs.
This document describes how to develop the HUKS core layer functions using the HUKS HDI APIs.
The HUKS core layer is supposed to support the following functions:
Generation of keys.
Import of keys.
Key operations, including encryption and decryption, signing and signature verification, key derivation, key agreement, and generation of message authentication codes (MACs).
Key access control.
Key attestation.
Export of the public key from a chipset.
Basic Concepts
- HUKS Core
HUKS Core is a core component that implements functions, including cryptographic calculation of keys, encryption and decryption, and key access control. Generally, it runs in a secure environment (such as a TEE or secure chipset) of a device to ensure that the keys in plaintext are never exposed outside the HUKS Core.
- Key session
A key session holds the key information, including the key operation data, key properties, and access control attributes, when a key is used. You need to pass in a key alias to create a session for the key. The HUKS generates a globally unique handle for each session. A general key operation involves creating a session, passing in data and parameters, and finishing the session (or aborting the session).
- TEE
A TEE is a secure area created by isolating software and hardware resources to protect the applications and data in the secure area from unauthorized access. This isolation mechanism yields two execution environments: TEE and Rich Execution Environment (REE). Each execution environment has independent internal data path and memory, protecting the data inside the TEE from being disclosed. The applications in an REE cannot access resources in a TEE. The applications in a TEE cannot access resources in another TEE without authorization.
Working Principles
The HUKS is divided into the following layers: - Application layer: provides APIs for applications. - Service layer: processes key management requests from applications and performs key ciphertext management, identity verification, and key session management. - Core layer: implements core functions, such as key generation, key operations, key access control, and key attestation.
Figure 1 HUKS architecture
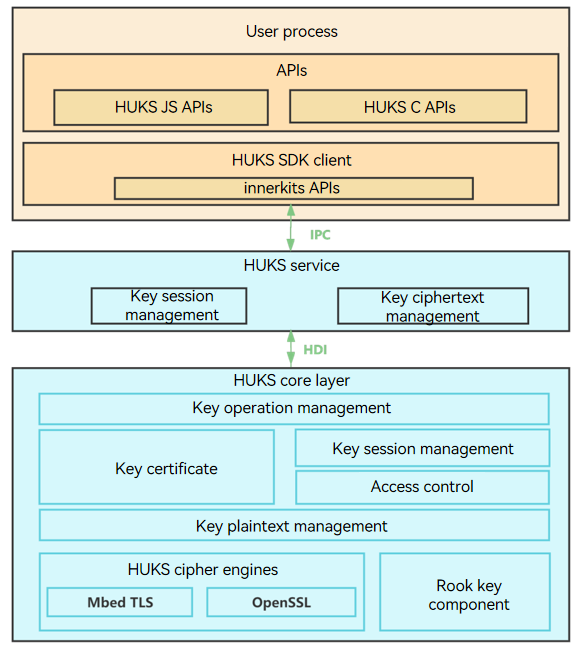
Constraints
- Keys in a secure environment in lifecycle
In the lifecycle of a key, the plaintext will never be exposed outside the HUKS Core. For the devices with a TEE or secure chipset, the HUKS Core runs in the TEE or secure chipset. This prevents the key plaintext from being disclosed even if the REE is cracked. That is why the key materials used in all HUKS passthrough HDI APIs are in ciphertext.
- Encrypted keys for storage
The service keys are encrypted based on the device root key. If supported by the device, certain keys can be further protected by a password.
- Strict access control over keys
Only authorized services can access keys. For security-critical services, user identity authentication can be enabled for key access. - Key attestation
The HUKS provides attestation for hardware-backed key storage. It proves that the key has not been tampered with, is stored in the hardware-backed HUKS Core, and has correct key properties.
- Key material format
When a key (key pair, public key, or private key) is imported or exported, the key material format must meet HUKS requirements. For details, see Key Material Formats.
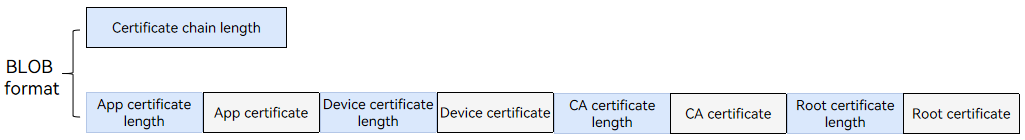
- Certificate chain format
The certificate chain returned by AttestKey() must be assembled in the sequence of the application certificate, device certificate, CA certificate, and root certificate, with the certificate length added before each certificate. The certificate chain and its length are in the binary large object (BLOB) format. If you want to define the certificate format, the format must be the same as that parsed by the server.
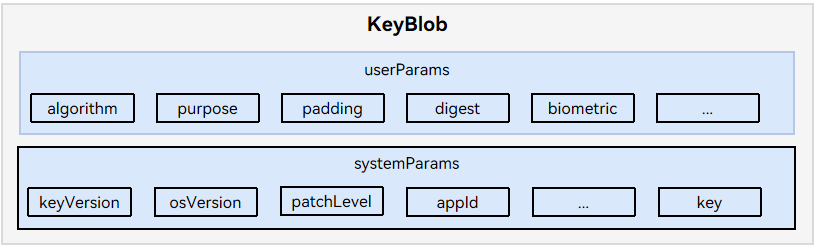
- KeyBlob The key returned by the APIs must be assembled into a KeyBlob based on the key storage status. For details about the APIs that must comply with this constraint, see Available APIs.
How to Develop
When to Use
The HUKS Core provides KeyStore capabilities for applications, including key management and cryptographic operations. If you want to replace the HUKS Core with your own implementation, you need to implement the following APIs.
Available APIs
Table 1 Available APIs
| API | Description | Constraints | JS API |
|---|---|---|---|
| ModuleInit() | Initializes the HUKS Core. | N/A | N/A |
| ModuleDestroy() | Destroys the HUKS Core. | N/A | N/A |
| GenerateKey() | Generates a key based on the cryptographic algorithm parameters. | The key output must be in the KeyBlob format. | generateKey(keyAlias: string, options: HuksOptions) |
| ImportKey() | Imports a key in plaintext. | The key output must be in the KeyBlob format. | importKey(keyAlias: string, options: HuksOptions) |
| ImportWrappedKey() | Imports a wrapped (encrypted) key. | The key output must be in the KeyBlob format. | importWrappedKey(keyAlias: string, wrappingKeyAlias: string, options: HuksOptions) |
| ExportPublicKey() | Exports the public key of a key pair. | N/A | exportKey(keyAlias: string, options: HuksOptions) |
| Init() | Initializes a key session. This API returns a key session handle and an authentication token (optional). | N/A | init(keyAlias: string, options: HuksOptions) |
| Update() | Updates key operation data. | The input parameters for signature verification must be the raw data. | update(handle: number, token?: Uint8Array, options: HuksOptions) |
| Finish() | Finishes a key session. | The input parameter for signature verification must be the signed data. | finish(handle: number, options: HuksOptions) |
| Abort() | Aborts a key session. | N/A | abort(handle: number, options: HuksOptions) |
| CheckKeyValidity() | Checks the key material (ciphertext) validity. | N/A | N/A |
| AttestKey() | Attests a key. | The output parameter must be in the certificate chain format. | attestKey(keyAlias: string, options: HuksOptions) |
| ExportChipsetPlatformPublicKey() | Exports the public key of a chipset key pair. | The output parameters are the raw data of ECC P-256 x-axis and y-axis values, each of which are of 32 bytes. | N/A |
| UpgradeKey() | Updates the key file. | N/A | N/A |
| GenerateRandom() | Generates a random number. | N/A | N/A |
| Encrypt() | Encrypts data. | N/A | N/A |
| Decrypt() | Decrypts data. | N/A | N/A |
| Sign() | Signs data. | N/A | N/A |
| Verify() | Verifies a signature. | N/A | N/A |
| AgreeKey() | Performs key agreement. | N/A | N/A |
| DeriveKey() | Derives a key. | N/A | N/A |
| Mac() | Generates a MAC. | N/A | N/A |
ModuleInit
API Description
Initializes the HUKS Core. You can use this API to initialize global variables, such as the global thread locks, algorithm library, and the AuthToken key and root key used for access control.
Prototype
int32_t ModuleInit(struct IHuks *self);Parameters
struct IHuks *self Pointer to the HUKS HDI struct.
Return Value
HKS_SUCCESS (the value is 0): The operation is successful.
Other values (negative number): The operation fails. For details, see HksErrorCode.
ModuleDestroy
API Description
Destroys the HUKS Core. You can use this API to release global variables including the locks and destroy the AuthToken key and root key in the memory.
Prototype
int32_t ModuleDestroy(struct IHuks *self);Parameters
struct IHuks *self Pointer to the HUKS HDI struct.
Return Value
HKS_SUCCESS: The operation is successful.
Other values: The operation fails.
GenerateKey
API Description
Generate a key based on the paramSet.
Prototype
int32_t GenerateKey(struct IHuks *self, const struct HuksBlob *keyAlias, const struct HuksParamSet *paramSet,
const struct HuksBlob *keyIn, struct HuksBlob *encKeyOut);Parameters
struct IHuks *self
Pointer to the HUKS HDI struct.
const struct HuksBlob *keyAlias
Pointer to the alias of the key to generate. The value must meet the following requirements:
1. keyAlias != null
2. keyAlias -> data != null
3. keyAlias -> dataLen != 0
const struct HuksParamSet *paramSet
Pointer to the parameters for generating the key.
const struct HuksBlob *keyIn
Pointer to the original key material to be passed in if the key is generated through key agreement or key derivation. This parameter is optional.
struct HuksBlob *encKeyOut
Pointer to the key generated in ciphertext. It holds the paramSet and the key ciphertext in the KeyBlob format.
Constraints
Check parameters in the API. For example, check for null pointers and whether the key algorithm is supported.
keyOut must be in the KeyBlob format.
Return Value
HKS_SUCCESS: The operation is successful.
Other values: The operation fails.
ImportKey
API Description
Imports a key in plaintext.
Prototype
int32_t ImportKey(struct IHuks *self, const struct HuksBlob *keyAlias, const struct HuksBlob *key,
const struct HuksParamSet *paramSet, struct HuksBlob *encKeyOut);Parameters
struct IHuks *self
Pointer to the HUKS HDI struct.
const struct HuksBlob *keyAlias
Pointer to the alias of the key to import. The alias must meet the following requirements:
1. keyAlias != null
2. keyAlias -> data != null
3. keyAlias -> dataLen != 0
const struct HuksBlob *key
Pointer to the plaintext key material to import. For details about the key material format, see Key Material Formats. The value must meet the following requirements:
1. key != null
2. key -> data != null
3. key -> dataLen != 0
const struct HuksParamSet *paramSet
Pointer to the parameters of the key to import.
struct HuksBlob *encKeyOut
Pointer to the imported key in ciphertext. It holds the paramSet and the imported key ciphertext in the KeyBlob format.
Constraints
Check parameters in the API. For example, check for null pointers and whether the key algorithm is supported.
Check that encKeyOut is in the KeyBlob format.
Return Value
HKS_SUCCESS: The operation is successful.
Other values: The operation fails.
ImportWrappedKey
API Description
Imports a wrapped key.
Prototype
int32_t ImportWrappedKey(struct IHuks *self, const struct HuksBlob *wrappingKeyAlias,
const struct HuksBlob *wrappingEncKey, const struct HuksBlob *wrappedKeyData, const struct HuksParamSet *paramSet,
struct HuksBlob *encKeyOut);Parameters
struct IHuks *self
Pointer to the HUKS HDI struct.
const struct HuksBlob *wrappingKeyAlias
Pointer to the alias of the key used to encrypt the key to import (it is not the alias of the key to import). The value must meet the following requirements:
1. wrappingKeyAlias != null
2. wrappingKeyAlias -> data != null
3. wrappingKeyAlias -> dataLen != 0
const struct HuksBlob *wrappingEncKey
Pointer to the key used to encrypt the key to import. The value must meet the following requirements:
1. wrappingEncKey != null
2. wrappingEncKey -> data != null
3. wrappingEncKey -> dataLen != 0
const struct HuksBlob *wrappedKeyData
Pointer to the key material of the key to import. For details abut the key material format, see Importing a Key Securely. The value must meet the following requirements:
1. wrappedKeyData != null
2. wrappedKeyData -> data != null
3. wrappedKeyData -> dataLen != 0
const struct HuksParamSet *paramSet
Pointer to the properties of the key to import.
struct HuksBlob *encKeyOut
Pointer to the imported key material (ciphertext) in the KeyBlob format.
Constraints
Check parameters in the API. For example, check for null pointers and whether the key algorithm is supported.
Check that encKeyOut is in the KeyBlob format.
Return Value
HKS_SUCCESS: The operation is successful.
Other values: The operation fails.
ExportPublicKey
API Description
Exports the public key of a key pair.
Prototype
int32_t ExportPublicKey(struct IHuks *self, const struct HuksBlob *encKey,
const struct HuksParamSet *paramSet, struct HuksBlob *keyOut);Parameters
struct IHuks *self
Pointer to the HUKS HDI struct.
const struct HuksBlob *encKey
Pointer to the key pair material. The value must meet the following requirements:
1. encKey != null
2. encKey -> data != null
3. encKey -> dataLen != 0
const struct HuksParamSet *paramSet
Pointer to the parameters for exporting the public key. By default, this parameter is left blank.
struct HuksBlob *keyOut
Pointer to the public key exported.
Return Value
HKS_SUCCESS: The operation is successful.
Other values: The operation fails.
Init
API Description
Initializes a key session. You need to pass in the key material in ciphertext. The HUKS Core decrypts the ciphertext and generates a key session handle and an authentication token (if required).
Prototype
int32_t Init(struct IHuks *self, const struct HuksBlob *encKey, const struct HuksParamSet *paramSet,
struct HuksBlob *handle, struct HuksBlob *token);Parameters
struct IHuks *self
Pointer to the HUKS HDI struct.
const struct HuksBlob *encKey
Pointer to the ciphertext material of the key to be operated. The value must meet the following requirements:
1. encKey != null
2. encKey -> data != null
3. encKey -> dataLen != 0
const struct HuksParamSet *paramSet
Pointer to the parameters for initializing the key session.
struct HuksBlob *handle
Pointer to the key session handle generated, which identifies the key session in Update(), Finish(), and Abort().
struct HuksBlob *token
Pointer to the authentication token generated for key access control (if required).
Constraints
This API must be used with Update(), Finish(), and Abort() together.
Return Value
HKS_SUCCESS: The operation is successful.
Other values: The operation fails.
Update
API Description
Updates data for the key operation by segment according to the cryptographic algorithm requirements.
Prototype
int32_t Update(struct IHuks *self, const struct HuksBlob *handle, const struct HuksParamSet *paramSet,
const struct HuksBlob *inData, struct HuksBlob *outData);Parameters
struct IHuks *self
Pointer to the HUKS HDI struct.
const struct HuksBlob *handle
Pointer to the handle of the key session.
const struct HuksParamSet *paramSet
Pointer to the parameters for the update operation.
const struct HuksBlob *inData
Pointer to the data to be passed in.
struct HuksBlob *outData
Pointer to the result of the update operation.
Constraints
This API must be used with Init(), Finish(), and Abort() together.
inData must pass in the raw data when signature verification is performed.
Return Value
HKS_SUCCESS: The operation is successful.
Other values: The operation fails.
Finish
API Description
Finishes the key session.
Prototype
int32_t Finish(struct IHuks *self, const struct HuksBlob *handle, const struct HuksParamSet *paramSet,
const struct HuksBlob *inData, struct HuksBlob *outData);Parameters
struct IHuks *self
Pointer to the HUKS HDI struct.
const struct HuksBlob *handle
Pointer to the handle of the key session.
const struct HuksParamSet *paramSet
Pointer to the parameters for the last operation.
const struct HuksBlob *inData
Pointer to the last data to be passed in.
struct HuksBlob *outData
Pointer to the result of the key operation.
Constraints
This API must be used with Init(), Update(), and Abort() together.
In signature verification, inData must pass in the signature data to be verified. The return value indicates whether the signature has passed the verification.
Return Value
HKS_SUCCESS: The operation is successful.
Other values: The operation fails.
Abort
API Description
Aborts the key session. When an error occurs in any of the Init, Update, and Finish operations, call this API to terminate the key session.
Prototype
int32_t Abort(struct IHuks *self, const struct HuksBlob *handle, const struct HuksParamSet *paramSet);Parameters
struct IHuks *self Pointer to the HUKS HDI struct.
const struct HuksBlob *handle Pointer to the handle of the key session.
const struct HuksParamSet *paramSet Pointer to the parameters of the Abort operation.
Constraints
This API must be used with Init(), Update(), and Finish() together.
Return Value
HKS_SUCCESS: The operation is successful.
Other values: The operation fails.
CheckKeyValidity
API Description
Checks key validity.
Prototype
int32_t CheckKeyValidity(struct IHuks *self, const struct HuksParamSet *paramSet,
const struct HuksBlob *encKey);Parameters
struct IHuks *self
Pointer to the HUKS HDI struct.
const struct HuksParamSet *paramSet
Pointer to the parameters for checking the key integrity. By default, this parameter is left empty.
const struct HuksBlob *encKey
Pointer to the key material (ciphertext) to be checked.
Return Value
HKS_SUCCESS: The operation is successful.
Other values: The operation fails.
AttestKey
API Description
Attests a key.
Prototype
int32_t AttestKey(struct IHuks *self, const struct HuksBlob *encKey, const struct HuksParamSet *paramSet,
struct HuksBlob *certChain);Parameters
struct IHuks *self
Pointer to the HUKS HDI struct.
const struct HuksBlob *encKey
Pointer to the key pair material in ciphertext.
const struct HuksParamSet *paramSet
Pointer to the parameters (such as the challenge) for obtaining the key certificate chain.
struct HuksBlob *certChain
Pointer to the certificate chain obtained.
Constraints
certChain must comply with the certificate chain described in Constraints.
Return Value
HKS_SUCCESS: The operation is successful.
Other values: The operation fails.
ExportChipsetPlatformPublicKey
API Description
Exports the public key of a chipset key pair.
Prototype
int32_t ExportChipsetPlatformPublicKey(struct IHuks *self, const struct HuksBlob *salt,
enum HuksChipsetPlatformDecryptScene scene, struct HuksBlob *publicKey);Parameters
struct IHuks *self
Pointer to the HUKS HDI struct.
const struct HuksBlob *salt
Pointer to the factor used to derive the chipset key pair.
enum HuksChipsetPlatformDecryptScene scene
Expected chipset decryption scenario.
struct HuksBlob *publicKey
Pointer to the raw data of ECC P-256 x-axis and y-axis values, each of which are of 32 bytes.
Constraints
The input parameter salt must be of 16 bytes, and the content of the last byte will be ignored and filled by HUKS based on scene. Currently, the chipset key pairs of HUKS are implemented by software. An ECC P-256 key pair is hard-coded, and the salt value is ignored. That is, the derived keys are the same regardless of the salt. In the hardware-based implementation of chipset key pairs, salt is a factor used to derive the key. That is, the key pair derived varies with the salt value.
Return Value
HKS_SUCCESS: The operation is successful.
Other values: The operation fails.
UpgradeKey
API Description
Updates the key file when the key file version is earlier than the latest version.
Prototype
int32_t UpgradeKey(struct IHuks *self, const struct HuksBlob *encOldKey, const struct HuksParamSet *paramSet,
struct HuksBlob *encNewKey);Parameters
struct IHuks *self
Pointer to the HUKS HDI struct.
const struct HuksBlob *encOldKey
Pointer to the key file data to update.
const struct HuksParamSet *paramSet
Pointer to the parameters for updating the key file data.
struct HuksBlob *newKey
Pointer to the new key file data.
Return Value
HKS_SUCCESS: The operation is successful.
Other values: The operation fails.
GenerateRandom
API Description
Generates a random number.
Prototype
int32_t GenerateRandom(struct IHuks *self, const struct HuksParamSet *paramSet, struct HuksBlob *random);Parameters
struct IHuks *self Pointer to the HUKS HDI struct.
const struct HuksParamSet *paramSet Pointer to the parameters of the random number to generate, such as the length.
struct HuksBlob *random Pointer to the random number generated.
Return Value
HKS_SUCCESS: The operation is successful.
Other values: The operation fails.
Sign
API Description
Signs data.
Prototype
int32_t Sign(struct IHuks *self, const struct HuksBlob *encKey, const struct HuksParamSet *paramSet,
const struct HuksBlob *srcData, struct HuksBlob *signature);Parameters
struct IHuks *self
Pointer to the HUKS HDI struct.
const struct HuksBlob *encKey
Pointer to the key pair material (ciphertext) used for signing.
const struct HuksParamSet *paramSet
Pointer to the parameters used for signing, such as the digest mode.
const struct HuksBlob *srcData
Pointer to the data to be signed.
struct HuksBlob *signature
Pointer to the signature generated.
Return Value
HKS_SUCCESS: The operation is successful.
Other values: The operation fails.
Verify
API Description
Verifies a digital signature.
Prototype
int32_t Verify(struct IHuks *self, const struct HuksBlob *encKey, const struct HuksParamSet *paramSet,
const struct HuksBlob *srcData, const struct HuksBlob *signature);Parameters
struct IHuks *self
Pointer to the HUKS HDI struct.
const struct HuksBlob *encKey
Pointer to the key pair material (ciphertext) used for signature verification.
const struct HuksParamSet *paramSet
Pointer to the parameters for signature verification, such as the digest mode.
const struct HuksBlob *srcData
Pointer to the data with the signature to be verified.
const struct HuksBlob *signature
Pointer to the signature to verify.
Return Value
HKS_SUCCESS: The operation is successful.
Other values: The operation fails.
Encrypt
API Description
Encrypts data. Different from the key session APIs that must be used together, this API completes data encryption in a single call.
Prototype
int32_t Encrypt(struct IHuks *self, const struct HuksBlob *encKey, const struct HuksParamSet *paramSet,
const struct HuksBlob *plainText, struct HuksBlob *cipherText);Parameters
struct IHuks *self
Pointer to the HUKS HDI struct.
const struct HuksBlob *encKey
Pointer to the key material (ciphertext) used for encryption.
const struct HuksParamSet *paramSet
Pointer to the key parameters for encryption, such as the key working mode and padding mode.
const struct HuksBlob *plainText
Pointer to the plaintext data to encrypt.
const struct HuksBlob *cipherText
Pointer to the encrypted data (data in ciphertext).
Return Value
HKS_SUCCESS: The operation is successful.
Other values: The operation fails.
Decrypt
API Description
Decrypts data. Different from the key session APIs that must be used together, this API completes data decryption in a single call.
Prototype
int32_t Decrypt(struct IHuks *self, const struct HuksBlob *encKey, const struct HuksParamSet *paramSet,
const struct HuksBlob *cipherText, struct HuksBlob *plainText);Parameters
struct IHuks *self
Pointer to the HUKS HDI struct.
const struct HuksBlob *encKey
Pointer to the key material (ciphertext) used for decryption.
const struct HuksParamSet *paramSet
Pointer to the key parameters for decryption, such as the key working mode and padding mode.
const struct HuksBlob *cipherText
Pointer to the data to decrypt.
const struct HuksBlob *plainText
Pointer to the encrypted data in plaintext.
Return Value
HKS_SUCCESS: The operation is successful.
Other values: The operation fails.
AgreeKey
API Description
Performs key agreement. Different from the key session APIs that must be used together, this API returns an agreed key in a single call.
Prototype
int32_t AgreeKey(struct IHuks *self, const struct HuksParamSet *paramSet,
const struct HuksBlob *encPrivateKey, const struct HuksBlob *peerPublicKey, struct HuksBlob *agreedKey);Parameters
struct IHuks *self
Pointer to the HUKS HDI struct.
const struct HuksParamSet *paramSet
Pointer to the parameters for key agreement, such as the length of the agreed key.
const struct HuksBlob *encPrivateKey
Pointer to the private key material (ciphertext) used for key agreement.
const struct HuksBlob *peerPublicKey
Pointer to the public key (plaintext) used for key agreement.
struct HuksBlob *agreedKey
Pointer to the agreed key in plaintext.
Return Value
HKS_SUCCESS: The operation is successful.
Other values: The operation fails.
DeriveKey
API Description
Derives a key. Different from the key session APIs that must be used together, this API derives a key in a single call.
Prototype
int32_t DeriveKey(struct IHuks *self, const struct HuksParamSet *paramSet, const struct HuksBlob *encKdfKey,
struct HuksBlob *derivedKey);Parameters
struct IHuks *self
Pointer to the HUKS HDI struct.
const struct HuksParamSet *paramSet
Pointer to the parameters for key derivation, such as the length of the derived key.
const struct HuksBlob *encKdfKey
Pointer to the key material (ciphertext) used for deriving a key.
struct HuksBlob *derivedKey
Pointer to the derived key in plaintext.
Return Value
HKS_SUCCESS: The operation is successful.
Other values: The operation fails.
Mac
API Description
Generates a MAC based on the given key.
Prototype
int32_t Mac(struct IHuks *self, const struct HuksBlob *encKey, const struct HuksParamSet *paramSet,
const struct HuksBlob *srcData, struct HuksBlob *mac);Parameters
struct IHuks *self
Pointer to the HUKS HDI struct.
const struct HuksBlob *encKey
Pointer to the key material (ciphertext) used to generate the MAC.
const struct HuksParamSet *paramSet
Pointer to the parameters for generating the MAC.
const struct HuksBlob *srcData
Pointre to the source data for which the MAC is to be generated.
struct HuksBlob *mac
Pointer to the MAC generated.
Return Value
HKS_SUCCESS: The operation is successful.
Other values: The operation fails.
Development Procedure
Directory Structure
The code for HDI adaptation is in the following directory.
//drivers_peripheral/huks
├── BUILD.gn # Build script.
├── hdi_service # Dependency loaded from libhuks_engine_core_standard.z.so (software implementation of the HUKS Core for reference only) by using dlopen().
├── huks_sa_type.h # Defines the data structs used in the HUKS service layer.
├── huks_sa_hdi_struct.h # Defines the function pointer structs in libhuks_engine_core_standard.z.so.
├── huks_hdi_template.h # Defines the conversion between the data structs of the HUKS service layer and the HDI.
├── huks_hdi_service.c # Implementation of the HUKS passthrough HDI APIs.
└── huks_hdi_passthrough_adapter.c # Adaptation of HUKS passthrough HDI APIs to the HUKS Core.
└── test # Test code for the HUKS HDI APIs.
├── BUILD.gn # Build script.
├── fuzztest # Fuzz test.
└── unittest # Unit test.
The code of the HUKS Core software implementation is in the following directory.
//base/security/huks/services/huks_standard/huks_engine
├── BUILD.gn # Build script.
├── core_dependency # HUKS Core dependency.
└── core # Software implementation of the HUKS Core.
├── BUILD.gn # Build script.
├── include
└── src
├── hks_core_interfaces.c # Adaptation of the HDI to the HUKS Core.
└── hks_core_service.c # HUKS Core implementation.
└── ... # Code of other functions.
CAUTION
Root key
The root key is used to encrypt the HUKS service key and is generally derived from the device root key. It is hard-coded in the HUKS Core software implementation. For details, see hks_openssl_get_main_key.c.
Key for generating an HMAC on AuthToken
The key is used to generate an HMAC on AuthToken by the UserIAM for access control. The value is huks_default_user_auth_token_key and hard-coded in the HUKS Core software implementation. For details about the code, see hks_keyblob.c.
- Key for encrypting sensitive fields of AuthToken
The key is used to encrypt sensitive fields of AuthToken in access control. The value is huks_default_user_auth_token_key and hard-coded in the HUKS Core software implementation. For details about the code, see hks_keyblob.c.
Root certificate, device CA, and device certificate
The root certificate, device CA, and device certificate are used for key attestation and preset in the secure storage of the hardware device by the device certificate management module. These certificates are hard-coded in the HUKS Core software implementation. For details about the code, see dcm_certs_and_key.h.
Example
The following uses the adaptation of the key session APIs Init, Update, and Finish in the HUKS Core as an example. The sample code is for reference only and cannot be used directly. For details about the executable code, see HUKS source code.
- Create a handle to identify information about key operations in a session. With this handle, multiple operations on the same key can be performed.
// Initialize the key session.
int32_t HksCoreInit(const struct HuksBlob *key, const struct HuksParamSet *paramSet, struct HuksBlob *handle,
struct HuksBlob *token)
{
HKS_LOG_D("HksCoreInit in Core start");
uint32_t pur = 0;
uint32_t alg = 0;
// Check parameters.
if (key == NULL||paramSet == NULL||handle == NULL||token == NULL) {
HKS_LOG_E("the pointer param entered is invalid");
return HKS_FAILURE;
}
if (handle->size < sizeof(uint64_t)) {
HKS_LOG_E("handle size is too small, size : %u", handle->size);
return HKS_ERROR_INSUFFICIENT_MEMORY;
}
// Decrypt the key file.
struct HuksKeyNode *keyNode = HksCreateKeyNode(key, paramSet);
if (keyNode == NULL||handle == NULL) {
HKS_LOG_E("the pointer param entered is invalid");
return HKS_ERROR_BAD_STATE;
}
// Store information in a session based on the handle. The information stored can be used for the Update() and Finish() operations on the key.
handle->size = sizeof(uint64_t);
(void)memcpy_s(handle->data, handle->size, &(keyNode->handle), handle->size);
// Obtain the algorithm from the parameters.
int32_t ret = GetPurposeAndAlgorithm(paramSet, &pur, &alg);
if (ret != HKS_SUCCESS) {
HksDeleteKeyNode(keyNode->handle);
return ret;
}
// Check key parameters.
ret = HksCoreSecureAccessInitParams(keyNode, paramSet, token);
if (ret != HKS_SUCCESS) {
HKS_LOG_E("init secure access params failed");
HksDeleteKeyNode(keyNode->handle);
return ret;
}
// Obtain the initialization handler from the algorithm library based on the key purpose.
uint32_t i;
uint32_t size = HKS_ARRAY_SIZE(g_hksCoreInitHandler);
for (i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (g_hksCoreInitHandler[i].pur == pur) {
HKS_LOG_E("Core HksCoreInit [pur] = %d, pur = %d", g_hksCoreInitHandler[i].pur, pur);
ret = g_hksCoreInitHandler[i].handler(keyNode, paramSet, alg);
break;
}
}
// Check exception results.
if (ret != HKS_SUCCESS) {
HksDeleteKeyNode(keyNode->handle);
HKS_LOG_E("CoreInit failed, ret : %d", ret);
return ret;
}
if (i == size) {
HksDeleteKeyNode(keyNode->handle);
HKS_LOG_E("don't found purpose, pur : %u", pur);
return HKS_FAILURE;
}
HKS_LOG_D("HksCoreInit in Core end");
return ret;
}
Obtain the context based on the handle, and pass in data by segment to obtain the operation result or append data.
// Update data by segment. int32_t HksCoreUpdate(const struct HuksBlob *handle, const struct HuksParamSet *paramSet, const struct HuksBlob *inData, struct HuksBlob *outData) { HKS_LOG_D("HksCoreUpdate in Core start"); uint32_t pur = 0; uint32_t alg = 0; // Check parameters. if (handle == NULL||paramSet == NULL||inData == NULL) { HKS_LOG_E("the pointer param entered is invalid"); return HKS_FAILURE; } uint64_t sessionId; struct HuksKeyNode *keyNode = NULL; // Obtain the context required for the key session operation based on the handle. int32_t ret = GetParamsForUpdateAndFinish(handle, &sessionId, &keyNode, &pur, &alg); if (ret != HKS_SUCCESS) { HKS_LOG_E("GetParamsForCoreUpdate failed"); return ret; } // Verify key parameters. ret = HksCoreSecureAccessVerifyParams(keyNode, paramSet); if (ret != HKS_SUCCESS) { HksDeleteKeyNode(sessionId); HKS_LOG_E("HksCoreUpdate secure access verify failed"); return ret; } // Call the key handler from the corresponding algorithm library. uint32_t i; uint32_t size = HKS_ARRAY_SIZE(g_hksCoreUpdateHandler); for (i = 0; i < size; i++) { if (g_hksCoreUpdateHandler[i].pur == pur) { struct HuksBlob appendInData = { 0, NULL }; ret = HksCoreAppendAuthInfoBeforeUpdate(keyNode, pur, paramSet, inData, &appendInData); if (ret != HKS_SUCCESS) { HKS_LOG_E("before update: append auth info failed"); break; } ret = g_hksCoreUpdateHandler[i].handler(keyNode, paramSet, appendInData.data == NULL ? inData : &appendInData, outData, alg); if (appendInData.data != NULL) { HKS_FREE_BLOB(appendInData); } break; } } // Check exception results. if (ret != HKS_SUCCESS) { HksDeleteKeyNode(keyNode->handle); HKS_LOG_E("CoreUpdate failed, ret : %d", ret); return ret; } if (i == size) { HksDeleteKeyNode(sessionId); HKS_LOG_E("don't found purpose, pur : %u", pur); return HKS_FAILURE; } return ret; }Finish the key operation to obtain the result, and destroy the handle.
// Finish the key session operation.
int32_t HksCoreFinish(const struct HuksBlob *handle, const struct HuksParamSet *paramSet, const struct HuksBlob *inData,
struct HuksBlob *outData)
{
HKS_LOG_D("HksCoreFinish in Core start");
uint32_t pur = 0;
uint32_t alg = 0;
// Check parameters.
if (handle == NULL||paramSet == NULL||inData == NULL) {
HKS_LOG_E("the pointer param entered is invalid");
return HKS_FAILURE;
}
uint64_t sessionId;
struct HuksKeyNode *keyNode = NULL;
// Obtain the context required for the key session operation based on the handle.
int32_t ret = GetParamsForUpdateAndFinish(handle, &sessionId, &keyNode, &pur, &alg);
if (ret != HKS_SUCCESS) {
HKS_LOG_E("GetParamsForCoreUpdate failed");
return ret;
}
// Verify key parameters.
ret = HksCoreSecureAccessVerifyParams(keyNode, paramSet);
if (ret != HKS_SUCCESS) {
HksDeleteKeyNode(sessionId);
HKS_LOG_E("HksCoreFinish secure access verify failed");
return ret;
}
// Call the key handler from the corresponding algorithm library.
uint32_t i;
uint32_t size = HKS_ARRAY_SIZE(g_hksCoreFinishHandler);
for (i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (g_hksCoreFinishHandler[i].pur == pur) {
uint32_t outDataBufferSize = (outData == NULL) ? 0 : outData->size;
struct HuksBlob appendInData = { 0, NULL };
ret = HksCoreAppendAuthInfoBeforeFinish(keyNode, pur, paramSet, inData, &appendInData);
if (ret != HKS_SUCCESS) {
HKS_LOG_E("before finish: append auth info failed");
break;
}
ret = g_hksCoreFinishHandler[i].handler(keyNode, paramSet,
appendInData.data == NULL ? inData : &appendInData, outData, alg);
if (appendInData.data != NULL) {
HKS_FREE_BLOB(appendInData);
}
if (ret != HKS_SUCCESS) {
break;
}
// Append the end label of the key operation.
ret = HksCoreAppendAuthInfoAfterFinish(keyNode, pur, paramSet, outDataBufferSize, outData);
break;
}
}
if (i == size) {
HKS_LOG_E("don't found purpose, pur : %d", pur);
ret = HKS_FAILURE;
}
// Delete the session.
HksDeleteKeyNode(sessionId);
HKS_LOG_D("HksCoreFinish in Core end");
return ret;
}
Debugging
Use HUKS JS APIs to develop a JavaScript application to verify HUKS capabilities.
The JS APIs corresponding to HDI APIs are provided in Available APIs. You can use the JS APIs to verify the capabilities of the corresponding HDI APIs or perform complete key operations to verify the capabilities of the APIs.
The following JS test code is for reference only. If the entire process goes properly, the HDI APIs are functioning. For more key operation types and samples, see huks-guidelines.md.
Generating an AES Key and Encrypting Data
- Import the HUKS module.
import huks from '@ohos.security.huks'
- Use generateKey() to generate a key.
import { BusinessError } from '@ohos.base';
let aesKeyAlias = 'test_aesKeyAlias';
let handle = 0;
let IV = '001122334455';
class HuksProperties {
tag: huks.HuksTag = huks.HuksTag.HUKS_TAG_ALGORITHM;
value: huks.HuksKeyAlg|huks.HuksKeySize|huks.HuksKeyPurpose = huks.HuksKeyAlg.HUKS_ALG_ECC;
}
class HuksProperties1 {
tag: huks.HuksTag = huks.HuksTag.HUKS_TAG_ALGORITHM;
value: huks.HuksKeyAlg|huks.HuksKeySize|huks.HuksKeyPurpose|huks.HuksKeyPadding|huks.HuksCipherMode|Uint8Array = huks.HuksKeyAlg.HUKS_ALG_ECC;
}
function GetAesGenerateProperties() {
let properties: HuksProperties[] = [
{
tag: huks.HuksTag.HUKS_TAG_ALGORITHM,
value: huks.HuksKeyAlg.HUKS_ALG_AES
},
{
tag: huks.HuksTag.HUKS_TAG_KEY_SIZE,
value: huks.HuksKeySize.HUKS_AES_KEY_SIZE_128
},
{
tag: huks.HuksTag.HUKS_TAG_PURPOSE,
value: huks.HuksKeyPurpose.HUKS_KEY_PURPOSE_ENCRYPT|
huks.HuksKeyPurpose.HUKS_KEY_PURPOSE_DECRYPT
}
];
return properties;
}
async function GenerateAesKey() {
let genProperties = GetAesGenerateProperties();
let options: huks.HuksOptions = {
properties: genProperties
}
await huks.generateKeyItem(aesKeyAlias, options).then((data) => {
console.log("generateKeyItem success");
}).catch((error: BusinessError) => {
console.log("generateKeyItem failed");
})
}
- Use huks.initSession and huks.finishSession to encrypt data.
let plainText = '123456';
function StringToUint8Array(str: string) {
let arr: number[] = [];
for (let i = 0, j = str.length; i < j; ++i) {
arr.push(str.charCodeAt(i));
}
return new Uint8Array(arr);
}
function GetAesEncryptProperties() {
let properties: HuksProperties1[] = [
{
tag: huks.HuksTag.HUKS_TAG_ALGORITHM,
value: huks.HuksKeyAlg.HUKS_ALG_AES
},
{
tag: huks.HuksTag.HUKS_TAG_KEY_SIZE,
value: huks.HuksKeySize.HUKS_AES_KEY_SIZE_128
},
{
tag: huks.HuksTag.HUKS_TAG_PURPOSE,
value: huks.HuksKeyPurpose.HUKS_KEY_PURPOSE_ENCRYPT
},
{
tag: huks.HuksTag.HUKS_TAG_PADDING,
value: huks.HuksKeyPadding.HUKS_PADDING_PKCS7
},
{
tag: huks.HuksTag.HUKS_TAG_BLOCK_MODE,
value: huks.HuksCipherMode.HUKS_MODE_CBC
},
{
tag: huks.HuksTag.HUKS_TAG_IV,
value: StringToUint8Array(IV)
}
]
return properties;
}
async function EncryptData() {
let encryptProperties = GetAesEncryptProperties();
let options: huks.HuksOptions = {
properties: encryptProperties,
inData: StringToUint8Array(plainText)
}
await huks.initSession(aesKeyAlias, options).then((data) => {
handle = data.handle;
}).catch((error: BusinessError) => {
console.log("initSession failed");
})
await huks.finishSession(handle, options).then((data) => {
console.log("finishSession success");
}).catch((error: BusinessError) => {
console.log("finishSession failed");
})
}
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙AI Framework Development Guide
harmony 鸿蒙Neural Network Runtime Device Access
harmony 鸿蒙Application Privilege Configuration
harmony 鸿蒙Setting Up a Development Environment
harmony 鸿蒙Development Guidelines
harmony 鸿蒙Application Framework Overview
harmony 鸿蒙ArkCompiler Development
harmony 鸿蒙Window Title Bar Customization Development (ArkTS)
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签: