harmony 鸿蒙Starting UIAbility in the Same Application
Starting UIAbility in the Same Application
UIAbility is the minimum unit that can be scheduled by the system. Redirection between functional modules in a device involves starting of specific UIAbility components, which belong to the same or a different application (for example, starting the UIAbility of a third-party payment application).
This topic describes how to start the UIAbility component that belongs to the same application. For details about component redirection between applications, see Application Redirection. For details about cross-device application component interaction, see Inter-Device Application Component Interaction (Hopping).
- Starting UIAbility in the Same Application
- Starting UIAbility in the Same Application and Obtaining the Return Result
- Starting a Specified Page of UIAbility
- Starting UIAbility with Window Mode Specified (for System Applications Only)
- Using Call to Implement UIAbility Interaction (for System Applications Only)
Starting UIAbility in the Same Application
This scenario is possible when an application contains multiple UIAbility components. For example, in a payment application, you may need to start the payment UIAbility from the entry UIAbility.
Assume that your application has two UIAbility components: EntryAbility and FuncAbility, either in the same module or different modules. To start FuncAbility from EntryAbility, proceed as follows:
In EntryAbility, call startAbility() and pass the want parameter to start the UIAbility instance. In the want parameter, bundleName indicates the bundle name of the application to start; abilityName indicates the name of the UIAbility to start; moduleName is required only when the target UIAbility belongs to a different module from EntryAbility; parameters is used to carry custom information. For details about how to obtain the context in the example, see Obtaining the Context of UIAbility.
import { common, Want } from '@kit.AbilityKit'; import { hilog } from '@kit.PerformanceAnalysisKit'; import { BusinessError } from '@kit.BasicServicesKit'; const TAG: string = '[Page_UIAbilityComponentsInteractive]'; const DOMAIN_NUMBER: number = 0xFF00; @Entry @Component struct Page_UIAbilityComponentsInteractive { private context = this.getUIContext().getHostContext() as common.UIAbilityContext; build() { Column() { //... List({ initialIndex: 0 }) { ListItem() { Row() { //... } .onClick(() => { // Context is a member of the ability object and is required for invoking inside a non-ability object. // Pass in the Context object. let wantInfo: Want = { deviceId: '', // An empty deviceId indicates the local device. bundleName: 'com.samples.stagemodelabilitydevelop', moduleName: 'entry', // moduleName is optional. abilityName: 'FuncAbilityA', parameters: { // Custom information. info: 'From Page_UIAbilityComponentsInteractive of EntryAbility', }, }; // context is the UIAbilityContext of the initiator UIAbility. this.context.startAbility(wantInfo).then(() => { hilog.info(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, 'startAbility success.'); }).catch((error: BusinessError) => { hilog.error(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, 'startAbility failed.'); }); }) } //... } //... } //... } }In FuncAbility, use onCreate() or onNewWant() to receive the parameters passed in by EntryAbility.
import { AbilityConstant, UIAbility, Want } from '@kit.AbilityKit'; export default class FuncAbilityA extends UIAbility { onCreate(want: Want, launchParam: AbilityConstant.LaunchParam): void { // Receive the parameters passed by the initiator UIAbility. let funcAbilityWant = want; let info = funcAbilityWant?.parameters?.info; } //... }NOTE
In FuncAbility started, you can obtain the PID and bundle name of the UIAbility through parameters in the passed want parameter.
To stop the UIAbility instance after the FuncAbility service is not needed, call terminateSelf() in FuncAbility.
import { common } from '@kit.AbilityKit'; import { hilog } from '@kit.PerformanceAnalysisKit'; const TAG: string = '[Page_FromStageModel]'; const DOMAIN_NUMBER: number = 0xFF00; @Entry @Component struct Page_FromStageModel { build() { Column() { //... Button('FuncAbilityB') .onClick(() => { let context = this.getUIContext().getHostContext() as common.UIAbilityContext; // UIAbilityContext // context is the UIAbilityContext of the UIAbility instance to stop. context.terminateSelf((err) => { if (err.code) { hilog.error(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, `Failed to terminate self. Code is ${err.code}, message is ${err.message}`); return; } }); }) } //... } }NOTE
When terminateSelf() is called to stop the UIAbility instance, the snapshot of the instance is retained by default. That is, the mission corresponding to the instance is still displayed in Recents. If you do not want to retain the snapshot, set removeMissionAfterTerminate under the abilities tag to true in the module.json5 file of the corresponding UIAbility.
To stop all UIAbility instances of the application, call killAllProcesses() of ApplicationContext.
Starting UIAbility in the Same Application and Obtaining the Return Result
When starting FuncAbility from EntryAbility, you may want the result to be returned after the FuncAbility service is finished. For example, after the sign-in operation is finished in the sign-in UIAbility of your application, you want the sign-in result to be returned to the entry UIAbility.
In EntryAbility, call startAbilityForResult() to start FuncAbility. Use data in the asynchronous callback to receive information returned after FuncAbility stops itself. For details about how to obtain the context in the example, see Obtaining the Context of UIAbility.
import { common, Want } from '@kit.AbilityKit'; import { hilog } from '@kit.PerformanceAnalysisKit'; import { BusinessError } from '@kit.BasicServicesKit'; const TAG: string = '[Page_UIAbilityComponentsInteractive]'; const DOMAIN_NUMBER: number = 0xFF00; @Entry @Component struct Page_UIAbilityComponentsInteractive { build() { Column() { //... List({ initialIndex: 0 }) { ListItem() { Row() { //... } .onClick(() => { let context = this.getUIContext().getHostContext() as common.UIAbilityContext; // UIAbilityContext const RESULT_CODE: number = 1001; let want: Want = { deviceId: '', // An empty deviceId indicates the local device. bundleName: 'com.samples.stagemodelabilitydevelop', moduleName: 'entry', // moduleName is optional. abilityName: 'FuncAbilityA', parameters: { // Custom information. info: 'From UIAbilityComponentsInteractive of EntryAbility', } }; context.startAbilityForResult(want).then((data) => { if (data?.resultCode === RESULT_CODE) { // Parse the information returned by the target UIAbility. let info = data.want?.parameters?.info; hilog.info(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, JSON.stringify(info) ?? ''); if (info !== null) { this.getUIContext().getPromptAction().showToast({ message: JSON.stringify(info) }); } } hilog.info(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, JSON.stringify(data.resultCode) ?? ''); }).catch((err: BusinessError) => { hilog.error(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, `Failed to start ability for result. Code is ${err.code}, message is ${err.message}`); }); }) } //... } //... } //... } }Call terminateSelfWithResult() to stop FuncAbility. Use the input parameter abilityResult to carry the information that FuncAbility needs to return to EntryAbility.
import { common } from '@kit.AbilityKit'; import { hilog } from '@kit.PerformanceAnalysisKit'; const TAG: string = '[Page_FuncAbilityA]'; const DOMAIN_NUMBER: number = 0xFF00; @Entry @Component struct Page_FuncAbilityA { build() { Column() { //... List({ initialIndex: 0 }) { ListItem() { Row() { //... } .onClick(() => { let context = this.getUIContext().getHostContext() as common.UIAbilityContext; // UIAbilityContext const RESULT_CODE: number = 1001; let abilityResult: common.AbilityResult = { resultCode: RESULT_CODE, want: { bundleName: 'com.samples.stagemodelabilitydevelop', moduleName: 'entry', // moduleName is optional. abilityName: 'FuncAbilityB', parameters: { info: 'From the Index page of FuncAbility', }, }, }; context.terminateSelfWithResult(abilityResult, (err) => { if (err.code) { hilog.error(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, `Failed to terminate self with result. Code is ${err.code}, message is ${err.message}`); return; } }); }) } //... } //... } //... } }After FuncAbility stops itself, EntryAbility uses startAbilityForResult() to receive the information returned by FuncAbility. The value of RESULT_CODE must be the same as that specified in the preceding step.
import { common, Want } from '@kit.AbilityKit'; import { hilog } from '@kit.PerformanceAnalysisKit'; import { BusinessError } from '@kit.BasicServicesKit'; const TAG: string = '[Page_UIAbilityComponentsInteractive]'; const DOMAIN_NUMBER: number = 0xFF00; @Entry @Component struct Page_UIAbilityComponentsInteractive { build() { Column() { //... List({ initialIndex: 0 }) { ListItem() { Row() { //... } .onClick(() => { let context = this.getUIContext().getHostContext() as common.UIAbilityContext; // UIAbilityContext const RESULT_CODE: number = 1001; let want: Want = { deviceId: '', // An empty deviceId indicates the local device. bundleName: 'com.samples.stagemodelabilitydevelop', moduleName: 'entry', // moduleName is optional. abilityName: 'FuncAbilityA', parameters: { // Custom information. info: 'From UIAbilityComponentsInteractive of EntryAbility', } }; context.startAbilityForResult(want).then((data) => { if (data?.resultCode === RESULT_CODE) { // Parse the information returned by the target UIAbility. let info = data.want?.parameters?.info; hilog.info(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, JSON.stringify(info) ?? ''); if (info !== null) { this.getUIContext().getPromptAction().showToast({ message: JSON.stringify(info) }); } } hilog.info(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, JSON.stringify(data.resultCode) ?? ''); }).catch((err: BusinessError) => { hilog.error(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, `Failed to start ability for result. Code is ${err.code}, message is ${err.message}`); }); }) } //... } //... } //... } }
Starting a Specified Page of UIAbility
Overview
A UIAbility component can have multiple pages that each display in specific scenarios.
A UIAbility component can be started in two modes:
- Cold start: The UIAbility instance is totally closed before being started. This requires that the code and resources of the UIAbility instance be completely loaded and initialized.
- Hot start: The UIAbility instance has been started, running in the foreground, and then switched to the background before being started again. In this case, the status of the UIAbility instance can be quickly restored.
This section describes how to start a specified page in both modes: cold start and hot start. Before starting a specified page, you will learn how to specify a startup page on the initiator UIAbility.
Specifying a Startup Page
When the initiator UIAbility starts another UIAbility, it usually needs to redirect to a specified page of the target UIAbility. For example, with FuncAbility, which contains two pages, starting FuncAbility means to redirect to either of the pages: Index (corresponding to the home page) and Second (corresponding to feature A page). You can configure the specified page URL in the want parameter by adding a custom parameter to parameters in want. For details about how to obtain the context in the example, see Obtaining the Context of UIAbility.
import { common, Want } from '@kit.AbilityKit';
import { hilog } from '@kit.PerformanceAnalysisKit';
import { BusinessError } from '@kit.BasicServicesKit';
const TAG: string = '[Page_UIAbilityComponentsInteractive]';
const DOMAIN_NUMBER: number = 0xFF00;
@Entry
@Component
struct Page_UIAbilityComponentsInteractive {
build() {
Column() {
//...
List({ initialIndex: 0 }) {
ListItem() {
Row() {
//...
}
.onClick(() => {
let context = this.getUIContext().getHostContext() as common.UIAbilityContext; // UIAbilityContext
let want: Want = {
deviceId: '', // An empty deviceId indicates the local device.
bundleName: 'com.samples.stagemodelabilityinteraction',
moduleName: 'entry', // moduleName is optional.
abilityName: 'FuncAbility',
parameters: { // Custom parameter used to pass the page information.
router: 'funcA'
}
};
// context is the UIAbilityContext of the initiator UIAbility.
context.startAbility(want).then(() => {
hilog.info(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, 'Succeeded in starting ability.');
}).catch((err: BusinessError) => {
hilog.error(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, `Failed to start ability. Code is ${err.code}, message is ${err.message}`);
});
})
}
//...
}
//...
}
//...
}
}
Cold Starting UIAbility
In cold start mode, obtain the parameters from the initiator UIAbility through the onCreate() callback of the target UIAbility. Then, in the onWindowStageCreate() callback of the target UIAbility, parse the want parameter passed by the EntryAbility to obtain the URL of the page to be loaded, and pass the URL to the windowStage.loadContent() method.
import { AbilityConstant, Want, UIAbility } from '@kit.AbilityKit';
import { hilog } from '@kit.PerformanceAnalysisKit';
import { window, UIContext } from '@kit.ArkUI';
const DOMAIN_NUMBER: number = 0xFF00;
const TAG: string = '[EntryAbility]';
export default class EntryAbility extends UIAbility {
funcAbilityWant: Want|undefined = undefined;
uiContext: UIContext|undefined = undefined;
onCreate(want: Want, launchParam: AbilityConstant.LaunchParam): void {
// Receive the parameters passed by the initiator UIAbility.
this.funcAbilityWant = want;
}
onWindowStageCreate(windowStage: window.WindowStage): void {
// Main window is created. Set a main page for this UIAbility.
hilog.info(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, '%{public}s', 'Ability onWindowStageCreate');
// Main window is created. Set a main page for this UIAbility.
let url = 'pages/Index';
if (this.funcAbilityWant?.parameters?.router && this.funcAbilityWant.parameters.router === 'funcA') {
url = 'pages/Page_ColdStartUp';
}
windowStage.loadContent(url, (err, data) => {
// ...
});
}
}
Hot Starting UIAbility
If the target UIAbility has been started, the initialization logic is not executed again. Instead, the onNewWant() lifecycle callback is directly triggered. To implement redirection, parse the required parameters in onNewWant().
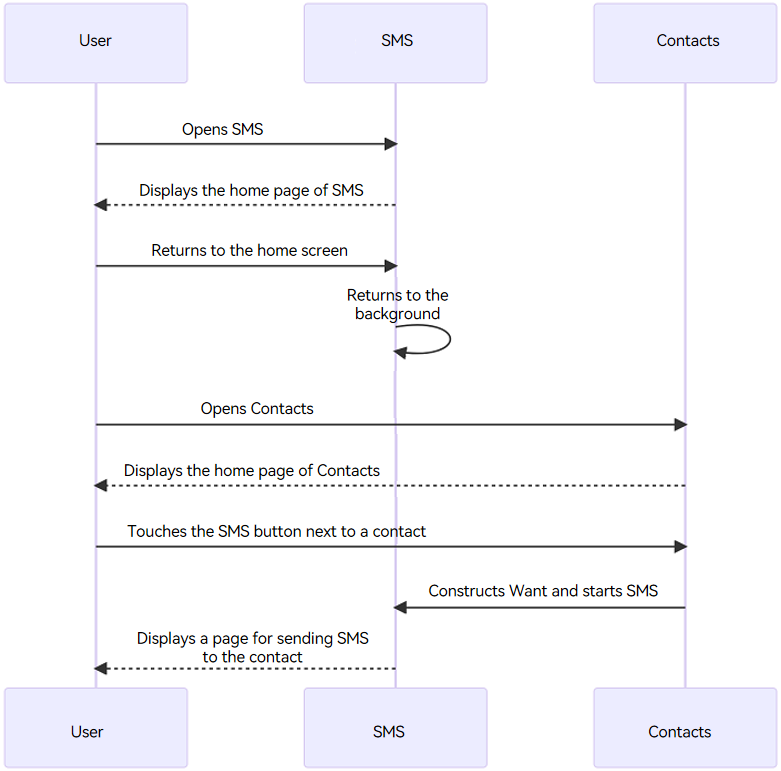
An example scenario is as follows:
- A user opens the SMS application. The UIAbility instance of the SMS application is started, and the home page of the application is displayed.
- The user returns to the home screen, and the SMS application switches to the background.
- The user opens the Contacts application and finds a contact.
- The user touches the SMS button next to the contact. The UIAbility instance of the SMS application is restarted.
- Since the UIAbility instance of the SMS application has been started, the onNewWant() callback of the UIAbility is triggered, and the initialization logic such as onCreate() and onWindowStageCreate() is skipped.
Figure 1 Hot starting the target UIAbility
The development procedure is as follows:
When the UIAbility instance of the SMS application is cold started, call getUIContext() in the onWindowStageCreate() lifecycle callback to obtain the UIContext.
import { hilog } from '@kit.PerformanceAnalysisKit'; import { Want, UIAbility } from '@kit.AbilityKit'; import { window, UIContext } from '@kit.ArkUI'; const DOMAIN_NUMBER: number = 0xFF00; const TAG: string = '[EntryAbility]'; export default class EntryAbility extends UIAbility { funcAbilityWant: Want|undefined = undefined; uiContext: UIContext|undefined = undefined; // ... onWindowStageCreate(windowStage: window.WindowStage): void { // Main window is created. Set a main page for this UIAbility. hilog.info(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, '%{public}s', 'Ability onWindowStageCreate'); let url = 'pages/Index'; if (this.funcAbilityWant?.parameters?.router && this.funcAbilityWant.parameters.router === 'funcA') { url = 'pages/Page_ColdStartUp'; } windowStage.loadContent(url, (err, data) => { if (err.code) { return; } let windowClass: window.Window; windowStage.getMainWindow((err, data) => { if (err.code) { hilog.error(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, `Failed to obtain the main window. Code is ${err.code}, message is ${err.message}`); return; } windowClass = data; this.uiContext = windowClass.getUIContext(); }); hilog.info(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, 'Succeeded in loading the content. Data: %{public}s', JSON.stringify(data) ?? ''); }); } }Parse the want parameter passed in the onNewWant() callback of the UIAbility of the SMS application, call getRouter() in the UIContext class to obtain a Router instance, and specify the target page. When the UIAbility instance of the SMS application is started again, the specified page of the UIAbility instance of the SMS application is displayed.
import { AbilityConstant, Want, UIAbility } from '@kit.AbilityKit'; import { hilog } from '@kit.PerformanceAnalysisKit'; import type { Router, UIContext } from '@kit.ArkUI'; import type { BusinessError } from '@kit.BasicServicesKit'; const DOMAIN_NUMBER: number = 0xFF00; const TAG: string = '[EntryAbility]'; export default class EntryAbility extends UIAbility { funcAbilityWant: Want|undefined = undefined; uiContext: UIContext|undefined = undefined; // ... onNewWant(want: Want, launchParam: AbilityConstant.LaunchParam): void { if (want?.parameters?.router && want.parameters.router === 'funcA') { let funcAUrl = 'pages/Page_HotStartUp'; if (this.uiContext) { let router: Router = this.uiContext.getRouter(); router.pushUrl({ url: funcAUrl }).catch((err: BusinessError) => { hilog.error(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, `Failed to push url. Code is ${err.code}, message is ${err.message}`); }); } } } }
NOTE
When the launch type of the target UIAbility is set to multiton, a new instance is created each time the target UIAbility is started. In this case, the onNewWant() callback will not be invoked.
Starting UIAbility with Window Mode Specified (for System Applications Only)
By specifying the window mode when starting the UIAbility of an application, you can have the application displayed in the specified window mode, which can be full-screen, floating window, or split-screen.
In full-screen mode, an application occupies the entire screen after being started. Users cannot view other windows or applications. This mode is suitable for an application that requires users to focus on a specific task or UI.
In floating window mode, an application is displayed on the screen as a floating window after being started. Users can easily switch to other windows or applications. This mode is suitable for an application that allows users to process multiple tasks at the same time.
In split-screen mode, two applications occupy the entire screen, side by side, horizontally or vertically. This mode helps users improve multi-task processing efficiency.
The window mode is specified by the windowMode field in the StartOptions parameter of startAbility().
NOTE
- If the windowMode field is not specified, the UIAbility is started in the default window mode.
- To ensure that the application can be displayed in the required window mode, check the supportWindowMode field under abilities in the module.json5 file of the UIAbility and make sure the specified window mode is supported.
The following describes how to start the FuncAbility from the EntryAbility page and display it in floating window mode.
- Add the StartOptions parameter in startAbility().
- Set the windowMode field in the StartOptions parameter to WINDOW_MODE_FLOATING. This setting applies only to a system application.
- In the case of a third-party application, set the displayId field instead.
For details about how to obtain the context in the example, see Obtaining the Context of UIAbility.
import { AbilityConstant, common, Want, StartOptions } from '@kit.AbilityKit';
import { hilog } from '@kit.PerformanceAnalysisKit';
import { BusinessError } from '@kit.BasicServicesKit';
const TAG: string = '[Page_UIAbilityComponentsInteractive]';
const DOMAIN_NUMBER: number = 0xFF00;
@Entry
@Component
struct Page_UIAbilityComponentsInteractive {
build() {
Column() {
//...
List({ initialIndex: 0 }) {
ListItem() {
Row() {
//...
}
.onClick(() => {
let context = this.getUIContext().getHostContext() as common.UIAbilityContext; // UIAbilityContext
let want: Want = {
deviceId: '', // An empty deviceId indicates the local device.
bundleName: 'com.samples.stagemodelabilitydevelop',
moduleName: 'entry', // moduleName is optional.
abilityName: 'FuncAbilityB',
parameters: {
// Custom information.
info: 'From the Index page of EntryAbility',
}
};
let options: StartOptions = {
windowMode: AbilityConstant.WindowMode.WINDOW_MODE_FLOATING
};
// context is the UIAbilityContext of the initiator UIAbility.
context.startAbility(want, options).then(() => {
hilog.info(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, 'Succeeded in starting ability.');
}).catch((err: BusinessError) => {
hilog.error(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, `Failed to start ability. Code is ${err.code}, message is ${err.message}`);
});
})
}
//...
}
//...
}
//...
}
}
The display effect is shown below.
Using Call to Implement UIAbility Interaction (for System Applications Only)
Call is an extension of the UIAbility capability. It enables the UIAbility to be invoked by and communicate with external systems. The UIAbility invoked can be either started in the foreground or created and run in the background. You can use the call to implement data sharing between two UIAbility instances (CallerAbility and CalleeAbility) through IPC.
The core API used for the call is startAbilityByCall(), which differs from startAbility() in the following ways:
startAbilityByCall() supports UIAbility launch in the foreground and background, whereas startAbility() supports UIAbility launch in the foreground only.
The CallerAbility can use the Caller object returned by startAbilityByCall() to communicate with the CalleeAbility, but startAbility() does not provide the communication capability.
Call is usually used in the following scenarios:
Communicating with the CalleeAbility
Starting the CalleeAbility in the background
Table 1 Terms used in the call
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| CallerAbility | UIAbility that triggers the call. |
| CalleeAbility | UIAbility invoked by the call. |
| Caller | Object returned by startAbilityByCall and used by the CallerAbility to communicate with the CalleeAbility. |
| Callee | Object held by the CalleeAbility to communicate with the CallerAbility. |
The following figure shows the call process.
Figure 1 Call process

The CallerAbility uses startAbilityByCall() to obtain a Caller object and uses call of the Caller object to send data to the CalleeAbility.
The CalleeAbility, which holds a Callee object, uses on of the Callee object to register a callback. This callback is invoked when the CalleeAbility receives data from the CallerAbility.
NOTE
Currently, only system applications can use the call.
The launch type of the CalleeAbility must be singleton.
Both local (intra-device) and cross-device calls are supported. The following describes how to initiate a local call. For details about how to initiate a cross-device call, see Using Cross-Device Call.
Available APIs
The following table describes the main APIs used for the call. For details, see AbilityContext.
Table 2 Call APIs
| API | Description |
|---|---|
| startAbilityByCall(want: Want): Promise<Caller> | Starts a UIAbility in the foreground (through the want configuration) or background (default) and obtains the caller object for communication with the UIAbility. For details, see AbilityContext or ServiceExtensionContext. |
| on(method: string, callback: CalleeCallBack): void | Callback invoked when the CalleeAbility registers a method. |
| off(method: string): void | Callback invoked when the CalleeAbility deregisters a method. |
| call(method: string, data: rpc.Parcelable): Promise<void> | Sends agreed parcelable data to the CalleeAbility. |
| callWithResult(method: string, data: rpc.Parcelable): Promise<rpc.MessageSequence> | Sends agreed parcelable data to the CalleeAbility and obtains the agreed parcelable data returned by the CalleeAbility. |
| release(): void | Releases the caller object. |
| on(type: “release”, callback: OnReleaseCallback): void | Callback invoked when the caller object is released. |
The implementation of using the call for UIAbility interaction involves two parts:
Creating a CalleeAbility
For the CalleeAbility, implement the callback to receive data and the methods to marshal and unmarshal data. When data needs to be received, use on to register a listener. When data does not need to be received, use off to deregister the listener.
- Configure the launch type of the UIAbility.
For example, set the launch type of the CalleeAbility to singleton. For details, see UIAbility Component Launch Type.
- Import the UIAbility module.
import { UIAbility } from '@kit.AbilityKit';
- Define the agreed parcelable data.
The data formats sent and received by the CallerAbility and CalleeAbility must be consistent. In the following example, the data formats are number and string.
```ts
import { rpc } from '@kit.IPCKit';
class MyParcelable {
num: number = 0;
str: string = '';
constructor(num: number, string: string) {
this.num = num;
this.str = string;
}
mySequenceable(num: number, string: string): void {
this.num = num;
this.str = string;
}
marshalling(messageSequence: rpc.MessageSequence): boolean {
messageSequence.writeInt(this.num);
messageSequence.writeString(this.str);
return true;
}
unmarshalling(messageSequence: rpc.MessageSequence): boolean {
this.num = messageSequence.readInt();
this.str = messageSequence.readString();
return true;
}
}
```
- Implement Callee.on and Callee.off.
The time to register a listener for the CalleeAbility depends on your application. The data sent and received before the listener is registered and that after the listener is deregistered are not processed. In the following example, the ‘MSG_SEND_METHOD’ listener is registered in onCreate of the UIAbility and deregistered in onDestroy. After receiving parcelable data, the application processes the data and returns the data result. You need to implement processing based on service requirements. The sample code is as follows:
```ts
import { AbilityConstant, UIAbility, Want, Caller } from '@kit.AbilityKit';
import { hilog } from '@kit.PerformanceAnalysisKit';
import { rpc } from '@kit.IPCKit';
const MSG_SEND_METHOD: string = 'CallSendMsg';
const DOMAIN_NUMBER: number = 0xFF00;
const TAG: string = '[CalleeAbility]';
class MyParcelable {
num: number = 0;
str: string = '';
constructor(num: number, string: string) {
this.num = num;
this.str = string;
}
mySequenceable(num: number, string: string): void {
this.num = num;
this.str = string;
}
marshalling(messageSequence: rpc.MessageSequence): boolean {
messageSequence.writeInt(this.num);
messageSequence.writeString(this.str);
return true;
}
unmarshalling(messageSequence: rpc.MessageSequence): boolean {
this.num = messageSequence.readInt();
this.str = messageSequence.readString();
return true;
}
}
function sendMsgCallback(data: rpc.MessageSequence): rpc.Parcelable {
hilog.info(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, '%{public}s', 'CalleeSortFunc called');
// Obtain the parcelable data sent by the CallerAbility.
let receivedData: MyParcelable = new MyParcelable(0, '');
data.readParcelable(receivedData);
hilog.info(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, '%{public}s', `receiveData[${receivedData.num}, ${receivedData.str}]`);
let num: number = receivedData.num;
// Process the data.
// Return the parcelable data result to the CallerAbility.
return new MyParcelable(num + 1, `send ${receivedData.str} succeed`) as rpc.Parcelable;
}
export default class CalleeAbility extends UIAbility {
caller: Caller|undefined;
onCreate(want: Want, launchParam: AbilityConstant.LaunchParam): void {
try {
this.callee.on(MSG_SEND_METHOD, sendMsgCallback);
} catch (error) {
hilog.error(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, '%{public}s', `Failed to register. Error is ${error}`);
}
}
releaseCall(): void {
try {
if (this.caller) {
this.caller.release();
this.caller = undefined;
}
hilog.info(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, '%{public}s', 'caller release succeed');
} catch (error) {
hilog.info(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, '%{public}s', `caller release failed with ${error}`);
}
}
onDestroy(): void {
try {
this.callee.off(MSG_SEND_METHOD);
hilog.info(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, '%{public}s', 'Callee OnDestroy');
this.releaseCall();
} catch (error) {
hilog.error(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, '%{public}s', `Failed to register. Error is ${error}`);
}
}
}
```
Accessing the CalleeAbility
The UIAbilityContext attribute implements startAbilityByCall to obtain the Caller object for communication. The following example uses this.context to obtain the UIAbilityContext, uses startAbilityByCall to start the CalleeAbility, obtain the Caller object, and register the onRelease listener of the CallerAbility. You need to implement processing based on service requirements.
```ts
import { common, Want, Caller } from '@kit.AbilityKit';
import { hilog } from '@kit.PerformanceAnalysisKit';
import { BusinessError } from '@kit.BasicServicesKit';
const TAG: string = '[Page_UIAbilityComponentsInteractive]';
const DOMAIN_NUMBER: number = 0xFF00;
@Entry
@Component
struct Page_UIAbilityComponentsInteractive {
caller: Caller|undefined = undefined;
// Register the onRelease() listener of the CallerAbility.
private regOnRelease(caller: Caller): void {
hilog.info(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, `caller is ${caller}`);
try {
caller.on('release', (msg: string) => {
hilog.info(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, `caller onRelease is called ${msg}`);
})
hilog.info(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, 'succeeded in registering on release.');
} catch (err) {
let code = (err as BusinessError).code;
let message = (err as BusinessError).message;
hilog.error(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, `Failed to caller register on release. Code is ${code}, message is ${message}`);
}
};
build() {
Column() {
// ...
List({ initialIndex: 0 }) {
// ...
ListItem() {
Row() {
// ...
}
.onClick(() => {
let context = this.getUIContext().getHostContext() as common.UIAbilityContext; // UIAbilityContext
let want: Want = {
bundleName: 'com.samples.stagemodelabilityinteraction',
abilityName: 'CalleeAbility',
parameters: {
// Custom information.
info: 'CallSendMsg'
}
};
context.startAbilityByCall(want).then((caller: Caller) => {
hilog.info(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, `Succeeded in starting ability.Code is ${caller}`);
if (caller === undefined) {
hilog.info(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, 'get caller failed');
return;
}
else {
hilog.info(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, 'get caller success');
this.regOnRelease(caller);
this.getUIContext().getPromptAction().showToast({
message: 'CallerSuccess'
});
try {
caller.release();
} catch (releaseErr) {
console.log('Caller.release catch error, error.code: ' + JSON.stringify(releaseErr.code) +
' error.message: ' + JSON.stringify(releaseErr.message));
}
}
}).catch((err: BusinessError) => {
hilog.error(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, `Failed to start ability. Code is ${err.code}, message is ${err.message}`);
});
})
}
// ...
}
// ...
}
// ...
}
}
```
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙Obtaining Reasons for Abnormal Application Exits
harmony 鸿蒙UIAbility Backup and Restore
harmony 鸿蒙Using Explicit Want to Start an Application Component
harmony 鸿蒙Introduction to Ability Kit
harmony 鸿蒙AbilityStage Component Container
harmony 鸿蒙Accessing a DataAbility
harmony 鸿蒙Accessing a DataShareExtensionAbility from the FA Model
harmony 鸿蒙Common action and entities Values (Not Recommended)
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签: