harmony 鸿蒙USB
USB
Introduction
Function Description
USB devices are classified into two types: USB host and USB device. On OpenHarmony, you can use the port service to switch between the host mode and device mode. In host mode, you can obtain the list of connected USB devices, manage device access permissions, and perform bulk transfer or control transfer between the host and connected devices. In device mode, you can switch between functions including HDC (debugging), ACM (serial port), and ECM (Ethernet port).
Basic Concepts
- USB service
An abstraction of underlying hardware-based USB devices. Your application can access the USB devices via the USB service. With the APIs provided by the USB service, you can obtain the list of connected USB devices, manage device access permissions, and perform data transfer or control transfer between the host and connected devices.
- USB API
A collection of JS APIs provided for the upper layer through NAPI. Your application can use USB APIs to implement various basic functions, for example, query of the USB device list, USB device plug notification, USB host and device mode switching, bulk transfer, control transfer, right management, and function switching in device mode.
- USB Service layer
A layer implemented by using the C++ programming language. It consists of four modules: Host, Device, Port, and Right. HDI-based APIs provided by USB Service are mainly used to implement management of USB device list, USB functions, USB ports, and USB device access permissions. The USB Service layer interacts with the HAL layer to receive, parse, and distribute data, manages foreground and background policies, and performs USB device management and right control.
- USB HAL layer
A layer implemented by using the C programming language. Based on the Host Driver Development Kit (SDK) and Device DDK, USB HAL encapsulates basic USB device operations, provides C++ APIs for the upper layer, and receives information from the kernel through the Hardware Driver Foundation (HDF) framework.
Working Principles
The USB subsystem logically consists of three parts: USB API, USB Service, and USB HAL. The following figure shows how the USB service is implemented.
Figure 1 USB service architecture
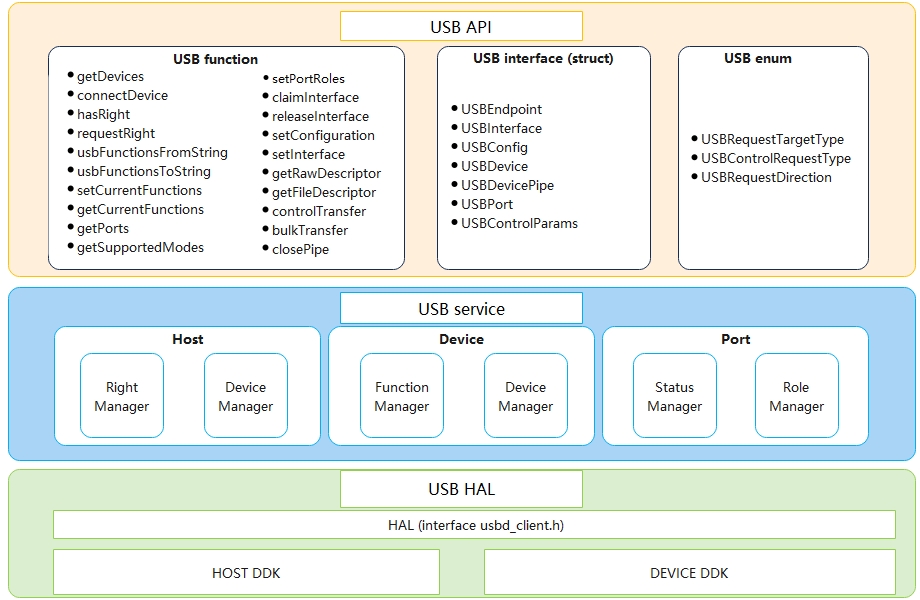
USB API: provides USB APIs that implement various basic functions, for example, query of the USB device list, bulk data transfer, control transfer, and right management.
USB Service: receives, parses, and distributes Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) data, manages and controls foreground and background policies, and manages devices.
USB HAL: provides driver capability APIs that can be directly called in user mode.
Usage Guidelines
When to Use
In Host mode, you can obtain the list of connected devices, enable or disable the devices, manage device access permissions, and perform data transfer or control transfer.
APIs
Table 1 Host-specific APIs
| API | Description |
|---|---|
| int32_t OpenDevice(const UsbDevice &device, USBDevicePipe &pip); | Opens a USB device to set up a connection. |
| bool HasRight(std::string deviceName); | Checks whether the application has the permission to access the device. |
| int32_t RequestRight(std::string deviceName); | Requests the temporary permission for a given application to access the USB device. |
| int32_t GetDevices(std::vector &deviceList); | Obtains the USB device list. |
| int32_t ClaimInterface(USBDevicePipe &pip, const UsbInterface &interface, bool force); | Claims a USB interface exclusively. This must be done before data transfer. |
| int32_t ReleaseInterface(USBDevicePipe &pip, const UsbInterface &interface); | Releases a USB interface. This is usually done after data transfer. |
| int32_t BulkTransfer(USBDevicePipe &pip, const USBEndpoint &endpoint, std::vector &vdata, int32_t timeout); | Performs a bulk transfer on a specified endpoint. The data transfer direction is determined by the endpoint direction. |
| int32_t ControlTransfer(USBDevicePipe &pip, const UsbCtrlTransfer &ctrl, std::vector &vdata); | Performs control transfer for endpoint 0 of the device. The data transfer direction is determined by the request type. |
| int32_t SetConfiguration(USBDevicePipe &pip, const USBConfig &config); | Sets the current configuration of the USB device. |
| int32_t SetInterface(USBDevicePipe &pipe, const UsbInterface &interface); | Sets the alternate settings for the specified USB interface. This allows you to switch between two interfaces with the same ID but different alternate settings. |
| int32_t GetRawDescriptors(std::vector &vdata); | Obtains the raw USB descriptor. |
| int32_t GetFileDescriptor(); | Obtains the file descriptor. |
| bool Close(const USBDevicePipe &pip); | Closes a USB device to release all system resources related to the device. |
| int32_t PipeRequestWait(USBDevicePipe &pip, int64_t timeout, UsbRequest &req); | Obtains the isochronous transfer result. |
| int32_t RequestInitialize(UsbRequest &request); | Initializes the isochronous transfer request. |
| int32_t RequestFree(UsbRequest &request); | Frees the isochronous transfer request. |
| int32_t RequestAbort(UsbRequest &request); | Cancels the data transfer request to be processed. |
| int32_t RequestQueue(UsbRequest &request); | Sends or receives requests for isochronous transfer on a specified endpoint. The data transfer direction is determined by the endpoint direction. |
| int32_t RegBulkCallback(USBDevicePipe &pip, const USBEndpoint &endpoint, const sptr |
Registers an asynchronous callback for bulk transfer. |
| int32_t UnRegBulkCallback(USBDevicePipe &pip, const USBEndpoint &endpoint); | Unregisters the asynchronous callback for bulk transfer. |
| int32_t BulkRead(USBDevicePipe &pip, const USBEndpoint &endpoint, sptr |
Reads data asynchronously during bulk transfer. |
| int32_t BulkWrite(USBDevicePipe &pip, const USBEndpoint &endpoint, sptr |
Writes data asynchronously during bulk transfer. |
| int32_t BulkCancel(USBDevicePipe &pip, const USBEndpoint &endpoint); | Cancels bulk transfer. The asynchronous read and write operations on the current USB interface will be cancelled. |
Table 2 Device-specific APIs
| API | Description |
|---|---|
| int32_t GetCurrentFunctions(int32_t &funcs); | Obtains the numeric mask combination for the current USB function list in Device mode. |
| int32_t SetCurrentFunctions(int32_t funcs); | Sets the current USB function list in Device mode. |
| int32_t UsbFunctionsFromString(std::string funcs); | Converts the string descriptor of a given USB function list to a numeric mask combination. |
| std::string UsbFunctionsToString(int32_t funcs); | Converts the numeric mask combination of a given USB function list to a string descriptor. |
Table 3 Port-specific APIs
| API | Description |
|---|---|
| int32_t GetSupportedModes(int32_t portId, int32_t &supportedModes); | Obtains the mask combination for the supported mode list of a given port. |
| int32_t SetPortRole(int32_t portId, int32_t powerRole, int32_t dataRole); | Sets the role types supported by a specified port, which can be powerRole (for charging) and dataRole (for data transfer). |
| int32_t GetPorts(std::vector &usbPorts); | Obtains the USB port descriptor list. |
How to Use
The following uses bulk transfer as an example to illustrate the development procedure.
Obtain a USB service instance.
static OHOS::USB::UsbSrvClient &g_usbClient = OHOS::USB::UsbSrvClient::GetInstance();Obtain the USB device list.
std::vector<OHOS::USB::UsbDevice> deviceList; int32_t ret = g_usbClient.GetDevices(deviceList);Apply for device access permissions.
int32_t ret = g_usbClient.RequestRight(device.GetName());Open a camera device.
USBDevicePipe pip; int32_t et = g_usbClient.OpenDevice(device, pip);Configure the USB interface.
// interface indicates an interface of the USB device in deviceList. ret = g_usbClient.ClaimInterface(pip, interface, true);Perform data transfer.
// pipe indicates the pipe for data transfer after the USB device is opened. endpoint indicates the endpoint for data transfer on the USB device. vdata indicates the binary data block to be transferred or read. timeout indicates the timeout duration of data transfer. srvClient.BulkTransfer(pipe, endpoint, vdata, timeout);Closes a device.
ret = g_usbClient.Close(pip);
Sample Code
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <mutex>
#include <sstream>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include "if_system_ability_manager.h"
#include "ipc_skeleton.h"
#include "iremote_object.h"
#include "iservice_registry.h"
#include "iusb_srv.h"
#include "string_ex.h"
#include "system_ability_definition.h"
#include "usb_common.h"
#include "usb_device.h"
#include "usb_errors.h"
#include "usb_request.h"
#include "usb_server_proxy.h"
#include "usb_srv_client.h"
const int32_t REQUESTYPE = ((1 << 7)|(0 << 5)|(0 & 0x1f));
const int32_t REQUESTCMD = 6;
const int32_t VALUE = (2 << 8) + 0;
const int32_t TIMEOUT = 5000;
const int32_t ITFCLASS = 10;
const int32_t PRAMATYPE = 2;
const int32_t BUFFERLENGTH = 21;
void GetType(OHOS::USB::USBEndpoint &tep, OHOS::USB::USBEndpoint &outEp, bool &outEpFlg)
{
if ((tep.GetType() == PRAMATYPE)) {
if (tep.GetDirection() == 0) {
outEp = tep;
outEpFlg = true;
}
}
}
bool SelectEndpoint(OHOS::USB::USBConfig config,
std::vector<OHOS::USB::UsbInterface> interfaces,
OHOS::USB::UsbInterface &interface,
OHOS::USB::USBEndpoint &outEp,
bool &outEpFlg)
{
for (int32_t i = 0; i < config.GetInterfaceCount(); ++i) {
OHOS::USB::UsbInterface tif = interfaces[i];
std::vector<OHOS::USB::USBEndpoint> mEndpoints = tif.GetEndpoints();
for (int32_t j = 0; j < tif.GetEndpointCount(); ++j) {
OHOS::USB::USBEndpoint tep = mEndpoints[j];
if ((tif.GetClass() == ITFCLASS) && (tif.GetSubClass() == 0) && (tif.GetProtocol() == PRAMATYPE)) {
GetType(tep, outEp, outEpFlg);
}
}
if (outEpFlg) {
interface = interfaces[i];
return true;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
return false;
}
int OpenDeviceTest(OHOS::USB::UsbSrvClient &Instran, OHOS::USB::UsbDevice device, OHOS::USB::USBDevicePipe &pip)
{
int ret = Instran.RequestRight(device.GetName());
std::cout << "device RequestRight ret = " << ret << std::endl;
if (0 != ret) {
std::cout << "device RequestRight failed = " << ret << std::endl;
}
ret = Instran.OpenDevice(device, pip);
return ret;
}
int CtrTransferTest(OHOS::USB::UsbSrvClient &Instran, OHOS::USB::USBDevicePipe &pip)
{
std::cout << "usb_device_test : << Control Transfer >> " << std::endl;
std::vector<uint8_t> vData;
const OHOS::USB::UsbCtrlTransfer tctrl = {REQUESTYPE, REQUESTCMD, VALUE, 0, TIMEOUT};
int ret = Instran.ControlTransfer(pip, tctrl, vData);
if (ret != 0) {
std::cout << "control message read failed width ret = " << ret << std::endl;
} else {
}
std::cout << "control message read success" << std::endl;
return ret;
}
int ClaimTest(OHOS::USB::UsbSrvClient &Instran,
OHOS::USB::USBDevicePipe &pip,
OHOS::USB::UsbInterface &interface,
bool interfaceFlg)
{
if (interfaceFlg) {
std::cout << "ClaimInterface InterfaceInfo:" << interface.ToString() << std::endl;
int ret = Instran.ClaimInterface(pip, interface, true);
if (ret != 0) {
std::cout << "ClaimInterface failed width ret = " << ret << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "ClaimInterface success" << std::endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
int BulkTransferTest(OHOS::USB::UsbSrvClient &Instran,
OHOS::USB::USBDevicePipe &pip,
OHOS::USB::USBEndpoint &outEp,
bool interfaceFlg,
bool outEpFlg)
{
if (interfaceFlg) {
std::cout << "usb_device_test : << Bulk transfer start >> " << std::endl;
if (outEpFlg) {
uint8_t buffer[50] = "hello world 123456789";
std::vector<uint8_t> vData(buffer, buffer + BUFFERLENGTH);
int ret = Instran.BulkTransfer(pip, outEp, vData, TIMEOUT);
if (ret != 0) {
std::cout << "Bulk transfer write failed width ret = " << ret << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "Bulk transfer write success" << std::endl;
}
return ret;
}
}
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
std::cout << "usb_device_test " << std::endl;
static OHOS::USB::UsbSrvClient &Instran = OHOS::USB::UsbSrvClient::GetInstance();
// GetDevices
std::vector<OHOS::USB::UsbDevice> deviceList;
int32_t ret = Instran.GetDevices(deviceList);
if (ret != 0) {
return OHOS::USB::UEC_SERVICE_INVALID_VALUE;
}
if (deviceList.empty()) {
return OHOS::USB::UEC_SERVICE_INVALID_VALUE;
}
OHOS::USB::UsbDevice device = deviceList[0];
std::vector<OHOS::USB::USBConfig> configs = device.GetConfigs();
OHOS::USB::USBConfig config = configs[0];
std::vector<OHOS::USB::UsbInterface> interfaces = config.GetInterfaces();
OHOS::USB::UsbInterface interface;
OHOS::USB::USBEndpoint outEp;
bool interfaceFlg = false;
bool outEpFlg = false;
interfaceFlg = SelectEndpoint(config, interfaces, interface, outEp, outEpFlg);
// OpenDevice
std::cout << "usb_device_test : << OpenDevice >> test begin -> " << std::endl;
OHOS::USB::USBDevicePipe pip;
ret = OpenDeviceTest(Instran, device, pip);
if (ret != 0) {
return OHOS::USB::UEC_SERVICE_INVALID_VALUE;
}
// ControlTransfer
CtrTransferTest(Instran, pip);
// ClaimInterface
ClaimTest(Instran, pip, interface, interfaceFlg);
// BulkTransferWrite
BulkTransferTest(Instran, pip, outEp, interfaceFlg, outEpFlg);
// CloseDevice
std::cout << "usb_device_test : << Close Device >> " << std::endl;
ret = Instran.Close(pip);
if (ret == 0) {
std::cout << "Close device failed width ret = " << ret << std::endl;
return OHOS::USB::UEC_SERVICE_INVALID_VALUE;
} else {
std::cout << "Close Device success" << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
Repositories Involved
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙AI Framework Development
harmony 鸿蒙Application Privilege Configuration Guide
harmony 鸿蒙Setting Up a Development Environment
harmony 鸿蒙Development Guidelines
harmony 鸿蒙Application Framework Overview
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签: