harmony 鸿蒙User File URI
User File URI
The uniform resource identifier (URI) is a unique identifier of a user file. It is usually used when a user file is accessed or modified.
NOTE
Do not use the URI segments for service code development.
URI Types
URIs can be classified into the following types:
- File URI: URI of a file selected or saved in a file manager directory, or obtained via the fileAccess module. For details, see Obtaining a File URI.
- Media file URI: URI of an image or video selected from Gallery; URI of an image or video obtained via the photoAccessHelper module; URI of an image, video, or audio file obtained via the userFileManager module. For details, see Obtaining a Media File URI.
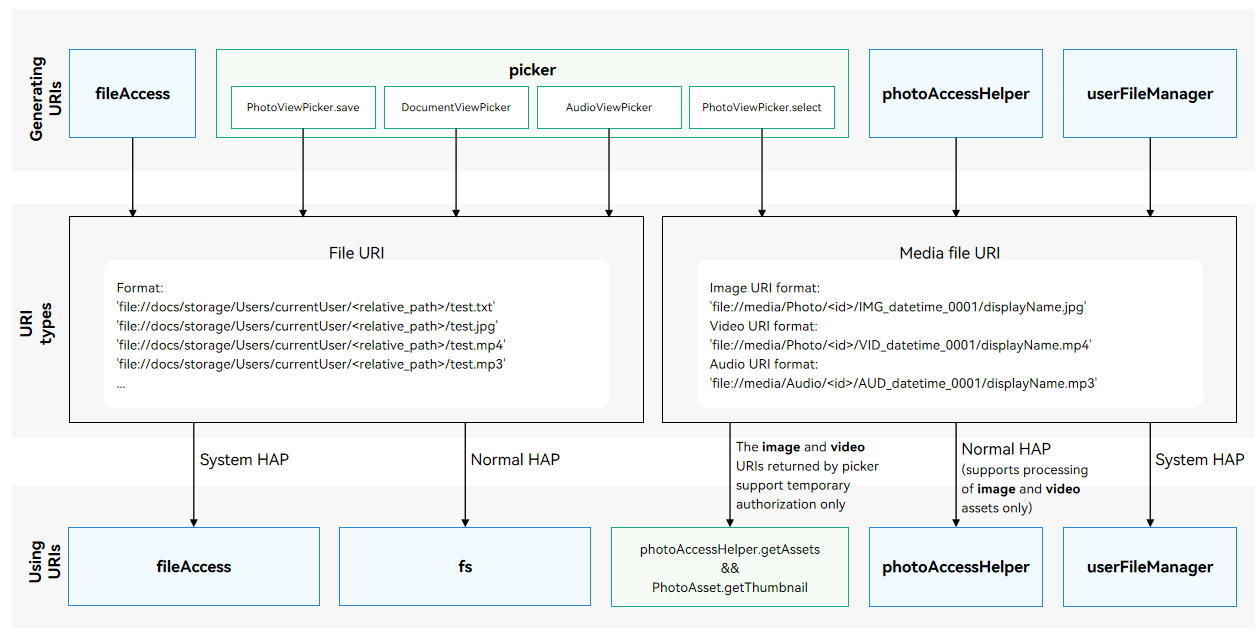
File URI
File URI Overview
File URIs are in the following format:
‘file://docs/storage/Users/currentUser/<relative_path>/test.txt’
The file URI contains the following fields:
| URI Field | Description |
|---|---|
| ‘file://docs/storage/Users/currentUser/’ | Root directory of the file manager. |
| ‘<relative_path>/’ | Relative path of the file. For example, Download/ and Documents/. |
| ‘test.txt’ | Name of the file stored in the user file system. The supported file types are all types supported by the file manager, for example, TXT, JPG, MP4, and MP3. |
Obtaining a File URI
Use select() or save() of DocumentViewPicker.
Use select() or save() of AudioViewPicker.
Use fileAccess. The FileInfo object returned contains the URI of the file or directory. However, only system applications can call the APIs of the fileAccess module. The file URIs of the following directories can be obtained:
- External storage directory
- Docs directory
- Download directory
- Desktop directory
- Documents directory
- Share directory of the shared disk
Using a File URI
Applications of the normal level can call APIs of the fs module only to use file URIs. “Permission denied” will be reported if an API of other modules is called to process the file URI. For details, see Selecting Documents and Saving Documents.
Applications of the system_basic or system_core level can call APIs of the fs and fileAccess modules to use file URIs. To call fileAccess APIs, the application must have the ohos.permission.FILE_ACCESS_MANAGER and ohos.permission.GET_BUNDLE_INFO_PRIVILEGED permissions declared in module.json5 file. “Permission denied” will be reported if the file URI is processed by an API of other modules. The following example shows how to use the fileAccess module to create a file and rename the file based on the file URI.
- Use fileAccess to create a file.
- Rename the file based on the file URI.
import { BusinessError } from '@ohos.base';
import Want from '@ohos.app.ability.Want';
import common from '@ohos.app.ability.common';
import fileAccess from '@ohos.file.fileAccess';
async example() {
let fileAccessHelper: fileAccess.FileAccessHelper;
// Obtain wantInfos by using getFileAccessAbilityInfo().
let wantInfos: Array<Want> = [
{
bundleName: "com.ohos.UserFile.ExternalFileManager",
abilityName: "FileExtensionAbility",
},
]
try {
// context is passed by EntryAbility.
let context = getContext(this) as common.UIAbilityContext;
fileAccessHelper = fileAccess.createFileAccessHelper(context, wantInfos);
if (!fileAccessHelper) {
console.error("createFileAccessHelper interface returns an undefined object");
}
// A built-in storage directory is used as an example.
// In the sample code, sourceUri indicates the Download directory. The URI is the URI in fileInfo.
// You can use the URI obtained.
let sourceUri: string = "file://docs/storage/Users/currentUser/Download";
let displayName: string = "file1.txt";
let fileUri: string;
try {
// Create a file. The URI of the file created is returned.
fileUri = await fileAccessHelper.createFile(sourceUri, displayName);
if (!fileUri) {
console.error("createFile return undefined object");
}
console.log("createFile success, fileUri: " + JSON.stringify(fileUri));
// Rename the file. The URI of the renamed file is returned.
let renameUri = await fileAccessHelper.rename(fileUri, "renameFile.txt");
console.log("rename success, renameUri: " + JSON.stringify(renameUri));
} catch (err) {
let error: BusinessError = err as BusinessError;
console.error("createFile failed, errCode:" + error.code + ", errMessage:" + error.message);
}
} catch (err) {
let error: BusinessError = err as BusinessError;
console.error("createFileAccessHelper failed, errCode:" + error.code + ", errMessage:" + error.message);
}
}
Media File URI
Media File URI Overview
Media file URIs are in the following formats:
- Image URI format:
‘file://media/Photo/<id>/IMG_datetime_0001/displayName.jpg’
- Video URI format:
‘file://media/Photo/<id>/VID_datetime_0001/displayName.mp4’
- Audio File URI format:
‘file://media/Audio/<id>/AUD_datetime_0001/displayName.mp3’
The media file URI contains the following fields:
| URI Field | Description |
|---|---|
| ‘file://media’ | Indicates a URI of a media file. |
| ‘Photo’ | Indicates a URI of an image or video file. |
| ‘Audio’ | Indicates a URI of an audio file. |
| ‘<id>’ | Indicates the ID of the file after the file is processed in multiple tables in the database. It is not the value in the file_id column in the table. Do not use this ID to query a file in the database. |
| ‘IMG_datetime_0001’ | Indicates the name of the image file stored in the user file system without the file name extension. |
| ‘VID_datetime_0001’ | Indicates the name of the video file stored in the user file system without the file name extension. |
| ‘AUD_datetime_0001’ | Indicates the name of the audio file stored in the user file system without the file name extension. |
| ‘displayName.jpg’ | Indicates the image file name displayed. You can use userFileManager.commitModify to rename it. The URI is changed if displayName is renamed. |
| ‘displayName.mp4’ | Indicates the video file name displayed. You can use userFileManager.commitModify to rename it. The URI is changed if displayName is renamed. |
| ‘displayName.mp3’ | Indicates the audio file name displayed. You can use userFileManager.commitModify to rename it. The URI is changed if displayName is renamed. |
Obtaining a Media File URI
Use PhotoViewPicker.select() to select a media file.
Use getAssets() or createAsset() in the photoAccessHelper module.
Use getPhotoAssets(), getAudioAssets(), createAudioAsset(), or createPhotoAsset() in the userFileManager module.
Using a Media File URI
Applications of the normal level can call APIs of the photoAccessHelper module to use the media file URI. For details about the sample code, see Obtaining an Image or Video by URI. To call the API, the application must have the permission’ohos.permission.READ_IMAGEVIDEO permission.
Applications of the system_basic or system_core level can call APIs of the photoAccessHelper and userFileManager modules to use the media file URI. For more details, see the API reference of these modules.
If an application of the normal level does not have the related permission, the application can call PhotoViewPicker.select() to obtain the file URI first. Then, photoAccessHelper.getAssets can be used to obtain the PhotoAsset object based on the URI. Based on the PhotoAsset object, you can use getThumbnail to obtain the image thumbnail or use get() to obtain information from PhotoKeys.
The following information can be obtained from PhotoKeys through temporary authorization:
| Name | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| URI | ‘uri’ | URI of the file. |
| PHOTO_TYPE | ‘media_type’ | Type of the media file. |
| DISPLAY_NAME | ‘display_name’ | File name displayed. |
| SIZE | ‘size’ | File size. |
| DATE_ADDED | ‘date_added’ | Date when the file was added. The value is the number of seconds elapsed since the Epoch time. |
| DATE_MODIFIED | ‘date_modified’ | Date when the file content (not the file name) was last modified. The value is the number of seconds elapsed since the Epoch time. |
| DURATION | ‘duration’ | Duration, in ms. |
| WIDTH | ‘width’ | Image width, in pixels. |
| HEIGHT | ‘height’ | Image height, in pixels. |
| DATE_TAKEN | ‘date_taken’ | Date when the file (photo) was taken. The value is the number of seconds elapsed since the Epoch time. |
| ORIENTATION | ‘orientation’ | Orientation of the image file. |
| TITLE | ‘title’ | Title in the file. |
The following example shows how to obtain the thumbnail and file information based on the media file URI with temporary authorization.
import picker from '@ohos.file.picker';
import photoAccessHelper from '@ohos.file.photoAccessHelper';
import { BusinessError } from '@ohos.base';
import dataSharePredicates from '@ohos.data.dataSharePredicates';
// Define a URI array to receive the URIs returned by PhotoViewPicker.select.
let uris: Array<string> = [];
const context = getContext(this);
// Call PhotoViewPicker.select to select an image.
async function photoPickerGetUri() {
try {
let PhotoSelectOptions = new picker.PhotoSelectOptions();
PhotoSelectOptions.MIMEType = picker.PhotoViewMIMETypes.IMAGE_TYPE;
PhotoSelectOptions.maxSelectNumber = 1;
let photoPicker = new picker.PhotoViewPicker();
photoPicker.select(PhotoSelectOptions).then((PhotoSelectResult: picker.PhotoSelectResult) => {
console.info('PhotoViewPicker.select successfully, PhotoSelectResult uri: ' + JSON.stringify(PhotoSelectResult));
uris = PhotoSelectResult.photoUris;
}).catch((err: BusinessError) => {
console.error('PhotoViewPicker.select failed with err: ' + JSON.stringify(err));
});
} catch (error) {
let err: BusinessError = error as BusinessError;
console.error('PhotoViewPicker failed with err: ' + JSON.stringify(err));
}
}
async function uriGetAssets() {
try {
let phAccessHelper = photoAccessHelper.getPhotoAccessHelper(context);
let predicates: dataSharePredicates.DataSharePredicates = new dataSharePredicates.DataSharePredicates();
// Configure search criteria to query the image based on the URI returned by PhotoViewPicker.select.
predicates.equalTo('uri', uris[0]);
let fetchOption: photoAccessHelper.FetchOptions = {
fetchColumns: [],
predicates: predicates
};
let fetchResult: photoAccessHelper.FetchResult<photoAccessHelper.PhotoAsset> = await phAccessHelper.getAssets(fetchOption);
// Obtain the PhotoAsset object corresponding to the URI. The file information is obtained from the PhotoAsset object.
const asset: photoAccessHelper.PhotoAsset = await fetchResult.getFirstObject();
console.info('asset displayName: ', asset.displayName);
console.info('asset uri: ', asset.uri);
console.info('asset photoType: ', asset.photoType);
console.info('asset width: ', asset.get(photoAccessHelper.PhotoKeys.WIDTH));
console.info('asset height: ', asset.get(photoAccessHelper.PhotoKeys.HEIGHT));
console.info('asset title: ' + asset.get(photoAccessHelper.PhotoKeys.TITLE));
// Obtain the thumbnail.
asset.getThumbnail((err, pixelMap) => {
if (err == undefined) {
console.info('getThumbnail successful ' + JSON.stringify(pixelMap));
} else {
console.error('getThumbnail fail', err);
}
});
} catch (error){
console.error('uriGetAssets failed with err: ' + JSON.stringify(error));
}
}
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙Accessing Application Files
harmony 鸿蒙Backup and Restoration Accessed by Applications
harmony 鸿蒙Application Data Backup and Restoration Overview
harmony 鸿蒙Backup and Restoration Triggered by System Applications
harmony 鸿蒙Application File Overview
harmony 鸿蒙Uploading and Downloading an Application File
harmony 鸿蒙Obtaining Application and File System Space Statistics
harmony 鸿蒙Application Sandbox Directory
harmony 鸿蒙Developing a File Manager Application (for System Applications Only)
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签:
热门推荐
-
2、 - 优质文章
-
3、 gate.io
-
8、 golang
-
9、 openharmony
-
10、 Vue中input框自动聚焦