harmony 鸿蒙Restrictions and Extensions
Restrictions and Extensions
Restrictions on Using ArkTS in Generators
ArkTS has the following restrictions on generators:
Expressions can be used only in character strings (${expression}), if/else statements, ForEach parameters, and component parameters.
No expressions should cause any application state variables (that is, variables decorated by @State, @Link, and @Prop) to change. Otherwise, undefined and potentially unstable framework behavior may occur.
The generator function cannot contain local variables.
None of the above restrictions applies to anonymous function implementations of event methods (such as onClick).
Two-Way Binding of Variables
ArkTS supports two-way binding through $$, which is usually used for variables whose state values change frequently.
- $$ supports variables of primitive types and variables decorated by @State, @Link, or @Prop.
- $$ supports only the show parameter of the bindPopup attribute method, the checked attribute of the <Radio> component, and the refreshing parameter of the <Refresh> component.
- When the variable bound to $$ changes, only the current component is rendered, which improves the rendering speed.
// xxx.ets
@Entry
@Component
struct bindPopupPage {
@State customPopup: boolean = false
build() {
Column() {
Button('Popup')
.margin(20)
.onClick(() => {
this.customPopup = !this.customPopup
})
.bindPopup($$this.customPopup, {
message: "showPopup"
})
}
}
}

Restrictions on Data Type Declarations of State Variables
The data types of state variables decorated by state decorators must be explicitly declared. They cannot be declared as any or Date.
Example:
// xxx.ets @Entry @Component struct DatePickerExample { // Incorrect: @State isLunar: any = false @State isLunar: boolean = false // Incorrect: @State selectedDate: Date = new Date('2021-08-08') private selectedDate: Date = new Date('2021-08-08') build() { Column() { Button('Switch Calendar') .margin({ top: 30 }) .onClick(() => { this.isLunar = !this.isLunar }) DatePicker({ start: new Date('1970-1-1'), end: new Date('2100-1-1'), selected: this.selectedDate }) .lunar(this.isLunar) .onChange((value: DatePickerResult) => { this.selectedDate.setFullYear(value.year, value.month, value.day) console.info('select current date is: ' + JSON.stringify(value)) }) }.width('100%') } }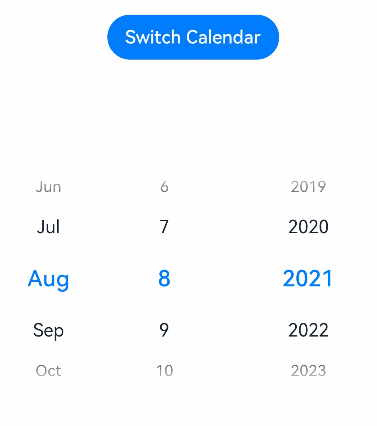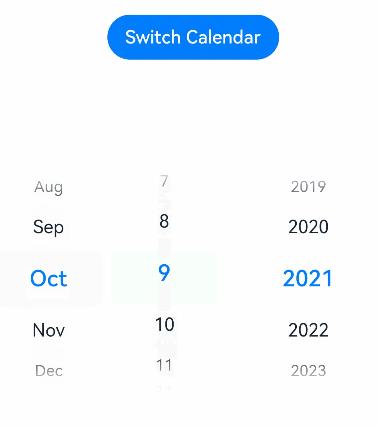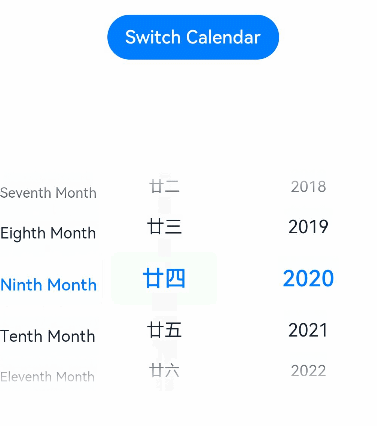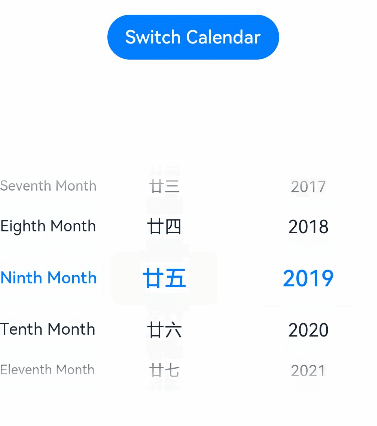
The data type declaration of the @State, @Provide, @Link, or @Consume decorated state variables can consist of only one of the primitive data types or reference data types.
The Length, ResourceStr, and ResourceColor types are combinations of primitive data types or reference data types. Therefore, they cannot be used by the aforementioned types of state variables. For details about the definitions of Length, ResourceStr, and ResourceColor, see Types.
Example:
// xxx.ets @Entry @Component struct IndexPage { // Incorrect: @State message: string|Resource = 'Hello World' @State message: string = 'Hello World' // Incorrect: @State message: ResourceStr = $r('app.string.hello') @State resourceStr: Resource = $r('app.string.hello') build() { Row() { Column() { Text(`${this.message}`) .fontSize(50) .fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold) } .width('100%') } .height('100%') } }
Initialization and Restrictions of Custom Components’ Member Variables
The member variables of a component can be initialized in either of the following ways:
- Local initialization:
@State counter: Counter = new Counter()
- Initialization using constructor parameters:
MyComponent({counter: $myCounter})
The allowed method depends on the decorator of the state variable, as shown in the following table.
| Decorator | Local Initialization | Initialization Using Constructor Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| @State | Mandatory | Optional |
| @Prop | Forbidden | Mandatory |
| @Link | Forbidden | Mandatory |
| @StorageLink | Mandatory | Forbidden |
| @StorageProp | Mandatory | Forbidden |
| @LocalStorageLink | Mandatory | Forbidden |
| @LocalStorageProp | Mandatory | Forbidden |
| @Provide | Mandatory | Optional |
| @Consume | Forbidden | Forbidden |
| @ObjectLink | Forbidden | Mandatory |
| Normal member variable | Recommended | Optional |
As indicated by the preceding table:
The @State decorated variables must be initialized locally. Their initial values can be overwritten by the constructor parameters.
The @Prop and @Link decorated variables must be initialized only by constructor parameters.
Comply with the following rules when using constructors to initialize member variables:
| From the Variable in the Parent Component (Right) to the Variable in the Child Component (Below) | regular | @State | @Link | @Prop | @Provide | @Consume | @ObjectLink |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| regular | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported | Not supported | Not supported | Supported |
| @State | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported |
| @Link | Not supported | Supported (1) | Supported (1) | Supported (1) | Supported (1) | Supported (1) | Supported (1) |
| @Prop | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported |
| @Provide | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported |
| @Consume | Not supported | Not supported | Not supported | Not supported | Not supported | Not supported | Not supported |
| @ObjectLink | Not supported | Not supported | Not supported | Not supported | Not supported | Not supported | Not supported |
| From the Variable in the Parent Component (Right) to the Variable in the Child Component (Below) | @StorageLink | @StorageProp | @LocalStorageLink | @LocalStorageProp |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| regular | Supported | Not supported | Not supported | Not supported |
| @State | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported |
| @Link | Supported (1) | Supported (1) | Supported (1) | Supported (1) |
| @Prop | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported |
| @Provide | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported |
| @Consume | Not supported | Not supported | Not supported | Not supported |
| @ObjectLink | Not supported | Not supported | Not supported | Not supported |
NOTE
Supported (1): The dollar sign ($) must be used, for example, this.$varA.
regular: refers to a regular variable that is not decorated by any decorator.
As indicated by the preceding tables:
The @ObjectLink decorated variable cannot be directly initialized from a decorated variable in the parent component. The source of the parent component must be an array item or object attribute decorated by @State, @Link, @Provide, @Consume, or @ObjectLink.
The regular variables of the parent component can be used to initialize the @State variable of the child component, but cannot be used to initialize the @Link, @Consume, and @ObjectLink variables.
The @State variable of the parent component can be used to initialize the @Prop, @Link (through $), or regular variables of the child component, but cannot be used to initialize the @Consume variable.
The @Link variable of the parent component cannot be used to initialize the @Consume and @ObjectLink variables of the child component.
The @Prop variable of the parent component cannot be used to initialize the @Consume and @ObjectLink variables of the child component.
@StorageLink, @StorageProp, @LocalStorageLink, and @LocalStorageProp variables cannot be initialized from the parent component.
In addition to the preceding rules, the TypeScript strong type rules need to be followed.
Example:
@Entry
@Component
struct Parent {
message: string = "Hello World"
build() {
Column() {
Child({
stateMessage: this.message,
/* ArkTS:ERROR The regular property 'message' cannot be assigned
to the @Link property 'linkMessage'.*/
linkMessage: this.$message
})
}
.width('100%')
}
}
@Component
struct Child {
@State stateMessage: string = "Hello World"
@Link linkMessage: string
build() {
Column() {
Text(this.stateMessage)
.fontSize(50)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
}
.width('100%')
}
}
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙app.json5 Configuration File
harmony 鸿蒙Internal Structure of the app Tag
harmony 鸿蒙Application Configuration File Overview (FA Model)
harmony 鸿蒙Application Configuration File Overview (Stage Model)
harmony 鸿蒙Application Installation and Uninstallation Process
harmony 鸿蒙Application Package Overview
harmony 鸿蒙Application Package Structure in FA Model
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签:
热门推荐
-
2、 - 优质文章
-
3、 gate.io
-
8、 golang
-
9、 openharmony
-
10、 Vue中input框自动聚焦