harmony 鸿蒙Basic Concepts
Basic Concepts
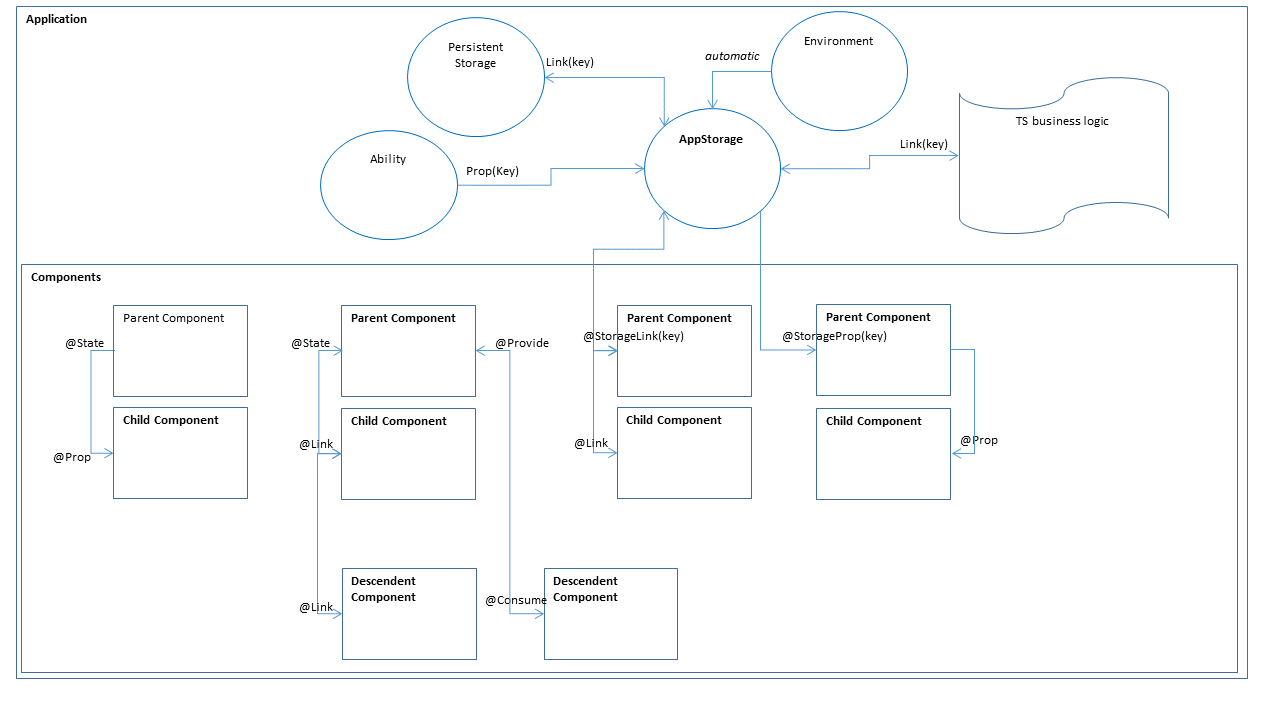
In the multi-dimensional state management mechanism for ArkUI, UI-related data can be used not only within a component, but also be transferred between different component levels (for example, between parent and child components, between grandparent and grandchild components, or globally). In addition, data transfer can be classified as one-way (read-only) or two-way (mutable). You can use these capabilities at your disposal to implement linkage between data and the UI.
State Management with Page-level Variables
| Decorator | Decorates… | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @State | Primitive data types, classes, and arrays | If the decorated state data is modified, the build method of the component will be called to update the UI. |
| @Prop | Primitive data types | This decorator is used to establish one-way data binding between the parent and child components. When the data associated with the parent component is modified, the UI of the current component is re-rendered. |
| @Link | Primitive data types, classes, and arrays | This decorator is used to establish two-way data binding between the parent and child components. The internal state data of the parent component is used as the data source. Any changes made to one component will be reflected to the other. |
| @Observed | Class | This decorator is used to indicate that the data changes in the class will be managed by the UI page. |
| @ObjectLink | Objects of @Observed decorated classes | When the decorated state variable is modified, the parent and sibling components that have the state variable will be notified for UI re-rendering. |
| @Provide | Primitive data types, classes, and arrays | As the data provider, @Provide can update the data of child nodes and trigger page re-rendering. |
| @Consume | Primitive data types, classes, and arrays | When the @Consume decorated variable detects the update of the @Provide decorated variable, the re-rendering of the current custom component is triggered. |
State Management with Application-level Variables
AppStorage is the central store of the application states in the entire UI. ArkUI creates a singleton AppStorage object for the application and provides the corresponding decorators and APIs for the application.
- @StorageLink: works in a way similar to that of @Consume. The difference is that the target object is obtained from the AppStorage based on the given name. @StorageLink establishes two-way binding between the decorated UI component and AppStorage to synchronize data.
- @StorageProp: synchronizes UI component attributes with the AppStorage unidirectionally. That is, the value change in the AppStorage will trigger an update of the corresponding UI component, but the change of the UI component will not cause an update of the attribute value in the AppStorage.
- Service logic implementation API: adds, reads, modifies, or deletes the state data of applications. The changes made by this API will be synchronized to the UI component for UI update.
- LocalStorage: provides ability-specific storage.
- @LocalStorageLink: establishes two-way data binding between a component and the LocalStorage. Specifically, this is achieved by decorating the component’s state variable with @LocalStorageLink(key). Wherein, key is the attribute key value in the LocalStorage.
- @LocalStorageProp: establishes one-way data binding between a component and the LocalStorage. Specifically, this is achieved by decorating the component’s state variable with @LocalStorageProp(key). Wherein, key is the attribute key value in the LocalStorage.
- PersistentStorage: provides a set of static methods for managing persistent data of applications. Persistent data with specific tags can be linked to the AppStorage, and then the persistent data can be accessed through the AppStorage APIs. Alternatively, the @StorageLink decorator can be used to access the variable that matches the specific key.
- Environment: provides the AppStorage with an array of environment state attributes that are required by the application and describe the device environment where the application runs. It is a singleton object created by the framework when the application is started.
For details about how to use state variables, see Restrictions on Data Type Declarations of State Variables.
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙app.json5 Configuration File
harmony 鸿蒙Internal Structure of the app Tag
harmony 鸿蒙Application Configuration File Overview (FA Model)
harmony 鸿蒙Application Configuration File Overview (Stage Model)
harmony 鸿蒙Application Installation and Uninstallation Process
harmony 鸿蒙Application Package Overview
harmony 鸿蒙Application Package Structure in FA Model
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签: